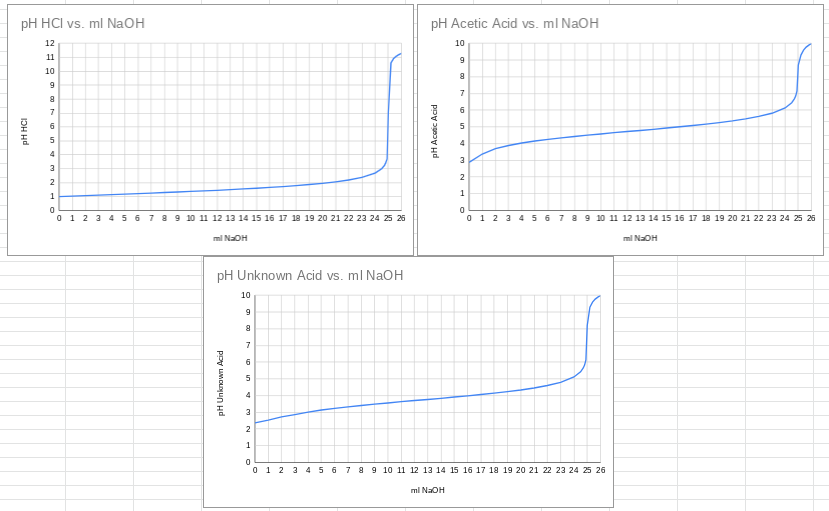
1. On each graph, identify an indicator that could be used in the titration, and write the name of the indicator and the effective pH range on the graph. 2. For the titration curves of the weak acids, (acetic acid and the unknown), identify the half neutralization point, and determine the pK, for each acid. Write the values on the graph. 3. Identify the unknown using the list of acids and their pK, values below. 4. Indicate the region of buffering activity on the titration curves of the weak acids. 5. Determine the pH at the equivalence point for each acid. (This is the point half the volume of NaOH added equals the volume of the sample, since the molarities of acid and base are the same). Show this on each graph. 6. Describe the main differences between the titration curves of the strong acid, HCI, and the weak acids. 7. Comment on which method (pH meter or indicators) you think would be the most accurate in determining equivalence points.
1. On each graph, identify an indicator that could be used in the titration, and write the name of the indicator and the effective pH range on the graph. 2. For the titration curves of the weak acids, (acetic acid and the unknown), identify the half neutralization point, and determine the pK, for each acid. Write the values on the graph. 3. Identify the unknown using the list of acids and their pK, values below. 4. Indicate the region of buffering activity on the titration curves of the weak acids. 5. Determine the pH at the equivalence point for each acid. (This is the point half the volume of NaOH added equals the volume of the sample, since the molarities of acid and base are the same). Show this on each graph. 6. Describe the main differences between the titration curves of the strong acid, HCI, and the weak acids. 7. Comment on which method (pH meter or indicators) you think would be the most accurate in determining equivalence points.
Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Chapter18: Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6STP
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:pH HCI vs. ml NaOH
pH Acetic Acid vs. ml NaOH
12
10
11
10
6
6
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 25
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
ml NaOH
ml NaOH
pH Unknown Acid vs. ml NaOH
10
7
6
3
2
1
0 1 2 3 45 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
ml NaOH
IOH Hd
pH Acatic Acid

Transcribed Image Text:1. On each graph, identify an indicator that could be used in the titration, and write the name
of the indicator and the effective pH range on the graph.
2. For the titration curves of the weak acids, (acetic acid and the unknown), identify the half
neutralization point, and determine the pK, for each acid. Write the values on the graph.
3. Identify the unknown using the list of acids and their pK, values below.
4. Indicate the region of buffering activity on the titration curves of the weak acids.
5. Determine the pH at the equivalence point for each acid. (This is the point half the
volume of NaOH added equals the volume of the sample, since the molarities of acid and
base are the same). Show this on each graph.
6. Describe the main differences between the titration curves of the strong acid, HCI, and
the weak acids.
7. Comment on which method (pH meter or indicators) you think would be the most
accurate in determining equivalence points.
Select weak acid pK, values
pK.
4.74
Acid
Acetic Acid
Benzoic Acid
4.20
Chlorous Acid
1.90
Formic Acid
Hydrocyanic Acid
Pyridinium chloride
3.74
9.21
5.20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning