While ethanol (CH,CH,OH) is produced naturally by fermentation, e.g. in beer- and wine-making, industrially it is synthesized by reacting ethylene (CH,CH,) with water vapor at elevated temperatures. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 75 L tank with 10. mol of ethylene gas and 5.4 mol of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 6.8 mol of ethylene gas and 2.2 mol of water vapor. The engineer then adds another 1.4 mol of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of ethanol after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. ||mol ?
While ethanol (CH,CH,OH) is produced naturally by fermentation, e.g. in beer- and wine-making, industrially it is synthesized by reacting ethylene (CH,CH,) with water vapor at elevated temperatures. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 75 L tank with 10. mol of ethylene gas and 5.4 mol of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 6.8 mol of ethylene gas and 2.2 mol of water vapor. The engineer then adds another 1.4 mol of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of ethanol after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. ||mol ?
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.101PAE: 12.101 An engineer working on a design to extract petroleum from a deep thermal reservoir wishes to...
Related questions
Question
Answer correctly please!
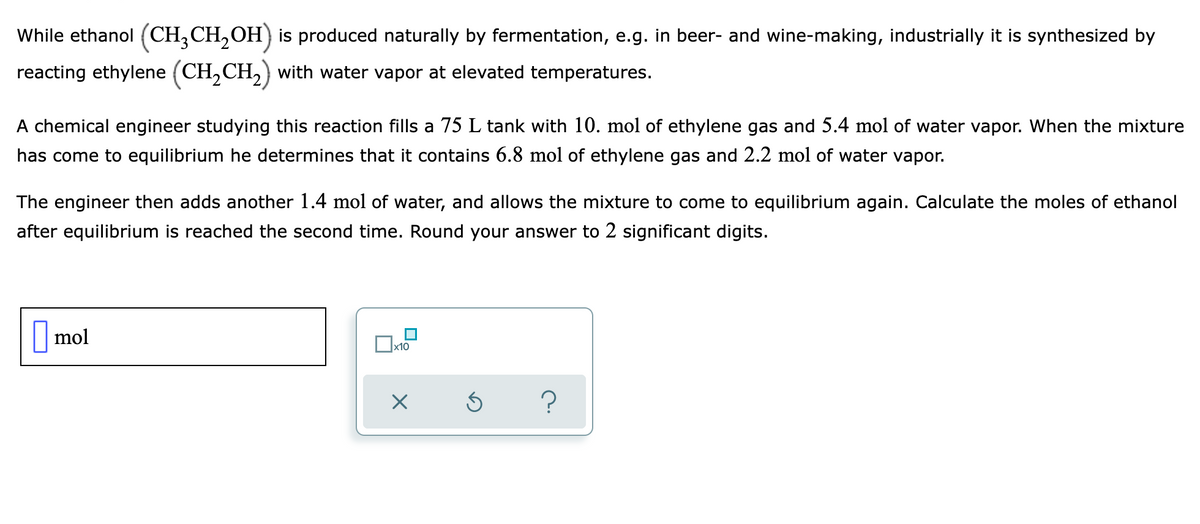
Transcribed Image Text:While ethanol (CH,CH,OH) is produced naturally by fermentation, e.g. in beer- and wine-making, industrially it is synthesized by
reacting ethylene (CH,CH,) with water vapor at elevated temperatures.
A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 75 L tank with 10. mol of ethylene gas and 5.4 mol of water vapor. When the mixture
has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 6.8 mol of ethylene gas and 2.2 mol of water vapor.
The engineer then adds another 1.4 mol of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of ethanol
after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
|mol
x10
O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning