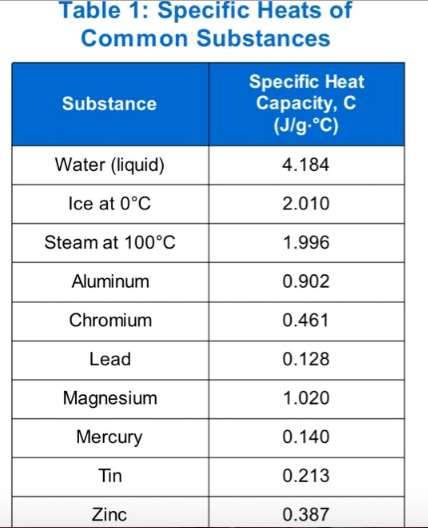
A coffee-cup calorimeter contains 70 mL of water with an initial temperature of 24.9°C. An unknown sample with a mass of 6.259 grams was placed inside making the water temperature rise up to 25.5°C. The initial temperature of the metal was 86.4°C. (Water: density = 1g/mL; specific heat = 4.184 J/g-°C). 1. How much heat (in Joules) was absorbed by the water in the calorimeter?_________ (Write your answer in 2 decimal places without the unit). 2. What is the specific heat (J/g-°C) of the unknown sample?___________ (Write your answer in 2 decimal places without the unit). 3. Based on the table of specific heat, what is the identity of the sample in the previous problem? (Write your answer in CAPITAL LETTERS). (PHOTOGRAPH
A coffee-cup calorimeter contains 70 mL of water with an initial temperature of 24.9°C. An unknown sample with a mass of 6.259 grams was placed inside making the water temperature rise up to 25.5°C. The initial temperature of the metal was 86.4°C.
(Water: density = 1g/mL; specific heat = 4.184 J/g-°C).
1. How much heat (in Joules) was absorbed by the water in the calorimeter?_________ (Write your answer in 2 decimal places without the unit).
2. What is the specific heat (J/g-°C) of the unknown sample?___________ (Write your answer in 2 decimal places without the unit).
3. Based on the table of specific heat, what is the identity of the sample in the previous problem? (Write your answer in CAPITAL LETTERS). (PHOTOGRAPH OF TABLE PROVIDED)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps









