A nonmetal element in the third row of the periodic table exists as two allotropes (two different physical forms of the same element). One allotrope exists as an extended network while the other exists as discrete molecules. In the lab, you gather the following evidence about two allotropes of this element: Physical Form of Element Melting Point Allotrope 1 Allotrope 2 Which allotrope do you predict likely exists as an extended network and why? 1. Allotrope 2 because strong covalent bonds within the molecule require a lot of energy to break when melting a substance from a solid to a liquid. 2. Allotrope 1 because small molecules require less energy due to the weaker interactions to overcome compared to breaking strong covalent bonds when an extended network melts (essentially disintegrating). 3. Allotrope 1 because its lower melting point suggests that it makes a good liquid. 4. The data is wrong as all allotropes of the same element must have the same properties. 5. It is impossible to tell from the given data whether the substance exists as an extended network or discrete molecules. 1 O 3 0 388 K 4 1687 K 2
A nonmetal element in the third row of the periodic table exists as two allotropes (two different physical forms of the same element). One allotrope exists as an extended network while the other exists as discrete molecules. In the lab, you gather the following evidence about two allotropes of this element: Physical Form of Element Melting Point Allotrope 1 Allotrope 2 Which allotrope do you predict likely exists as an extended network and why? 1. Allotrope 2 because strong covalent bonds within the molecule require a lot of energy to break when melting a substance from a solid to a liquid. 2. Allotrope 1 because small molecules require less energy due to the weaker interactions to overcome compared to breaking strong covalent bonds when an extended network melts (essentially disintegrating). 3. Allotrope 1 because its lower melting point suggests that it makes a good liquid. 4. The data is wrong as all allotropes of the same element must have the same properties. 5. It is impossible to tell from the given data whether the substance exists as an extended network or discrete molecules. 1 O 3 0 388 K 4 1687 K 2
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter20: The Representative Elements
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10RQ
Related questions
Question
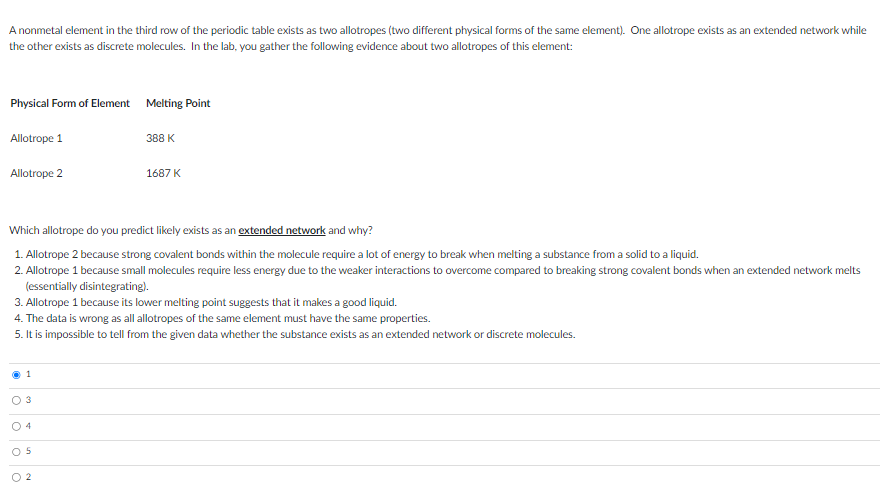
Transcribed Image Text:A nonmetal element in the third row of the periodic table exists as two allotropes (two different physical forms of the same element). One allotrope exists as an extended network while
the other exists as discrete molecules. In the lab, you gather the following evidence about two allotropes of this element:
Physical Form of Element Melting Point
Allotrope 1
Allotrope 2
03
Which allotrope do you predict likely exists as an extended network and why?
1. Allotrope 2 because strong covalent bonds within the molecule require a lot of energy to break when melting a substance from a solid to a liquid.
2. Allotrope 1 because small molecules require less energy due to the weaker interactions to overcome compared to breaking strong covalent bonds when an extended network melts
(essentially disintegrating).
3. Allotrope 1 because its lower melting point suggests that it makes a good liquid.
4. The data is wrong as all allotropes of the same element must have the same properties.
5. It is impossible to tell from the given data whether the substance exists as an extended network or discrete molecules.
04
ö
O
388 K
5
1687 K
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning