Write an expression for the internal energy U of a gas of N particles (that is, atoms or molecules) at temperature Tin terms of N and Tand any required constants, when the gas consists of a. Ne (neon atoms) b. N2 (nitrogen molecules), assuming all degrees of freedom are active.
Write an expression for the internal energy U of a gas of N particles (that is, atoms or molecules) at temperature Tin terms of N and Tand any required constants, when the gas consists of a. Ne (neon atoms) b. N2 (nitrogen molecules), assuming all degrees of freedom are active.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter21: The Kinetic Theory Of Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21.8OQ
Related questions
Question
Answer question three please.
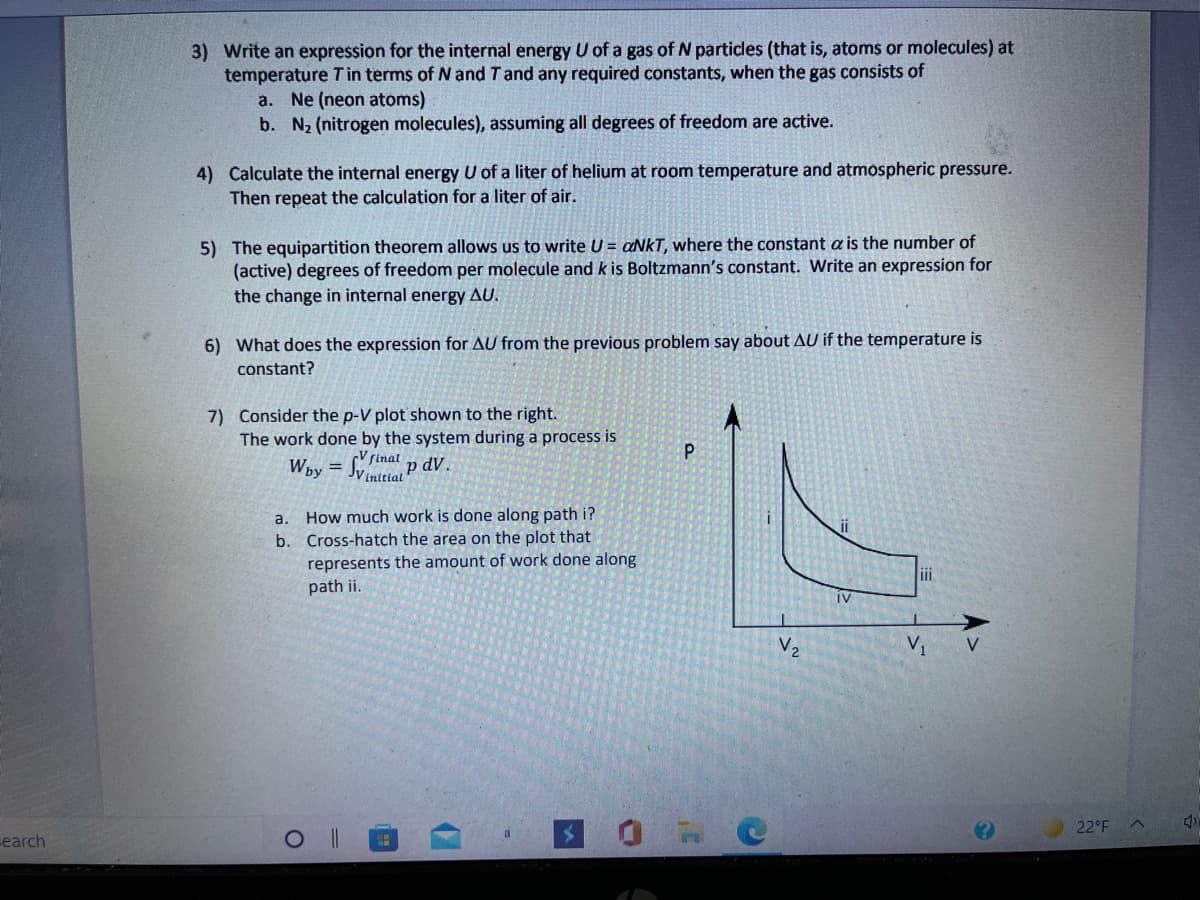
Transcribed Image Text:3) Write an expression for the internal energy U of a gas of N particles (that is, atoms or molecules) at
temperature Tin terms of N and Tand any required constants, when the gas consists of
a. Ne (neon atoms)
b. N2 (nitrogen molecules), assuming all degrees of freedom are active.
4) Calculate the internal energy U of a liter of helium at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Then repeat the calculation for a liter of air.
5) The equipartition theorem allows us to write U = aNkT, where the constant a is the number of
(active) degrees of freedom per molecule and k is Boltzmann's constant. Write an expression for
the change in internal energy AU.
6) What does the expression for AU from the previous problem say about AU if the temperature is
constant?
7) Consider the p-V plot shown to the right.
The work done by the system during a process is
Way = Sinat p dV.
%3D
JV initial
How much work is done along path i?
b. Cross-hatch the area on the plot that
represents the amount of work done along
path ii.
a.
iv
V2
V1
V
22°F
earch
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning