32. It would be very useful if we could use the inexpensive carbon in coal to make more complex organic molecules such as gaseous or liquid fuels. The formation of methane from coal and water is reactant-favored and thus canmot occur unless there is some energy transfer from outside. This problem examines the feasibility of other reactions using coal and water. a) Write three balanced equations for the reactions of coal (carbon) and steam to make ethane gas, C2H(g), propane gas, C,Hs(g), and liquid methanol, CH;OH((), with carbon dioxide as a by-product. b) Using the data in Appendix B, calculate AH°, AS°, and AG° for each reaction, and then comment on whether any of them would be a feasible way to make the stated products.
32. It would be very useful if we could use the inexpensive carbon in coal to make more complex organic molecules such as gaseous or liquid fuels. The formation of methane from coal and water is reactant-favored and thus canmot occur unless there is some energy transfer from outside. This problem examines the feasibility of other reactions using coal and water. a) Write three balanced equations for the reactions of coal (carbon) and steam to make ethane gas, C2H(g), propane gas, C,Hs(g), and liquid methanol, CH;OH((), with carbon dioxide as a by-product. b) Using the data in Appendix B, calculate AH°, AS°, and AG° for each reaction, and then comment on whether any of them would be a feasible way to make the stated products.
Chemistry for Engineering Students
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781285199023
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter10: Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.39PAE: How does the second law of thermodynamics explain a spontaneous change in a system that becomes more...
Related questions
Question
100%
32. Refer to the attached photo.
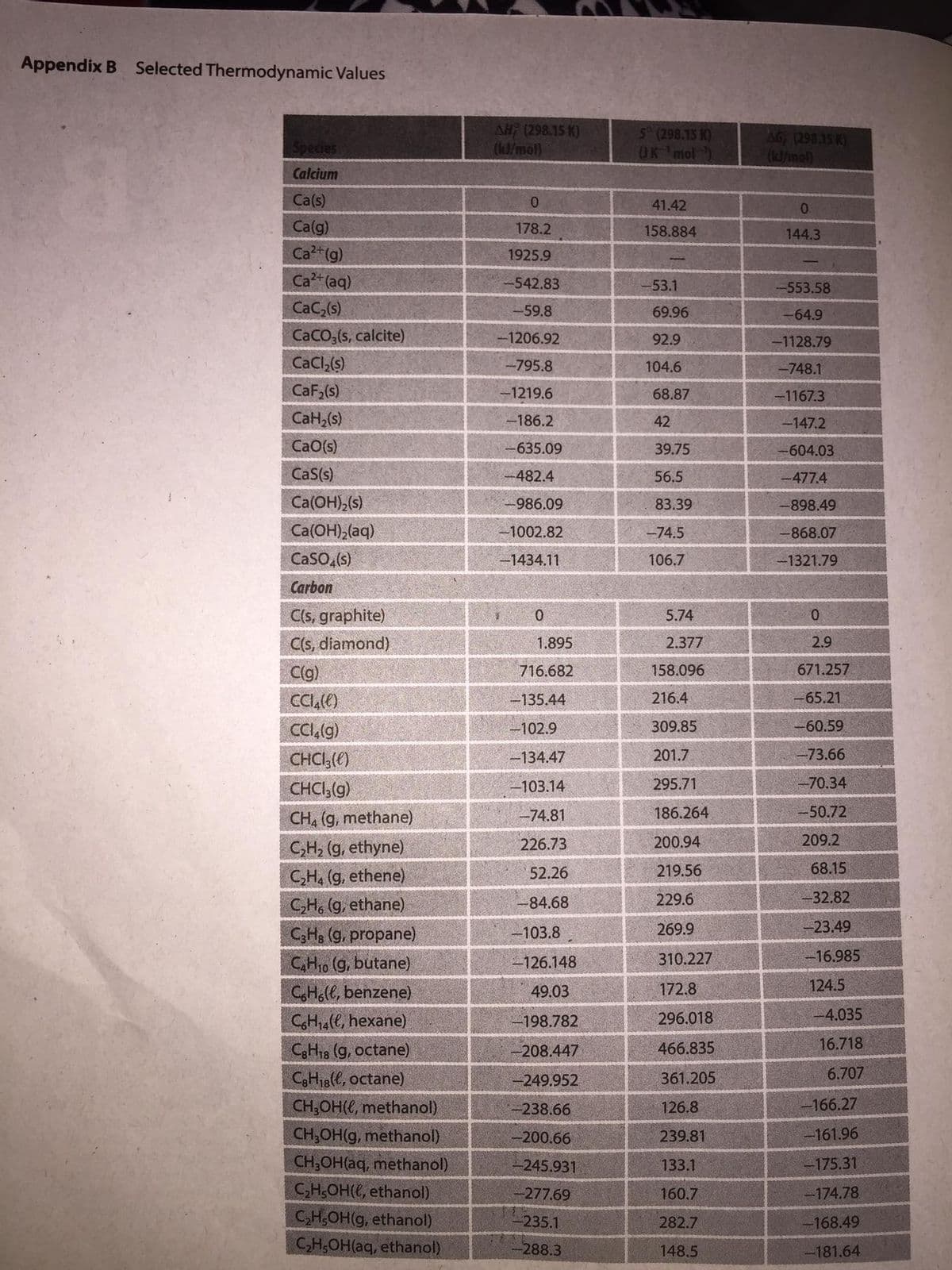
Transcribed Image Text:Appendix B Selected Thermodynamic Values
AH; (298.15 K)
(kd/mol)
5 (298.15 K)
OK mol)
AG (298.15 K)
(k3/mol)
Species
Calcium
Ca(s)
41.42
Ca(g)
178.2
158.884
144.3
Ca?+(g)
1925.9
Ca+ (aq)
542.83
53.1
-553.58
CaC,(s)
59.8
69.96
-64.9
CaCO,(s, calcite)
-1206.92
92.9
-1128.79
CaCl,(s)
-795.8
104.6
-748.1
CaF,(s)
-1219.6
68.87
1167.3
CaH,(s)
-186.2
42
-147.2
CaO(s)
-635.09
39.75
604.03
CaS(s)
-482.4
56.5
477.4
Ca(OH),(s)
986.09
83.39
-898.49
Ca(OH),(aq)
-1002.82
-74.5
-868.07
CaSo,(s)
-1434.11
106.7
-1321.79
Carbon
C(s, graphite)
C(s, diamond)
5.74
0.
1.895
2.377
2.9
C(g)
716.682
158.096
671.257
,(CCIA(Cי
-135.44
216.4
-65.21
-102.9
309.85
-60.59
CCl,(g)
CHCI,()
-134.47
201.7
-73.66
295.71
-70.34
CHCI, (g)
-103.14
CH, (g, methane)
-74.81
186.264
-50.72
C,H, (g, ethyne)
226.73
200.94
209.2
C,H, (g, ethene)
52.26
219.56
68.15
C,H, (g, ethane)
-84.68
229.6
-32.82
269.9
-23.49
C,H3 (g, propane)
C,Ho (g, butane)
CH(C, benzene)
-103.8
-126.148
310.227
-16.985
49.03
172.8
124.5
CH14(e, hexane)
296.018
4.035
198.782
16.718
CaH18 (g, octane)
CHjg(C, octane)
CH,OH(E, methanol)
-208.447
466.835
-249.952
361.205
6.707
-238.66
126.8
-166.27
CH,OH(g, methanol)
-200.66
239.81
-161.96
CH;OH(aq, methanol)
-245.931
133.1
175.31
C,H,OH(C, ethanol)
-277.69
160.7
-174.78
CH,OH(g, ethanol)
-235.1
282.7
-168.49
C,H,OH(aq, ethanol)
-288.3
148.5
-181.64

Transcribed Image Text:32. It would be very useful if we could use the inexpensive carbon in coal to make more complex organic molecules such as
gaseous or liquid fuels. The formation of methane from coal and water is reactant-favored and thus canmot occur unless
there is some energy transfer from outside. This problem examines the feasibility of other reactions using coal and
water.
a) Write three balanced equations for the reactions of coal (carbon) and steam to make ethane gas, C,H,(g), propane
gas, C3H3(g), and liquid methanol, CH;OH(), with carbon dioxide as a by-product.
b) Using the data in Appendix B, calculate AH°, AS°, and AG° for each reaction, and then comment on whether any of
them would be a feasible way to make the stated products.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning