7. Using the value given for K, for the equation in Problem 6, at 500°C, calculate (a) Ke for the reaction H2(6) + I) = 2 HI) (b) Keg for the reaction HI) = }H) +12(«) (c) Ke for the reaction H2) + I2) (d) K for the reaction 4 HI 2 H, 3. 2(g) HI) H2)+2 12)
7. Using the value given for K, for the equation in Problem 6, at 500°C, calculate (a) Ke for the reaction H2(6) + I) = 2 HI) (b) Keg for the reaction HI) = }H) +12(«) (c) Ke for the reaction H2) + I2) (d) K for the reaction 4 HI 2 H, 3. 2(g) HI) H2)+2 12)
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.37PAE: Again the experiment in Exercise 12.33 was redesigned. This time, 0.15 mol each of N, and O2 was...
Related questions
Question
Answer 7 only
Don't answer if you already answered this. If i see the same solutions, i'll downvote you.
Follow the instructions. Typewritten for upvote. No upvote for handwritten. Thank you
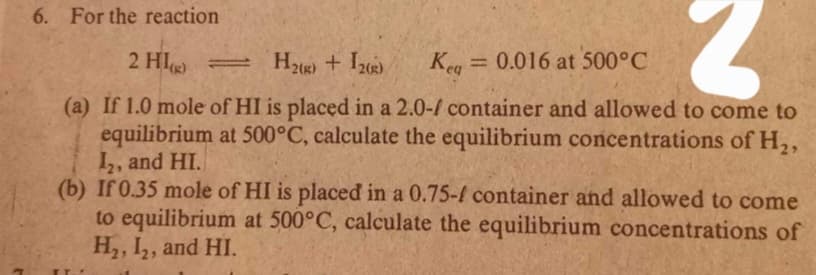
Transcribed Image Text:6. For the reaction
2 HI =
H2) + I2)
Keg = 0.016 at 500°C
(a) If 1.0 mole of HI is placed in a 2.0-/ container and allowed to come to
equilibrium at 500°C, calculate the equilibrium concentrations of H,,
I,, and HI.
(b) If 0.35 mole of HI is placed in a 0.75-f container and allowed to come
to equilibrium at 500°C, calculate the equilibrium concentrations of
H, I,, and HI.
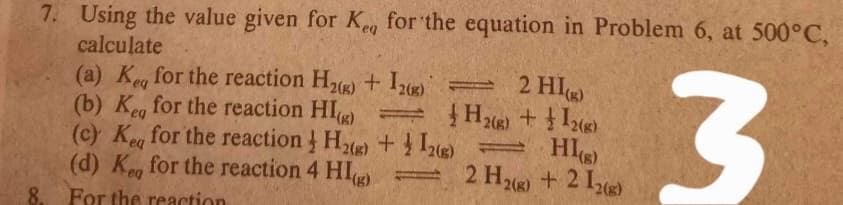
Transcribed Image Text:7. Using the value given for Ke, for the equation in Problem 6, at 500°C,
calculate
(a) Keg for the reaction H2(g) + Iz) =
(b) Keg for the reaction HI) = }
(c) Ke for the reaction He) + HI
(d) K, for the reaction 4 HI
2 HI
2(g)
eq
2 H26) +2 12)
8.
For the reaction
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning