A venturi meter is used to measure the flow speed of a fluid in a pipe. The meter is connected between two sections of the pipe (the figure); the cross-sectional area A of the entrance and exit of the meter matches the pipe's cross-sectional area. Between the entrance and exit, the fluid flows from the pipe with speed V and then through a narrow "throat" of cross-sectional area a with speed v. A manometer connects the wider portion of the meter to the narrower portion. The change in the fluid's speed is accompanied by a change Ap in the fluid's pressure, which causes a height difference h of the liquid in the two arms of the manometer. (Here Ap means pressure in the throat minus pressure in the pipe.) Suppose that the fluid is fresh water, that the cross- sectional areas are 93 cm2 in the pipe and 31 cm2 in the throat, and that the pressure is 53 kPa in the pipe and 44 kPa in the throat. What is the rate of water flow in cubic meters per second? Meter Meter entrance Venturi meter exit a Pipe 1 Pipe -Manometer
A venturi meter is used to measure the flow speed of a fluid in a pipe. The meter is connected between two sections of the pipe (the figure); the cross-sectional area A of the entrance and exit of the meter matches the pipe's cross-sectional area. Between the entrance and exit, the fluid flows from the pipe with speed V and then through a narrow "throat" of cross-sectional area a with speed v. A manometer connects the wider portion of the meter to the narrower portion. The change in the fluid's speed is accompanied by a change Ap in the fluid's pressure, which causes a height difference h of the liquid in the two arms of the manometer. (Here Ap means pressure in the throat minus pressure in the pipe.) Suppose that the fluid is fresh water, that the cross- sectional areas are 93 cm2 in the pipe and 31 cm2 in the throat, and that the pressure is 53 kPa in the pipe and 44 kPa in the throat. What is the rate of water flow in cubic meters per second? Meter Meter entrance Venturi meter exit a Pipe 1 Pipe -Manometer
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
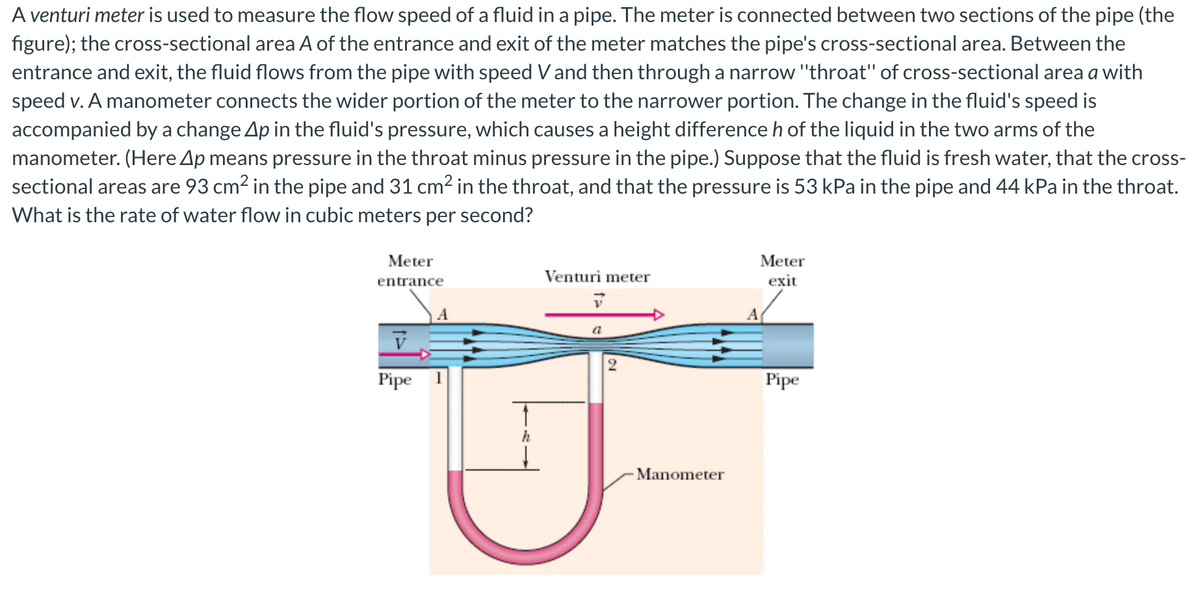
Transcribed Image Text:A venturi meter is used to measure the flow speed of a fluid in a pipe. The meter is connected between two sections of the pipe (the
figure); the cross-sectional area A of the entrance and exit of the meter matches the pipe's cross-sectional area. Between the
entrance and exit, the fluid flows from the pipe with speed Vand then through a narrow "throat" of cross-sectional area a with
speed v. A manometer connects the wider portion of the meter to the narrower portion. The change in the fluid's speed is
accompanied by a change Ap in the fluid's pressure, which causes a height difference h of the liquid in the two arms of the
manometer. (Here Ap means pressure in the throat minus pressure in the pipe.) Suppose that the fluid is fresh water, that the cross-
sectional areas are 93 cm2 in the pipe and 31 cm² in the throat, and that the pressure is 53 kPa in the pipe and 44 kPa in the throat.
What is the rate of water flow in cubic meters per second?
Meter
Meter
entrance
Venturi meter
exit
A
a
Pipe
Pipe
h
- Manometer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY