A single bank is considering two options: First, it can make a $200,000 mortgage loan for a customer with a 10 percent probability of default, or second, it can buy a $200,000 security representing a bundle of 100 mortgage loans, which break down as shown in the table below. You can calculate the weighted risk for each firm category by multiplying the percentage of loans represented (for example, the first tier includes 25 loans, which is 25/100 = 25% of the total) times the probability of default on loans of that category. Instructions: Round your answers to three decimal places. a. Calculate the weighted risk for each type of loan, then add together the weighted risks to come up with an overall expected default risk for this financial investment. Number of Loans 25 25 15 35 Probability of Default (1) 3 12 1.5 5 Weighted Risk 1 Adding together the weighted risks, the expected default risk for the security is: b. If the bank is willing to take on only projects for which the default risk is 6% or less, it should choose the Click to select) bundle of mortgages single mortgage loan
A single bank is considering two options: First, it can make a $200,000 mortgage loan for a customer with a 10 percent probability of default, or second, it can buy a $200,000 security representing a bundle of 100 mortgage loans, which break down as shown in the table below. You can calculate the weighted risk for each firm category by multiplying the percentage of loans represented (for example, the first tier includes 25 loans, which is 25/100 = 25% of the total) times the probability of default on loans of that category. Instructions: Round your answers to three decimal places. a. Calculate the weighted risk for each type of loan, then add together the weighted risks to come up with an overall expected default risk for this financial investment. Number of Loans 25 25 15 35 Probability of Default (1) 3 12 1.5 5 Weighted Risk 1 Adding together the weighted risks, the expected default risk for the security is: b. If the bank is willing to take on only projects for which the default risk is 6% or less, it should choose the Click to select) bundle of mortgages single mortgage loan
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter17: Making Decisions With Uncertainty
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17.5IP
Related questions
Question
Subject :- Economics
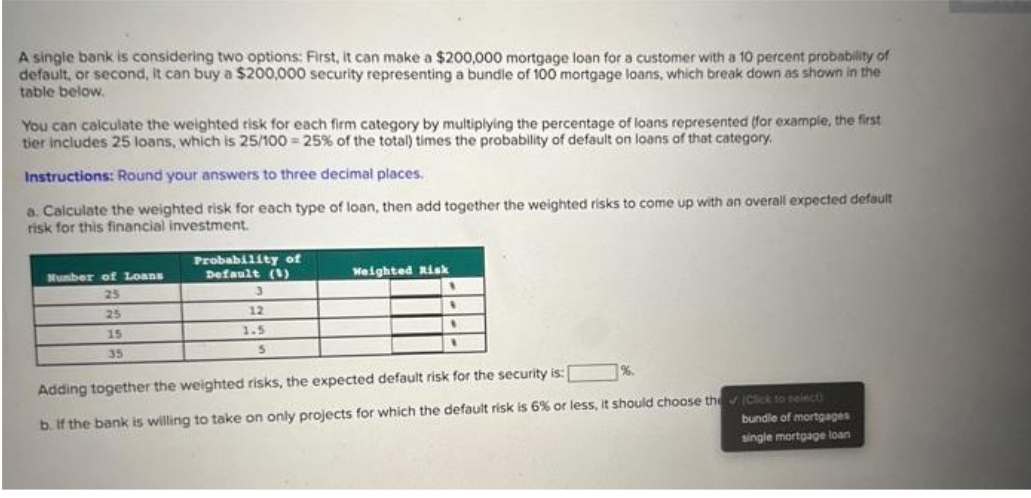
Transcribed Image Text:A single bank is considering two options: First, it can make a $200,000 mortgage loan for a customer with a 10 percent probability of
default, or second, it can buy a $200,000 security representing a bundle of 100 mortgage loans, which break down as shown in the
table below.
You can calculate the weighted risk for each firm category by multiplying the percentage of loans represented (for example, the first
tier includes 25 loans, which is 25/100 = 25% of the total) times the probability of default on loans of that category.
Instructions: Round your answers to three decimal places.
a. Calculate the weighted risk for each type of loan, then add together the weighted risks to come up with an overall expected default
risk for this financial investment.
Number of Loans
25
25
15
35
Probability of
Default (1)
12
1.5
5
Weighted Risk
Adding together the weighted risks, the expected default risk for the security is:
b. If the bank is willing to take on only projects for which the default risk is 6% or less, it should choose the✔ Click to select)
bundle of mortgages
single mortgage loan
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
