A necessary step in the manufacture of sulfuric acid is the formation of sulfur trioxide, SO3, from sulfur dioxide, SO, and oxygen, 02, shown here. At high temperatures, the rate of formation of SO, is higher, but the equilibrium amount (concentration or partial pressure) of SO, is lower than it would be at lower temperatures. The balanced reaction equation is 2SO,(g) + O,(g) → 250,(g) . What does the equilibrium constant for this reaction do as the temperature increases? A Remains the same B Increases Decreases Resets
A necessary step in the manufacture of sulfuric acid is the formation of sulfur trioxide, SO3, from sulfur dioxide, SO, and oxygen, 02, shown here. At high temperatures, the rate of formation of SO, is higher, but the equilibrium amount (concentration or partial pressure) of SO, is lower than it would be at lower temperatures. The balanced reaction equation is 2SO,(g) + O,(g) → 250,(g) . What does the equilibrium constant for this reaction do as the temperature increases? A Remains the same B Increases Decreases Resets
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.41PAE: Because calcium carbonate is a sink for CO32- in a lake, the student in Exercise 12.39 decides to go...
Related questions
Question
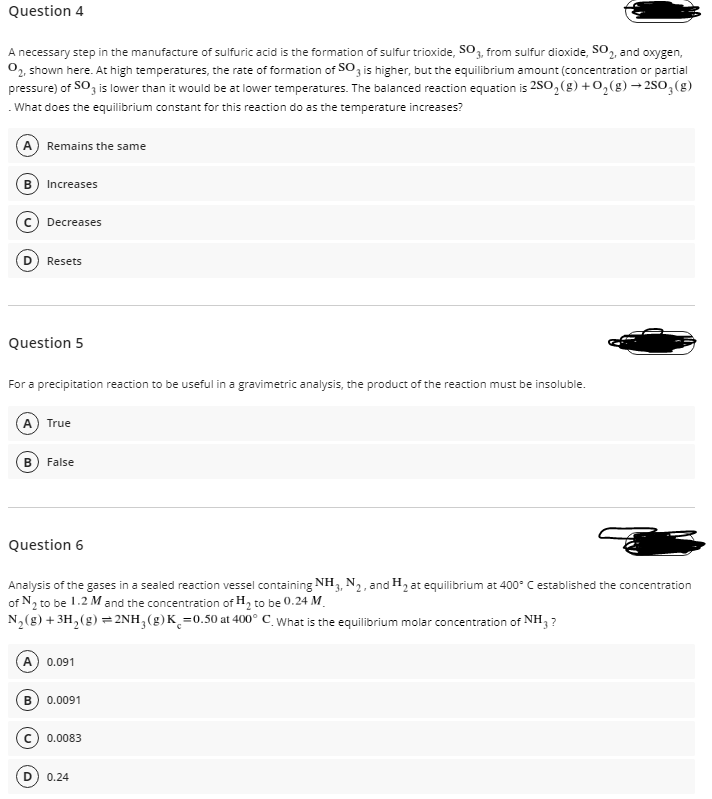
Transcribed Image Text:Question 4
A necessary step in the manufacture of sulfuric acid is the formation of sulfur trioxide, SO3, from sulfur dioxide, SO, and oxygen,
0, shown here. At high temperatures, the rate of formation of SO, is higher, but the equilibrium amount (concentration or partial
pressure) of SO, is lower than it would be at lower temperatures. The balanced reaction equation is 2S0, (g) +0,(g) → 2SO,(g)
What does the equilibrium constant for this reaction do as the temperature increases?
A Remains the same
Increases
Decreases
Resets
Question 5
For a precipitation reaction to be useful in a gravimetric analysis, the product of the reaction must be insoluble.
True
B) False
Question 6
Analysis of the gases in a sealed reaction vessel containing NH3, N2, and H2 at equilibrium at 400° C established the concentration
of N2 to be 1.2 M and the concentration of H, to be 0.24 M.
N,(g) + 3H,(g) =2NH,(g)K¸=0.50 at 400° C_ What is the equilibrium molar concentration of NH, ?
A
0.091
B) 0.0091
0.0083
0.24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning