1.96 Initial pH From your analysis of the titration curve: 23.203 mL of NaOH used to reach the equivalence point. Calculated Molarity of the unknown acid 0.09696 2.92 pH at the half-way to the equivalence point pKa the unknown acid Ka of the unknown acid Identity of unknown acid
1.96 Initial pH From your analysis of the titration curve: 23.203 mL of NaOH used to reach the equivalence point. Calculated Molarity of the unknown acid 0.09696 2.92 pH at the half-way to the equivalence point pKa the unknown acid Ka of the unknown acid Identity of unknown acid
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter14: Equilibria In Acid-base Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 32QAP: Enough water is added to the buffer in Question 30 to make the total volume 5.00 L. (a) Calculate...
Related questions
Question
100%
please show example on how to solve I'm so confused
Transcribed Image Text:unbe
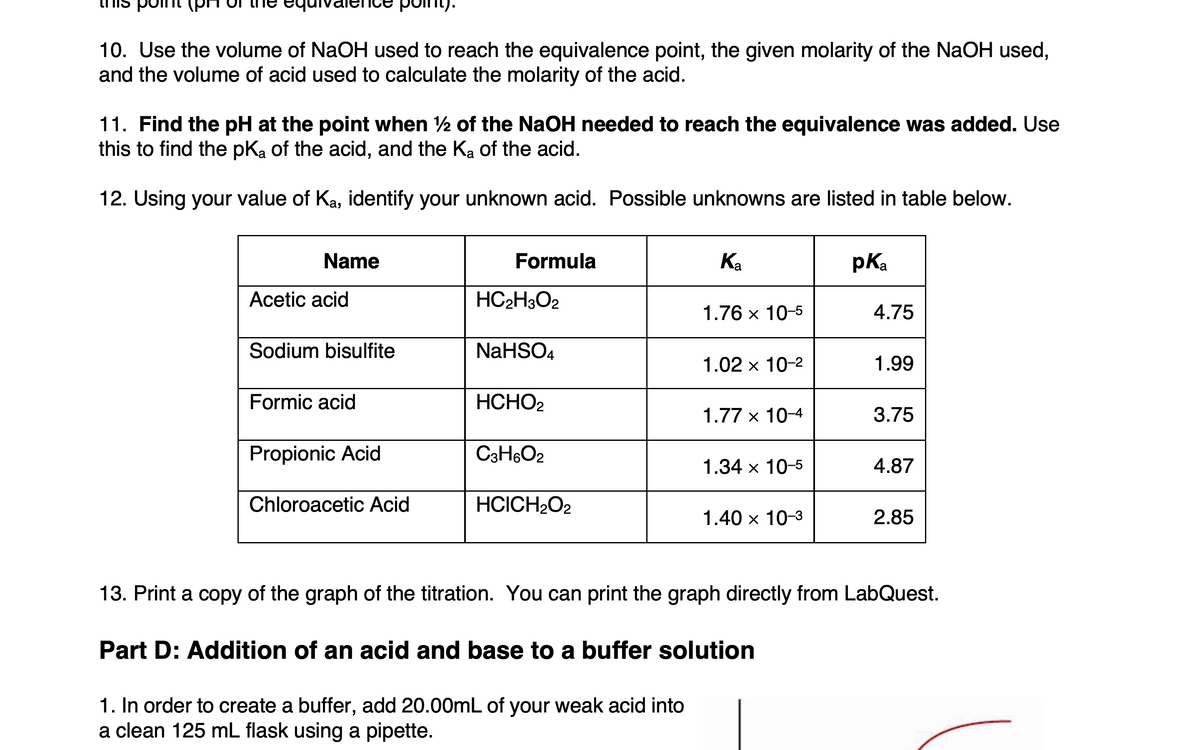
10. Use the volume of NaOH used to reach the equivalence point, the given molarity of the NaOH used,
and the volume of acid used to calculate the molarity of the acid.
11. Find the pH at the point when 2 of the NaOH needed to reach the equivalence was added. Use
this to find the pka of the acid, and the Ka of the acid.
12. Using your value of Ka, identify your unknown acid. Possible unknowns are listed in table below.
Name
Formula
Ка
pKa
Аcetic acid
HC2H3O2
1.76 x 10-5
4.75
Sodium bisulfite
NaHSO4
1.02 x 10-2
1.99
Formic acid
HCHO2
1.77 x 10-4
3.75
Propionic Acid
C3H6O2
1.34 x 10-5
4.87
Chloroacetic Acid
HCICH2O2
1.40 x 10-3
2.85
13. Print a copy of the graph of the titration. You can print the graph directly from LabQuest.
Part D: Addition of an acid and base to a buffer solution
1. In order to create a buffer, add 20.00mL of your weak acid into
a clean 125 mL flask using a pipette.
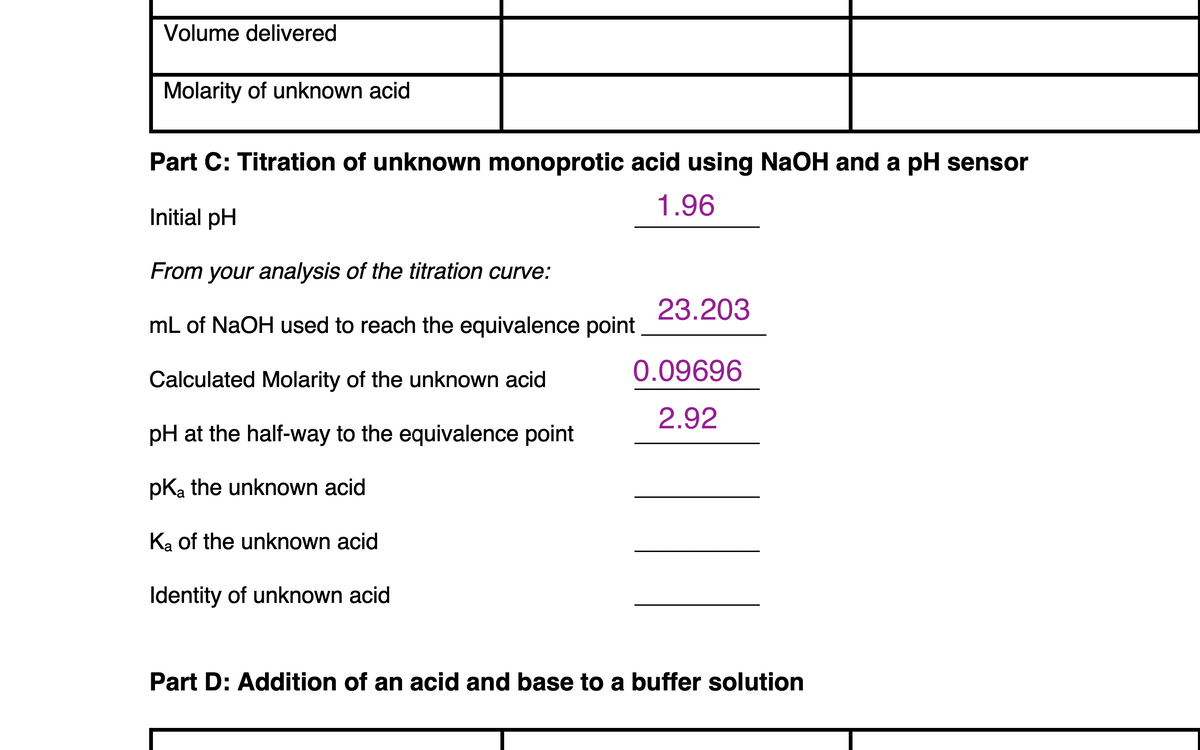
Transcribed Image Text:Volume delivered
Molarity of unknown acid
Part C: Titration of unknown monoprotic acid using NaOH and a pH sensor
1.96
Initial pH
From your analysis of the titration curve:
23.203
mL of NaOH used to reach the equivalence point
0.09696
Calculated Molarity of the unknown acid
2.92
pH at the half-way to the equivalence point
pKa the unknown acid
Ka of the unknown acid
Identity of unknown acid
Part D: Addition of an acid and base to a buffer solution
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning