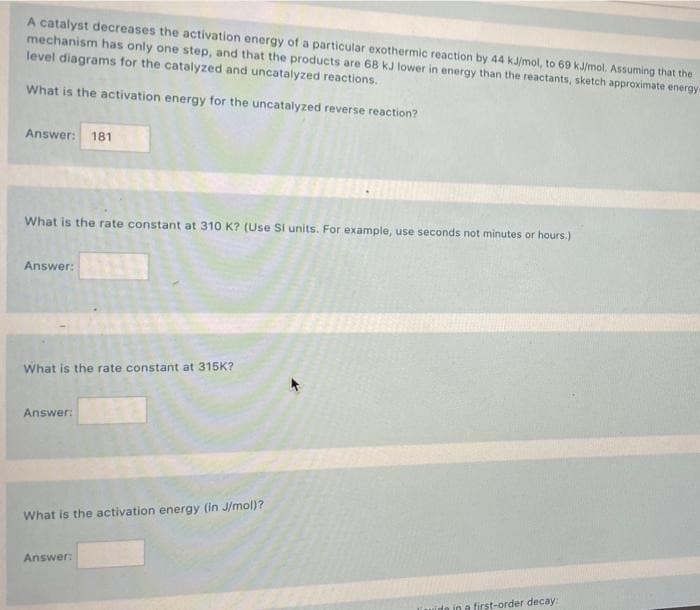
A catalyst decreases the activation energy of a particular exothermic reaction by 44 kJ/mol, to 69 kJ/mol. Assuming that the mechanism has only one step, and that the products are 68 kJ lower in energy than the reactants, sketch approximate energy level diagrams for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. What is the activation energy for the uncatalyzed reverse reaction? Answer: 181 What is the rate constant at 310 K? (Use Si units. For example, use seconds not minutes or hours.) Answer: What is the rate constant at 315K? Answer: What is the activation energy (in J/mol)? Answer: in a first-order decay:
A catalyst decreases the activation energy of a particular exothermic reaction by 44 kJ/mol, to 69 kJ/mol. Assuming that the mechanism has only one step, and that the products are 68 kJ lower in energy than the reactants, sketch approximate energy level diagrams for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. What is the activation energy for the uncatalyzed reverse reaction? Answer: 181 What is the rate constant at 310 K? (Use Si units. For example, use seconds not minutes or hours.) Answer: What is the rate constant at 315K? Answer: What is the activation energy (in J/mol)? Answer: in a first-order decay:
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter13: Chemical Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13.68QE
Related questions
Question
Must answer complete
Transcribed Image Text:A catalyst decreases the activation energy of a particular exothermic reaction by 44 kJ/mol, to 69 kJ/mol. Assuming that the
mechanism has only one step, and that the products are 68 kJ lower in energy than the reactants, sketch approximate energy-
level diagrams for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions.
What is the activation energy for the uncatalyzed reverse reaction?
Answer:
181
What is the rate constant at 310 K? (Use Si units. For example, use seconds not minutes or hours.)
Answer:
What is the rate constant at 315K?
Answer:
What is the activation energy (in J/mol)?
Answer:
ide in a first-order decay:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning