AH = -484. kJ AS = -1394. 2H, (g) + 0, (g) –→ 2H,0(g) AG = kJ Which is spontaneous? O this reaction the reverse reaction neither AH = 852. kJ AS = K Al, 0, (s) + 2Fe(s) → 2A1(s) + Fe,0,(s) AG = 0. kJ Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neither O O O
AH = -484. kJ AS = -1394. 2H, (g) + 0, (g) –→ 2H,0(g) AG = kJ Which is spontaneous? O this reaction the reverse reaction neither AH = 852. kJ AS = K Al, 0, (s) + 2Fe(s) → 2A1(s) + Fe,0,(s) AG = 0. kJ Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neither O O O
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter16: Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5E: Many plastic materials are organic polymers that contain carbon and hydrogen. The oxidation of these...
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:AH =
-484. kJ
J
AS = -1394.
K
2H, (g) + 0,(g) → 2H,0(g)
AG = kJ
Which is spontaneous?
this reaction
the reverse reaction
neither
AH = 852. kJ
AS = ||
K
Al, 0, (s) + 2Fe(s) → 2AI(s) + Fe,0, (s)
AG = 0. kJ
Which is spontaneous?
this reaction
the reverse reaction
neither
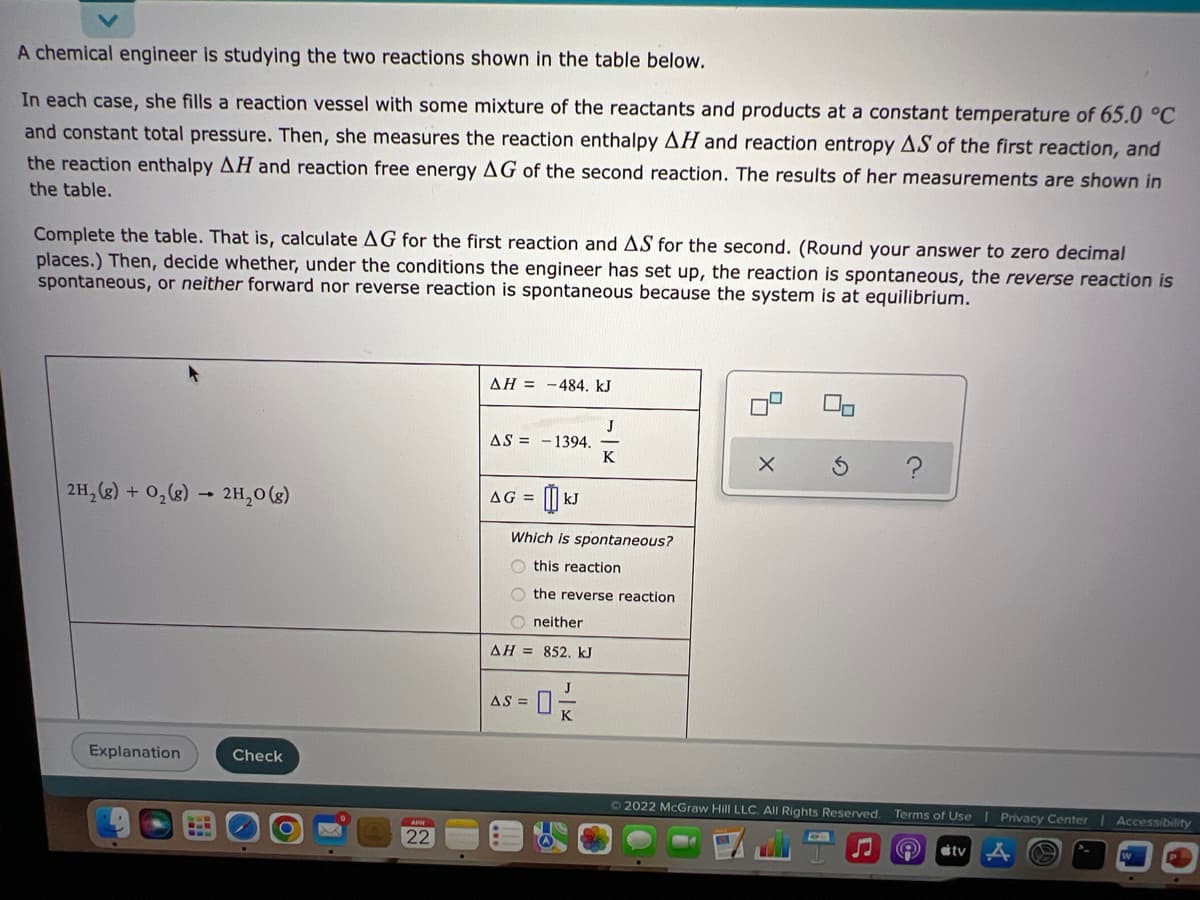
Transcribed Image Text:A chemical engineer is studying the two reactions shown in the table below.
In each case, she fills a reaction vessel with some mixture of the reactants and products at a constant temperature of 65.0 °C
and constant total pressure. Then, she measures the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS of the first reaction, and
the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction free energy AG of the second reaction. The results of her measurements are shown in
the table.
Complete the table. That is, calculate AG for the first reaction and AS for the second. (Round your answer to zero decimal
places.) Then, decide whether, under the conditions the engineer has set up, the reaction is spontaneous, the reverse reaction is
spontaneous, or neither forward nor reverse reaction is spontaneous because the system is at equilibrium.
AH = -484. kJ
J
AS = -1394.
K
2H, (2) + 0,(g) → 2H,0 (g)
AG =
kJ
Which is spontaneous?
this reaction
O the reverse reaction
O neither
AH = 852. kJ
J
AS =
Explanation
Check
72022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Terms of Use I Privacy Center
Accessibility
APH
22
ity
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning