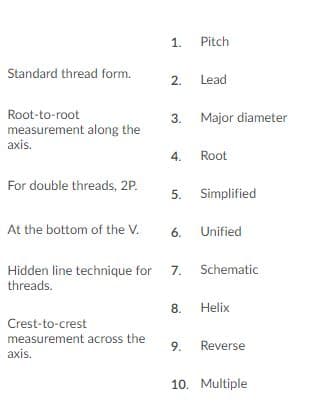
1. Pitch Standard thread form. 2. Lead Root-to-root 3. Major diameter measurement along the axis. 4 Root For double threads, 2P 5. Simplified At the bottom of the V. 6. Unified Schematic Hidden line technique for threads. 7. 8. Helix Crest-to-crest measurement across the axis. 9. Reverse 10. Multiple 1. Pitch Standard thread form. 6 2. Lead 3 Major diameter Root-to-root 1 measurement along the axis Root 4. For double threads, 2P. 2 5. Simplified At the bottom of the V. Unified 6 7. Schematic Hidden line technique for threads. 5 8. Helix Crest-to-crest 3 measurement across the axis 9 Reverse 10. Multiple Ln
Match each of the following terms to the phrase that describes it. Answers are used only once.
NOTE: I need the answers I provided in the 2nd image and in text below double checked for accuracy because I asked this question twice and received 2 different answers from different tutors on this site.
Other Answers:
The Unified standard thread form is used to define the various parameters of thread (pitch, height, major diameter, minor diameter, helix angle, etc) as well as the provided allowances, designations and the tolerances in thread.
The root to root measurement along the axis of the thread is called as Pitch. In other words it is distance between two consecutive crest of the thread along the axis of thread.
For the double threads, the lead is equal to twice of pitch.
The Root is the present at the bottom of the V-shaped thread. The V-shaped thread root is triangular in shape.
Simplified method is used for the hidden line technique.
The distance between the crest to crest across the axis of thread is known as major diameter of the thread.

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images


