An engineer wants to design a pendulum which consists of a uniform slender rod and a disk with a mass of m1 (kg) and m2 (kg), respectively as shown in Figure 3.2. If the angular velocity w of the pendulum is 18.2 rad/s when it is released at rest from t= 0 s to t = 4 s, suggest the mass of m, kg and m2 kg of the slender rod and disk that he should use in his design. Noted that this pendulum will be subjected to a torque at M = (10t2)N. m and a constant force of F= 40 N (which is always normal to the rod) and the motion of the pendulum is in the horizontal plane. F = 40 N 0.84 m 1 m 0.35 m G M = (10t²)N. m %3D kG = 0.5 m Figure 3.2 A pendulum
An engineer wants to design a pendulum which consists of a uniform slender rod and a disk with a mass of m1 (kg) and m2 (kg), respectively as shown in Figure 3.2. If the angular velocity w of the pendulum is 18.2 rad/s when it is released at rest from t= 0 s to t = 4 s, suggest the mass of m, kg and m2 kg of the slender rod and disk that he should use in his design. Noted that this pendulum will be subjected to a torque at M = (10t2)N. m and a constant force of F= 40 N (which is always normal to the rod) and the motion of the pendulum is in the horizontal plane. F = 40 N 0.84 m 1 m 0.35 m G M = (10t²)N. m %3D kG = 0.5 m Figure 3.2 A pendulum
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
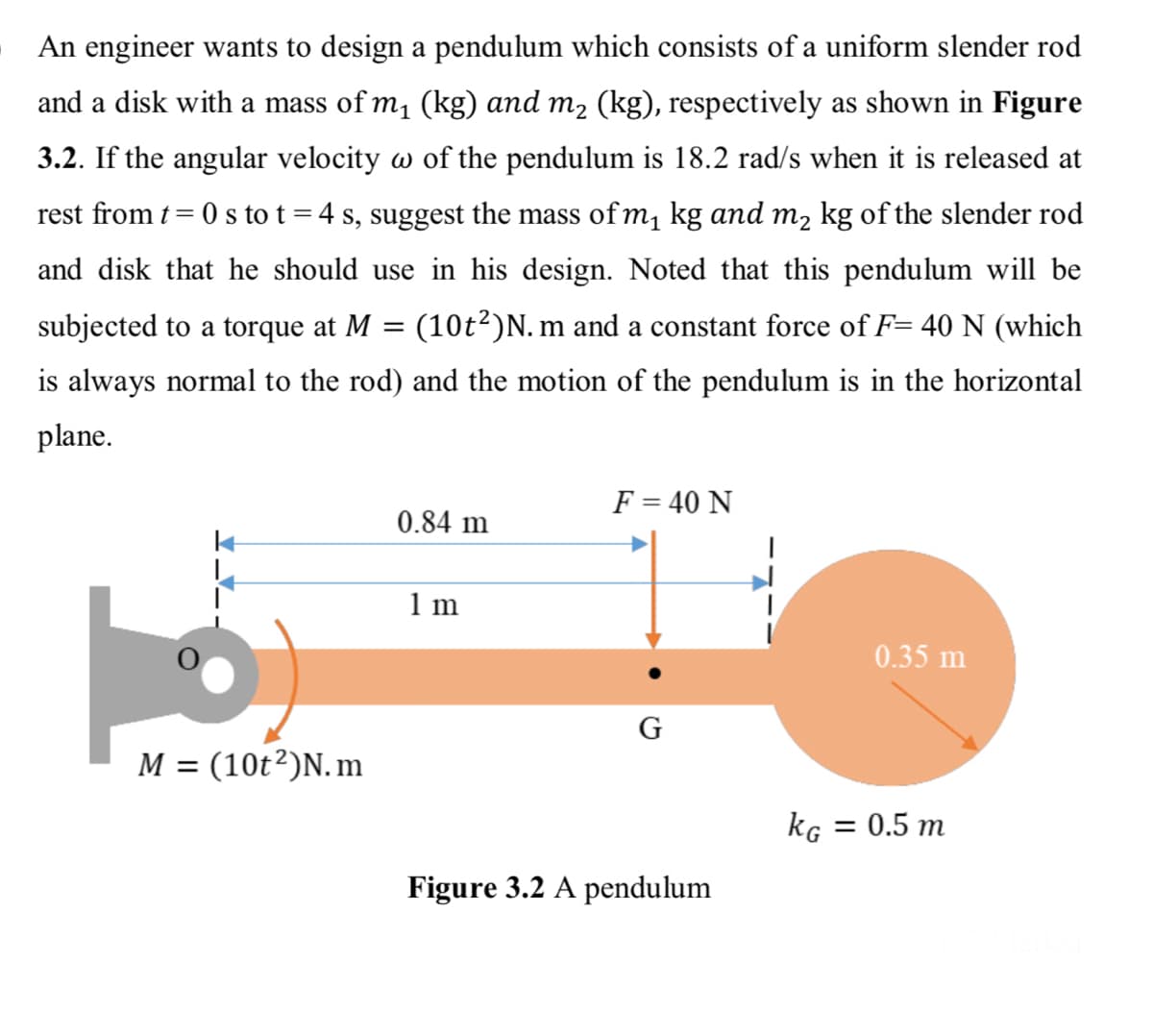
Transcribed Image Text:An engineer wants to design a pendulum which consists of a uniform slender rod
and a disk with a mass of m, (kg) and m2 (kg), respectively as shown in Figure
3.2. If the angular velocity w of the pendulum is 18.2 rad/s when it is released at
rest from t= 0 s to t =4 s, suggest the mass of m, kg and m, kg of the slender rod
and disk that he should use in his design. Noted that this pendulum will be
subjected to a torque at M = (10t²)N. m and a constant force of F= 40 N (which
is always normal to the rod) and the motion of the pendulum is in the horizontal
plane.
F = 40 N
0.84 m
1 m
0.35 m
G
M = (10t²)N. m
kg = 0.5 m
Figure 3.2 A pendulum
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY