3. Price controls in the Florida orange market The following graph shows the annual market for Florida oranges, which are sold in units of 90-pound boxes. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the folowing questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any coresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool (? Market for Florida Oranges 50 I Price (Dollars per box) 20 45 Supply Quantity Demanded (Millions of boxes) Quantity Supplied (Millions of boxes) 40 120 80 35 30 25 20 15 Demand 10 O 20 40 00 80 100 120 140 100 180 200 QUANTITY (MIlions of boxes) In this market, the equilibrium price is $ per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is million boxes For each of the prices listed in the following table, determine the quantity of oranges demanded, the quantity of oranges supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on prices in the absence of any price controls. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied (Dollars per box) (Millions of boxes) (Millions of boxes) Pressure on Prices 35 15 A price ceiling above $25 per box in this market will Because it takes many years before newly planted orange trees bear fruit, the supply curve in the short run is almost vertical. In the long run, farmers can decide whether to plant oranges on their land, to plant something else, or to sell their land altogether. Therefore, the long-run supply of oranges is much more price sensitive than the short-run supply of oranges. Assuming that the long-run demand tor oranges is the same as the short-run demand, you would expect a price ceiling that is set below the cquilibrium price to result in a v that is v in the long run than in the short run. +------
3. Price controls in the Florida orange market The following graph shows the annual market for Florida oranges, which are sold in units of 90-pound boxes. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the folowing questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any coresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool (? Market for Florida Oranges 50 I Price (Dollars per box) 20 45 Supply Quantity Demanded (Millions of boxes) Quantity Supplied (Millions of boxes) 40 120 80 35 30 25 20 15 Demand 10 O 20 40 00 80 100 120 140 100 180 200 QUANTITY (MIlions of boxes) In this market, the equilibrium price is $ per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is million boxes For each of the prices listed in the following table, determine the quantity of oranges demanded, the quantity of oranges supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on prices in the absence of any price controls. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied (Dollars per box) (Millions of boxes) (Millions of boxes) Pressure on Prices 35 15 A price ceiling above $25 per box in this market will Because it takes many years before newly planted orange trees bear fruit, the supply curve in the short run is almost vertical. In the long run, farmers can decide whether to plant oranges on their land, to plant something else, or to sell their land altogether. Therefore, the long-run supply of oranges is much more price sensitive than the short-run supply of oranges. Assuming that the long-run demand tor oranges is the same as the short-run demand, you would expect a price ceiling that is set below the cquilibrium price to result in a v that is v in the long run than in the short run. +------
Chapter4: Markets In Action
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2SQP
Related questions
Question
Solve the attahment.
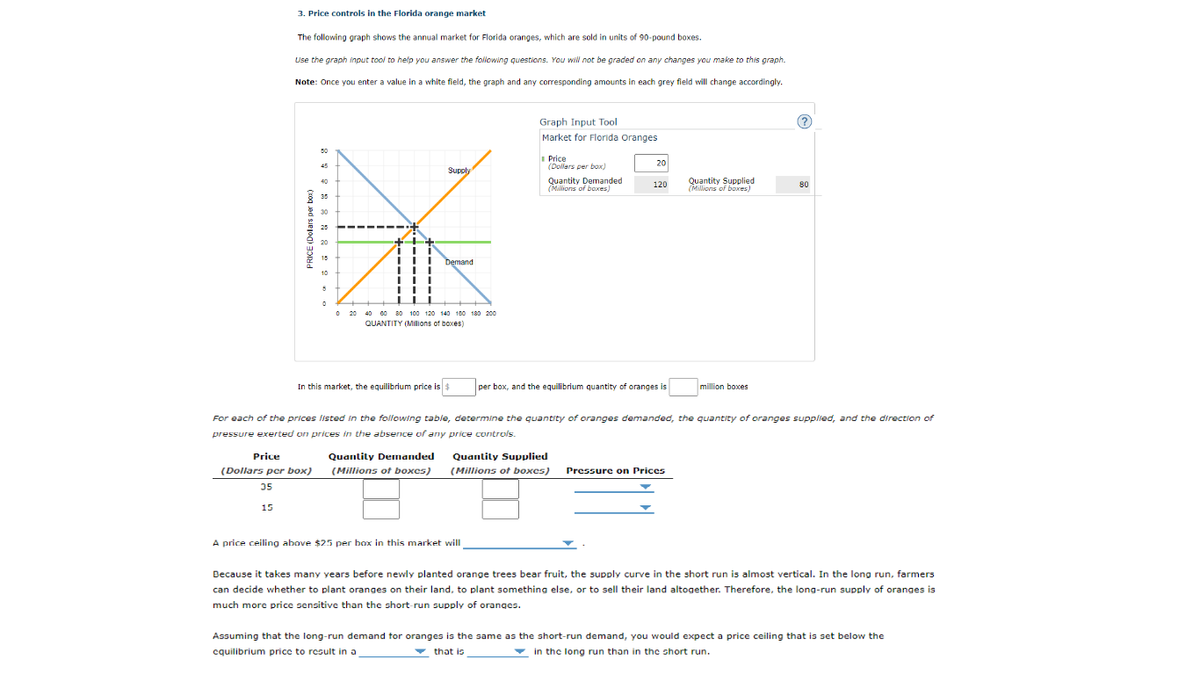
Transcribed Image Text:3. Price controls in the Florida orange market
The following graph shows the annual market for Florida oranges, which are sold in units of 90-pound boxes.
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the folowing questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any coresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.
Graph Input Tool
(?
Market for Florida Oranges
50
I Price
(Dollars per box)
20
45
Supply
Quantity Demanded
(Millions of boxes)
Quantity Supplied
(Millions of boxes)
40
120
80
35
30
25
20
15
Demand
10
O 20 40 00 80 100 120 140 100 180 200
QUANTITY (MIlions of boxes)
In this market, the equilibrium price is $
per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is
million boxes
For each of the prices listed in the following table, determine the quantity of oranges demanded, the quantity of oranges supplied, and the direction of
pressure exerted on prices in the absence of any price controls.
Price
Quantity Demanded
Quantity Supplied
(Dollars per box) (Millions of boxes)
(Millions of boxes)
Pressure on Prices
35
15
A price ceiling above $25 per box in this market will
Because it takes many years before newly planted orange trees bear fruit, the supply curve in the short run is almost vertical. In the long run, farmers
can decide whether to plant oranges on their land, to plant something else, or to sell their land altogether. Therefore, the long-run supply of oranges is
much more price sensitive than the short-run supply of oranges.
Assuming that the long-run demand tor oranges is the same as the short-run demand, you would expect a price ceiling that is set below the
cquilibrium price to result in a
v that is
v
in the long run than in the short run.
+------
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning