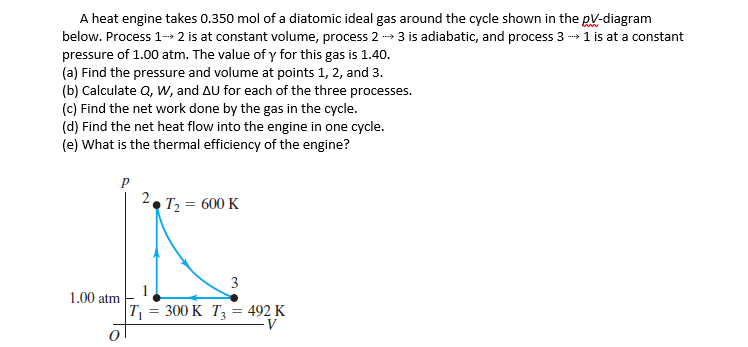
A heat engine takes 0.350 mol of a diatomic ideal gas around the cycle shown in the pV-diagram below. Process 1⤑ 2 is at constant volume, process 2 ⤑ 3 is adiabatic, and process 3 ⤑ 1 is at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm. The value of γ for this gas is 1.40. (a) Find the pressure and volume at points 1, 2, and 3.
A
pressure of 1.00 atm. The value of γ for this gas is 1.40.
(a) Find the pressure and volume at points 1, 2, and 3.
(b) Calculate Q, W, and ∆U for each of the three processes.
(c) Find the net work done by the gas in the cycle.
(d) Find the net heat flow into the engine in one cycle.
(e) What is the thermal efficiency of the engine?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps

Hello there. I noticed that the part c, d and e were not calculated. I figured out part A and B already but am not sure on what equations shold be used for part C to calculate Q, W, and DU since the initial equation used /taught is du=q-w.



