A mass sphere equal to 100 g is on horizontal surface without friction, and is attached to the extremely of a scorn of despicable and constant elastic as 9n / m. Another end of the spring is secured to a fixed holder, as shown in a figure (at the top right). Initially a sphere lies at rest and a spring at its natural length. A sphere is then reached by a pendulum of the same mass falling from a height equal to 0.5 m. Suppose the elastic collision and g = 10 m / s2. Calculate: a) such as sphere and immediate pendulum rates after collision;
A mass sphere equal to 100 g is on horizontal surface without friction, and is attached to the extremely of a scorn of despicable and constant elastic as 9n / m. Another end of the spring is secured to a fixed holder, as shown in a figure (at the top right). Initially a sphere lies at rest and a spring at its natural length. A sphere is then reached by a pendulum of the same mass falling from a height equal to 0.5 m. Suppose the elastic collision and g = 10 m / s2. Calculate: a) such as sphere and immediate pendulum rates after collision;
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
5th Edition
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Chapter3: Oscillations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.34P: Consider an undamped linear oscillator with a natural frequency ω0 = 0.5 rad/s and the step function...
Related questions
Question
Physic 1
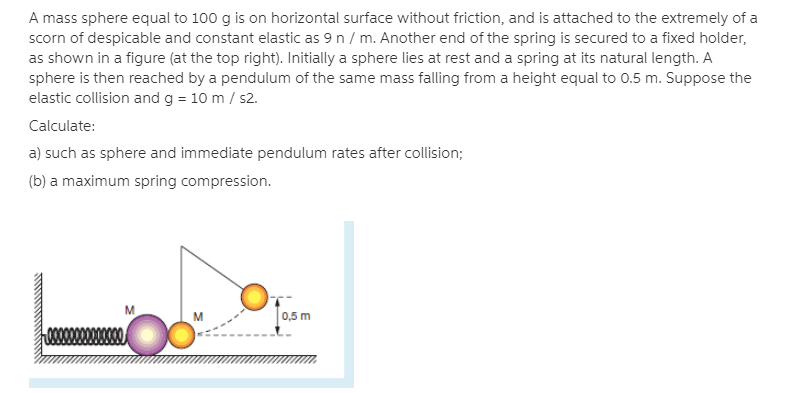
Transcribed Image Text:A mass sphere equal to 100 g is on horizontal surface without friction, and is attached to the extremely of a
scorn of despicable and constant elastic as 9 n / m. Another end of the spring is secured to a fixed holder,
as shown in a figure (at the top right). Initially a sphere lies at rest and a spring at its natural length. A
sphere is then reached by a pendulum of the same mass falling from a height equal to 0.5 m. Suppose the
elastic collision and g = 10 m / s2.
Calculate:
a) such as sphere and immediate pendulum rates after collision;
(b) a maximum spring compression.
0,5 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University