An engineer wants to know if producing metal bars using a new experimental treatment rather than the conventional treatment makes a difference in the tensile strength of the bars (the ability to resist tearing when pulled lengthwise). At a = 0.10, answer parts (a) through (e). Assume the population variances are equal and the samples are random. If convenient, use technology to solve the problem. D Tensile strengths (newtons per square millimeter) Treatment Experimental 380 418 441 409 373 402 417 Conventional 360 432 394 412 397 353 426 448 415 366 (a) Identify the claim and state Ho and H₂. The claim is "The new treatment in the tensile strength of the bars." "What are Ho and H₂? The null hypothesis, Ho, is "Which hypothesis is the claim? O The null hypothesis, Ho O The alternative hypothesis, Ha (b) Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s). Enter the critical value(s) below. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) The alternative hypothesis, H₂, is
An engineer wants to know if producing metal bars using a new experimental treatment rather than the conventional treatment makes a difference in the tensile strength of the bars (the ability to resist tearing when pulled lengthwise). At a = 0.10, answer parts (a) through (e). Assume the population variances are equal and the samples are random. If convenient, use technology to solve the problem. D Tensile strengths (newtons per square millimeter) Treatment Experimental 380 418 441 409 373 402 417 Conventional 360 432 394 412 397 353 426 448 415 366 (a) Identify the claim and state Ho and H₂. The claim is "The new treatment in the tensile strength of the bars." "What are Ho and H₂? The null hypothesis, Ho, is "Which hypothesis is the claim? O The null hypothesis, Ho O The alternative hypothesis, Ha (b) Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s). Enter the critical value(s) below. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) The alternative hypothesis, H₂, is
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.1: Measures Of Center
Problem 9PPS
Related questions
Question
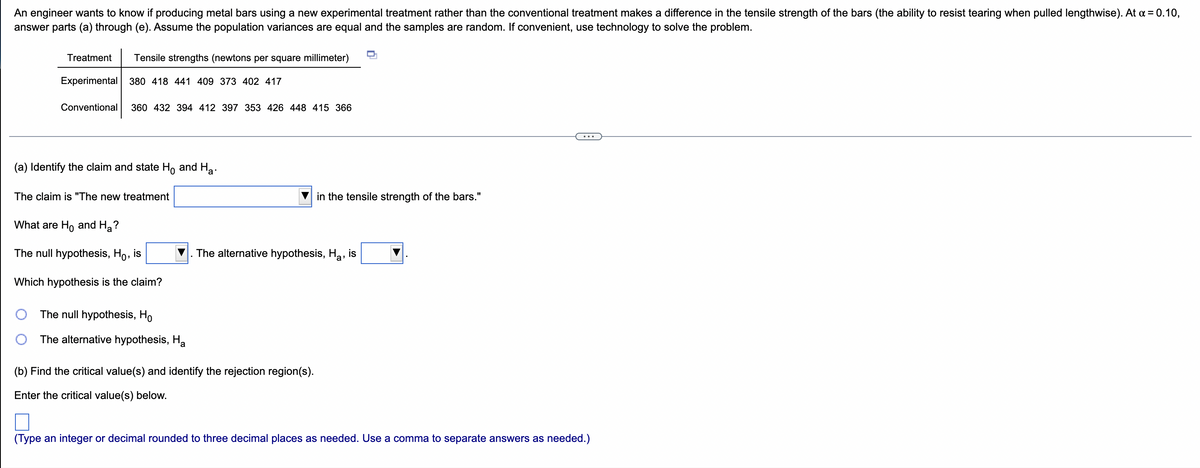
Transcribed Image Text:An engineer wants to know if producing metal bars using a new experimental treatment rather than the conventional treatment makes a difference in the tensile strength of the bars (the ability to resist tearing when pulled lengthwise). At x = 0.10,
answer parts (a) through (e). Assume the population variances are equal and the samples are random. If convenient, use technology to solve the problem.
Treatment
Tensile strengths (newtons per square millimeter)
Experimental 380 418 441 409 373 402 417
Conventional 360 432 394 412 397 353 426 448 415 366
(a) Identify the claim and state Ho and Ha
The claim is "The new treatment
in the tensile strength of the bars."
What are Ho and Ha?
The null hypothesis, Ho, is
Which hypothesis is the claim?
The null hypothesis, Ho
The alternative hypothesis, Ha
(b) Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s).
Enter the critical value(s) below.
(Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
The alternative hypothesis, Ha, is

Transcribed Image Text:An engineer wants to know if producing metal bars using a new experimental treatment rather than the conventional treatment makes a difference in the tensile strength of the bars (the ability to resist tearing when pulled lengthwise). At α = 0.10,
answer parts (a) through (e). Assume the population variances are equal and the samples are random. If convenient, use technology to solve the problem.
Treatment
Tensile strengths (newtons per square millimeter)
Experimental 380 418 441 409 373 402 417
Conventional 360 432 394 412 397 353 426 448 415 366
Select the correct rejection region(s) below.
A. t<-
< - to, t> to
B. -to <t<to
C. t>to
D. t< - to
(c) Find the standardized test statistic.
t=
(Type an integer or decimal rounded to the nearest thousandth as needed.)
(d) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
the null hypothesis.
(e) Interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
At the 10% significance level,
enough evidence to support the claim.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill