
Concept explainers
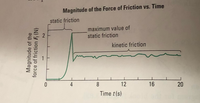
Use following scenario to answer parts a–f. (You may wish to use the graph on page 180
of your textbook to help you.)
You attach a force scale to a toboggan resting in the snow.
a) What is the minimum value of static frictional force and under what conditions
would you observe that value on your force scale?
b) What two (equal in magnitude and opposite in direction) forces is the scale
measuring when you start to pull on the toboggan but it remains stationary? Be
specific.
c) What happens to the number on the force scale as you start to pull on the
toboggan but it remains stationary? Explain.
d) What happens to the toboggan if your applied force exceeds the maximum static
frictional force?
e) What happens to the number on the force scale in the moment the toboggan
starts to move? Explain.
f) What two (equal in magnitude and opposite in direction) forces is the scale
measuring when you pull on the toboggan and it moves at a constant speed. Be
specific.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Problem 14: Using a rope, a man pulls a block of ice across a frozen pond at a constant velocity, as shown in the figure. While they coefficients of static and kinetic friction for ice are low, they are not zero. Consider this problem to involve friction. If necessary, use Fs for the force of static friction, and Fk as the force of kinetic friction. F. Jo Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for the block of ice. Add Force O Reset All F 45 X F total,x: + (pos) Ftotal,y: + (pos)arrow_forwardBlock 1 (9 kg) is located on the surface of a table. A hand pushes horizontally to the right on block 1 with a normal force of 108 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface equals 0.8.On a sheet of paper, draw the free body diagram for block 1 using the two-subscript notation from class. After completing the free body diagram, enter below each force and its x & y-components. Remember that the x-component is the "i" component and the y-component is the "j" component.FORCES on BLOCK 1Weight force on block 1 by Earth W1E = i + j N Normal force on block 1 by Surface N1S = i + j N Normal force on block 1 by Hand N1H = i + j N Frictional force on block 1 by Surface f1S = i + j N What is the acceleration a of block 1?a = i + j m/s2arrow_forwardConsider the system in the picture below: a cart of mass M with a static friction coefficient u is connected through a massless string to a hanging mass m. M is a capital letter, m is lower case. Write them as such, or vour equations will be confusing, M We want to find the maximum value of the hanging mass m such that the system is in equilibrium. 1. Free body diagram (FBD): Draw a FBD for each: the Cart and the hanging mass. Clearly show all the forces. 2. Clearly write the equilibrium equations for the cart in the horizontal and vertical direction. 3. Clearly write the equilibrium equation for the hanging mass. 4. Solve the system of the three equations above for the hanging mass m. Show your calculation to get credit. 5. What would happen if mass m exceeds this value? Explain.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





