22. Consider the same set up as in the previous exercise but now consider the case of incomplete information in which v is private information for B which can take two values, either vH or VL such that VH > VL- Suppose Pr (v = v#) = 0 E (0, 1) and Pr (v= v1) = 1 – 0 which is common knowledge for B and S. The strategic situation is represented below where S does not know if the game being played is the left matrix (which arises if B's type is vH) or the right matrix (which arises if B's type is v1). To simplify matters suppose Pm = PL in the case in which a B type offers PH and S demands Pr. PH PL PH PL VL – PL,0 VL – PL,0 (1) VH – PL,0 Vн — PL,0 PH VH – PH, PH PH VL - PH, PH - c - C PL 0, -c PL VH VL Determine the best responses for each type of B in the matrices in (1) given that B does know а. if she is either vH or vL. Then find the expected profit for each of S's strategies, for choosing PH or PL, given that S foresees the best responses of each type of B. Then compare the two expected profits in order to find the optimal choice of S. Determine the set of pure strategy Bayesian Nash (BN) equilibria for the incomplete information game given that v# > PH > PL = c> VL. b. Find the normal form representation payoff matrix using expected utility for both B and S where 0 € (0, 1) is assumed to be common knowledge. (Hint: B has two types where the strategy for both types can be labeled PHH, PHL, PLH and PLL; PHL means that B type vH chooses PH while B type vL chooses PL; this means row player B has four strategies while the column player has only two).
22. Consider the same set up as in the previous exercise but now consider the case of incomplete information in which v is private information for B which can take two values, either vH or VL such that VH > VL- Suppose Pr (v = v#) = 0 E (0, 1) and Pr (v= v1) = 1 – 0 which is common knowledge for B and S. The strategic situation is represented below where S does not know if the game being played is the left matrix (which arises if B's type is vH) or the right matrix (which arises if B's type is v1). To simplify matters suppose Pm = PL in the case in which a B type offers PH and S demands Pr. PH PL PH PL VL – PL,0 VL – PL,0 (1) VH – PL,0 Vн — PL,0 PH VH – PH, PH PH VL - PH, PH - c - C PL 0, -c PL VH VL Determine the best responses for each type of B in the matrices in (1) given that B does know а. if she is either vH or vL. Then find the expected profit for each of S's strategies, for choosing PH or PL, given that S foresees the best responses of each type of B. Then compare the two expected profits in order to find the optimal choice of S. Determine the set of pure strategy Bayesian Nash (BN) equilibria for the incomplete information game given that v# > PH > PL = c> VL. b. Find the normal form representation payoff matrix using expected utility for both B and S where 0 € (0, 1) is assumed to be common knowledge. (Hint: B has two types where the strategy for both types can be labeled PHH, PHL, PLH and PLL; PHL means that B type vH chooses PH while B type vL chooses PL; this means row player B has four strategies while the column player has only two).
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter19: The Problem Of Adverse Selection
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19.5IP
Related questions
Question
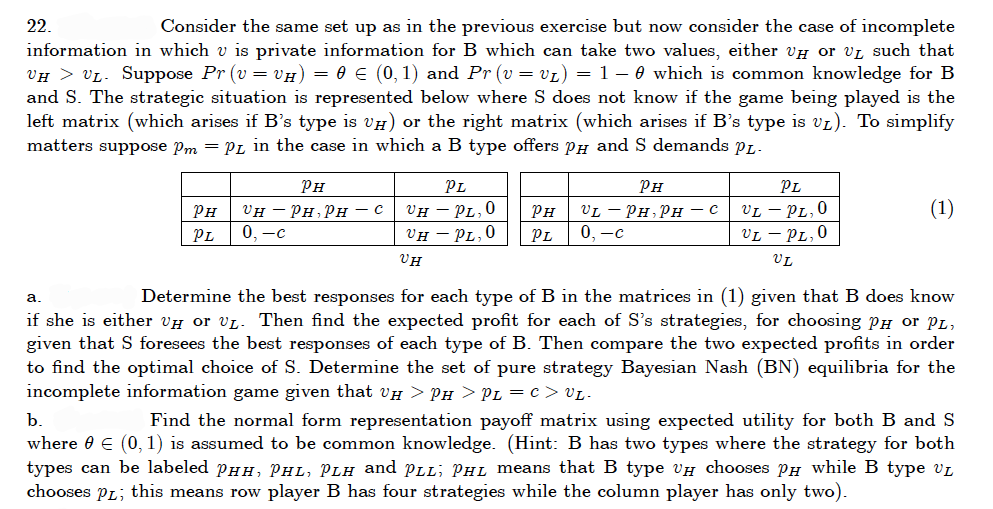
Transcribed Image Text:22.
Consider the same set up as in the previous exercise but now consider the case of incomplete
information in which v is private information for B which can take two values, either vH or vL such that
VH > VL. Suppose Pr (v = VH) = 0 E (0, 1) and Pr (v = VL) = 1 – 0 which is common knowledge for B
and S. The strategic situation is represented below where S does not know if the game being played is the
left matrix (which arises if B's type is vH) or the right matrix (which arises if B's type is vz). To simplify
matters suppose pm = PL in the case in which a B type offers PH and S demands PL-
PH
PL
PH
PL
VH – PL,0
VH – PL,0
VL – PL, 0
VL – PL,0
(1)
Vн — Рн,рн — с
0, —с
VL — Pн, Рн — с
0, —с
PH
PH
PL
PL
VH
UL
Determine the best responses for each type of B in the matrices in (1) given that B does know
а.
if she is either vH or vL. Then find the expected profit for each of S's strategies, for choosing PH or PL,
given that S foresees the best responses of each type of B. Then compare the two expected profits in order
to find the optimal choice of S. Determine the set of pure strategy Bayesian Nash (BN) equilibria for the
incomplete information game given that vH > PH > PL = c > VL.
b.
Find the normal form representation payoff matrix using expected utility for both B and S
where 0 € (0, 1) is assumed to be common knowledge. (Hint: B has two types where the strategy for both
types can be labeled PHH, PHL, PLH and PLL; PHL means that B type ví chooses PH while B type vL
chooses PL; this means row player B has four strategies while the column player has only two).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning