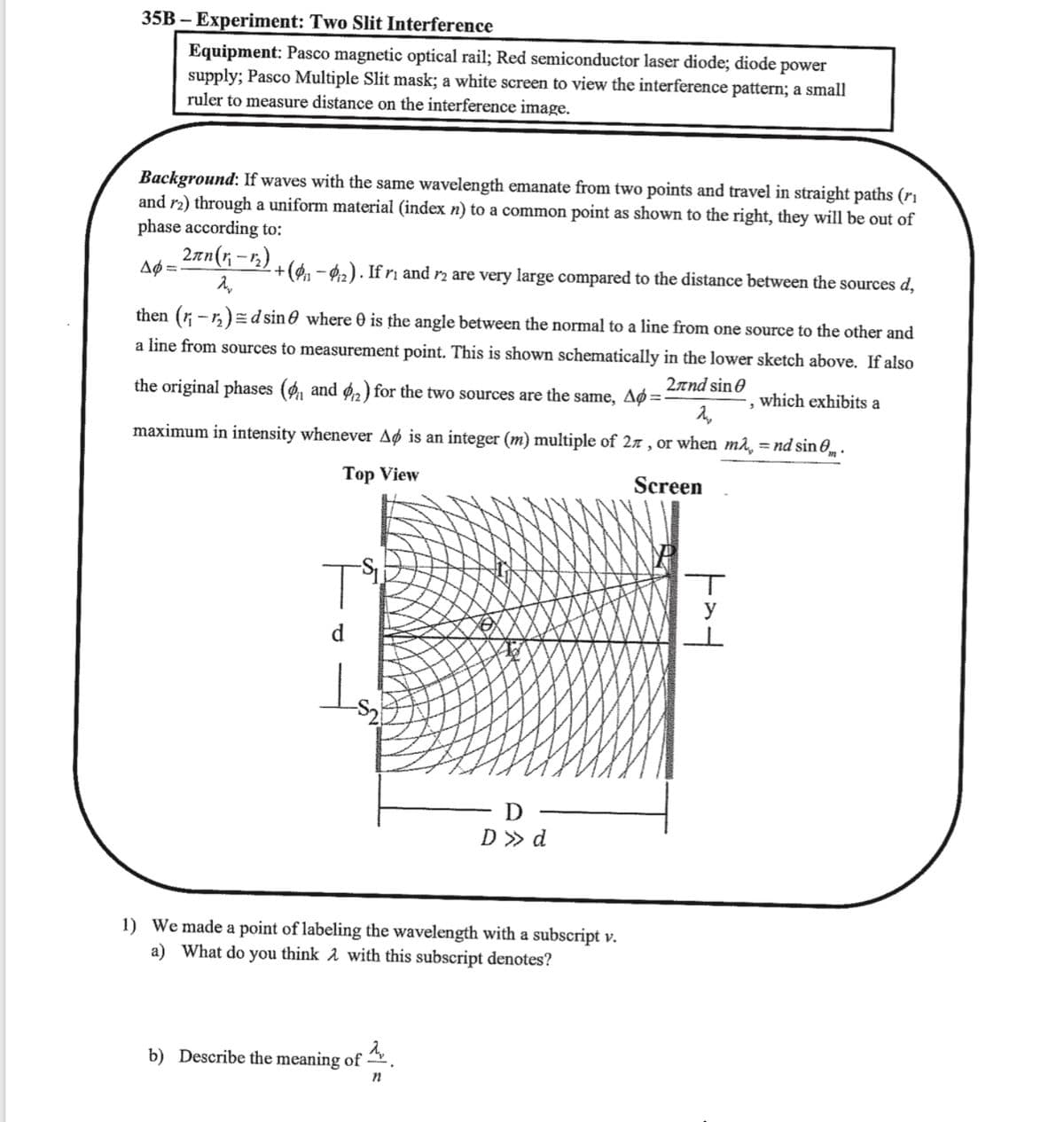
35B – Experiment: Two Slit Interference Equipment: Pasco magnetic optical rail; Red semiconductor laser diode; diode power supply; Pasco Multiple Slit mask; a white screen to view the interference pattern; a small ruler to measure distance on the interference image. Background: If waves with the same wavelength emanate from two points and travel in straight paths (ri and r2) through a uniform material (index n) to a common point as shown to the right, they will be out of phase according to: 2an(r-r). Aø =- +( – 42) . If rị and r2 are very large compared to the distance between the sources d, then (r -r,)Ed sin 0 where 0 is the angle between the normal to a line from one source to the other and a line from sources to measurement point. This is shown schematically in the lower sketch above. If also the original phases (, and 6, ) for the two sources are the same, Aø=: 2rnd sin e which exhibits a maximum in intensity whenever Aø is an integer (m) multiple of 27 , or when m2, = nd sin 0 . Top View Screen d. D D » d 1) We made a point of labeling the wavelength with a subscript v. a) What do you think 2 with this subscript denotes? b) Describe the meaning of
Atomic Spectra
According to the Bohr model of an atom, the electron in an atom moves around a nucleus in fixed orbits with specific energies known as energy levels. The orbital energies are quantized. The electrons remain in these energy levels until they emit or absorb a photon of a particular wavelength, the quantum of energy. If the electron emits a photon, it then falls back to a lower energy level, and if it absorbs a photon, the electron rises to higher energy levels. The photons released or absorbed in these transitions of an electron are studied and analyzed on a screen as atomic spectra.
Ruby Lasers
Lasers are devices that emit light using atoms or molecules at a certain wavelength and amplify the light to produce a narrow beam of radiation. It works as per the principle of electromagnetic radiation. Their source of emission contains the same frequency and same phase. It was invented in the year 1960 by the great noble scientist, Theodore Maiman.
Balmer Series
The spectrum of frequency observed when electromagnetic radiation is emitted from an atom when it goes from higher energy state to lower state, is known as emission spectrum. This transition occurs when an excited electron moves from higher to lower state. It has many possible electron transitions and each transition has a specific energy difference.
Emission Spectrum
Every state of matter tries to be at minimum potential energy or it can be said that the atoms of element/ substance arrange themselves such that overall energy is minimum.
describe the meaning of wavelength/n
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









