1. A disproportionation reaction is a specific type of redox reaction in which an element from a reaction undergoes both oxidation and reduction to form two different products. The disproportionation reaction shown below occurs in basic solution. Balance this reaction using the half-reaction method. CIO2 → ClO, + CIO; 2. Write the half reactions for the anode and the cathode as well as the overall cell reaction in the following galvanic cells. Then, calculate E"cell using the tabulated values of standard reduction potentials. Co(s) | Co² (aq) || Cu²*(aq) | Cu(s) Pb(s) | Pb²*(aq) || NO3 (aq), H*(aq), NO(g) | Pt(s) TABLE 20.1 Standard Electrode Potentials at 25 °C Reduction Half-Reaction E(V) Flgl + 2e 2F lag) 2.87 Stronger caidiring agent HOlagi + 2 H'lag) + 2e Weaker reducing agent 178 PhSo,(a 2 HOU) Mno,la- 2 Hou) Mr"(ag +4 H,OU - Aulal PbO,la + 4H"(agl + so"lagl + 2e 169 Mno, (ag + 4 H'lagl + 3e 168 Mno,"(agl + 8Hr(agl + 5e 151 Au"lagl + 3e 150 - Pt"(a+ 2 H,O - 20lag) Pbo,ls) + 4H"(agl + 20 146 Chlg+ 2 Crolagi + 14 H*lagi + 6e Oglgl + 4H'lagl +4e MnDla) + 4H"(ag+ 20 10, lagl+6H'lagl + 5e Bryn + 2e vo,lag) + 2 H"(ag +e 136 20agl + 7 H01n - 2 H,OUI - Mr"(ag + 2 H,OUI blagi + 3 HOn - 2 Brlag 133 123 121 1.20 109 vo"lagl + H,Un 100 NO, lag + 4H'lagl +3e NOlgl + 2 H,OIn 0.96 CIO,a +e Ag'lag) + CIO, lag 0.95 Aglal 0.80 Felag+e Fe"lag 0.77 Olgi + 2H(agl + 2 Mno, (ag +e H,O,lagi 0.70 Mno"lagi 0.56 bla + 2e Cu*lagl +e 0.54 Culs) 0.52 Olg + 2 H,01/ + 4e 4 OH (agl 0.40 Cư"lag) + 2e - Culs) 0.34 so lagl + 4 H'lagl+2e H,SOagl + Ho) 0.20 Cư"lag) e - Cu'lag 0.16 Sn"lag) + 2 e Sn"lag) 0.15 Hylal - Fels) 2H"lagl + 2e Fe*lag) + 3e" -0.036 Pt"(agl + 2e Sr"lag) + 2e NPlag+ 2 Pbl와 -0.13 Snlal -0.14 - Nie -0.23 Cdlagl 2e - Cdia) 0.40 Felag)- 2e - Felai 0.45 Crlag)+e - Clagi 0.50 Clag) + 3e Cris 0.73 Zr"(agl + 2e 2 HO 2 Znla 0.76 Hylal + 2 OH lagi - Mnla Mr"(a+ 2e -L18 AP lagl + 3e - Alla -166 Mg"(ag+2e - Mgls -237 -2.71 Nalal - Cals C lagl+2e -2.76 Be lagl +2e - Bale -2.90 Weaker caidiring agent Stronger reducing agent K'(ag +e Kisi -2.92 Llag) +e Lila -3.04
1. A disproportionation reaction is a specific type of redox reaction in which an element from a reaction undergoes both oxidation and reduction to form two different products. The disproportionation reaction shown below occurs in basic solution. Balance this reaction using the half-reaction method. CIO2 → ClO, + CIO; 2. Write the half reactions for the anode and the cathode as well as the overall cell reaction in the following galvanic cells. Then, calculate E"cell using the tabulated values of standard reduction potentials. Co(s) | Co² (aq) || Cu²*(aq) | Cu(s) Pb(s) | Pb²*(aq) || NO3 (aq), H*(aq), NO(g) | Pt(s) TABLE 20.1 Standard Electrode Potentials at 25 °C Reduction Half-Reaction E(V) Flgl + 2e 2F lag) 2.87 Stronger caidiring agent HOlagi + 2 H'lag) + 2e Weaker reducing agent 178 PhSo,(a 2 HOU) Mno,la- 2 Hou) Mr"(ag +4 H,OU - Aulal PbO,la + 4H"(agl + so"lagl + 2e 169 Mno, (ag + 4 H'lagl + 3e 168 Mno,"(agl + 8Hr(agl + 5e 151 Au"lagl + 3e 150 - Pt"(a+ 2 H,O - 20lag) Pbo,ls) + 4H"(agl + 20 146 Chlg+ 2 Crolagi + 14 H*lagi + 6e Oglgl + 4H'lagl +4e MnDla) + 4H"(ag+ 20 10, lagl+6H'lagl + 5e Bryn + 2e vo,lag) + 2 H"(ag +e 136 20agl + 7 H01n - 2 H,OUI - Mr"(ag + 2 H,OUI blagi + 3 HOn - 2 Brlag 133 123 121 1.20 109 vo"lagl + H,Un 100 NO, lag + 4H'lagl +3e NOlgl + 2 H,OIn 0.96 CIO,a +e Ag'lag) + CIO, lag 0.95 Aglal 0.80 Felag+e Fe"lag 0.77 Olgi + 2H(agl + 2 Mno, (ag +e H,O,lagi 0.70 Mno"lagi 0.56 bla + 2e Cu*lagl +e 0.54 Culs) 0.52 Olg + 2 H,01/ + 4e 4 OH (agl 0.40 Cư"lag) + 2e - Culs) 0.34 so lagl + 4 H'lagl+2e H,SOagl + Ho) 0.20 Cư"lag) e - Cu'lag 0.16 Sn"lag) + 2 e Sn"lag) 0.15 Hylal - Fels) 2H"lagl + 2e Fe*lag) + 3e" -0.036 Pt"(agl + 2e Sr"lag) + 2e NPlag+ 2 Pbl와 -0.13 Snlal -0.14 - Nie -0.23 Cdlagl 2e - Cdia) 0.40 Felag)- 2e - Felai 0.45 Crlag)+e - Clagi 0.50 Clag) + 3e Cris 0.73 Zr"(agl + 2e 2 HO 2 Znla 0.76 Hylal + 2 OH lagi - Mnla Mr"(a+ 2e -L18 AP lagl + 3e - Alla -166 Mg"(ag+2e - Mgls -237 -2.71 Nalal - Cals C lagl+2e -2.76 Be lagl +2e - Bale -2.90 Weaker caidiring agent Stronger reducing agent K'(ag +e Kisi -2.92 Llag) +e Lila -3.04
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter17: Electrochemistry And Its Applications
Section17.3: Voltaic Cells
Problem 17.3PSP
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1. A disproportionation reaction is a specific type of redox reaction in which an element from a reaction undergoes both
oxidation and reduction to form two different products. The disproportionation reaction shown below occurs in basic
solution. Balance this reaction using the half-reaction method.
CIO2 → ClO, + CIO;
2. Write the half reactions for the anode and the cathode as well as the overall cell reaction in the following galvanic cells.
Then, calculate E"cell using the tabulated values of standard reduction potentials.
Co(s) | Co² (aq) || Cu²*(aq) | Cu(s)
Pb(s) | Pb²*(aq) || NO3 (aq), H*(aq), NO(g) | Pt(s)
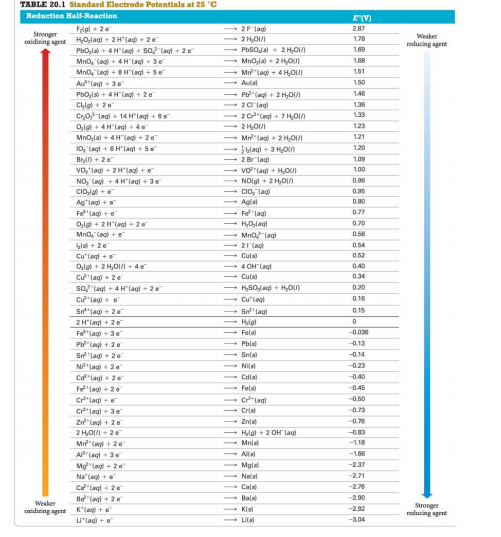
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 20.1 Standard Electrode Potentials at 25 °C
Reduction Half-Reaction
E(V)
Flgl + 2e
2F lag)
2.87
Stronger
caidiring agent HOlagi + 2 H'lag) + 2e
Weaker
reducing agent
178
PhSo,(a 2 HOU)
Mno,la- 2 Hou)
Mr"(ag +4 H,OU
- Aulal
PbO,la + 4H"(agl + so"lagl + 2e
169
Mno, (ag + 4 H'lagl + 3e
168
Mno,"(agl + 8Hr(agl + 5e
151
Au"lagl + 3e
150
- Pt"(a+ 2 H,O
- 20lag)
Pbo,ls) + 4H"(agl + 20
146
Chlg+ 2
Crolagi + 14 H*lagi + 6e
Oglgl + 4H'lagl +4e
MnDla) + 4H"(ag+ 20
10, lagl+6H'lagl + 5e
Bryn + 2e
vo,lag) + 2 H"(ag +e
136
20agl + 7 H01n
- 2 H,OUI
- Mr"(ag + 2 H,OUI
blagi + 3 HOn
- 2 Brlag
133
123
121
1.20
109
vo"lagl + H,Un
100
NO, lag + 4H'lagl +3e
NOlgl + 2 H,OIn
0.96
CIO,a +e
Ag'lag) +
CIO, lag
0.95
Aglal
0.80
Felag+e
Fe"lag
0.77
Olgi + 2H(agl + 2
Mno, (ag +e
H,O,lagi
0.70
Mno"lagi
0.56
bla + 2e
Cu*lagl +e
0.54
Culs)
0.52
Olg + 2 H,01/ + 4e
4 OH (agl
0.40
Cư"lag) + 2e
- Culs)
0.34
so lagl + 4 H'lagl+2e
H,SOagl + Ho)
0.20
Cư"lag) e
- Cu'lag
0.16
Sn"lag) + 2 e
Sn"lag)
0.15
Hylal
- Fels)
2H"lagl + 2e
Fe*lag) + 3e"
-0.036
Pt"(agl + 2e
Sr"lag) + 2e
NPlag+ 2
Pbl와
-0.13
Snlal
-0.14
- Nie
-0.23
Cdlagl 2e
- Cdia)
0.40
Felag)- 2e
- Felai
0.45
Crlag)+e
- Clagi
0.50
Clag) + 3e
Cris
0.73
Zr"(agl + 2e
2 HO 2
Znla
0.76
Hylal + 2 OH lagi
- Mnla
Mr"(a+ 2e
-L18
AP lagl + 3e
- Alla
-166
Mg"(ag+2e
- Mgls
-237
-2.71
Nalal
- Cals
C lagl+2e
-2.76
Be lagl +2e
- Bale
-2.90
Weaker
caidiring agent
Stronger
reducing agent
K'(ag +e
Kisi
-2.92
Llag) +e
Lila
-3.04
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning