Are freshmen psychology majors more likely to change their major before they graduate compared to freshmen business majors? 428 of the 639 freshmen psychology majors from a recent study changed their major before they graduated and 502 of the 783 freshmen business majors changed their major before they graduated. What can be concluded at the a = 0.10 level of significance? %3! For this study, we should use Select an answer a. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho: Select an answer v Select an answer Select an answer v H1: Select an answer v Select an answer v Select an answer b. The test statistic ? (please show your answer to 2 decimal places.) %3D c. The p-value d. The p-value is ? a e. Based on this, we should Select an answer v the null hypothesis. f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.10, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major. O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.10, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of the 639 freshmen psychology majors who changed their major is greater than the proportion of the 783 freshmen business majors who change their major. O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.10, so there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is the same as the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major. O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.10, so there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major.
Are freshmen psychology majors more likely to change their major before they graduate compared to freshmen business majors? 428 of the 639 freshmen psychology majors from a recent study changed their major before they graduated and 502 of the 783 freshmen business majors changed their major before they graduated. What can be concluded at the a = 0.10 level of significance? %3! For this study, we should use Select an answer a. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho: Select an answer v Select an answer Select an answer v H1: Select an answer v Select an answer v Select an answer b. The test statistic ? (please show your answer to 2 decimal places.) %3D c. The p-value d. The p-value is ? a e. Based on this, we should Select an answer v the null hypothesis. f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.10, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major. O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.10, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of the 639 freshmen psychology majors who changed their major is greater than the proportion of the 783 freshmen business majors who change their major. O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.10, so there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is the same as the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major. O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.10, so there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
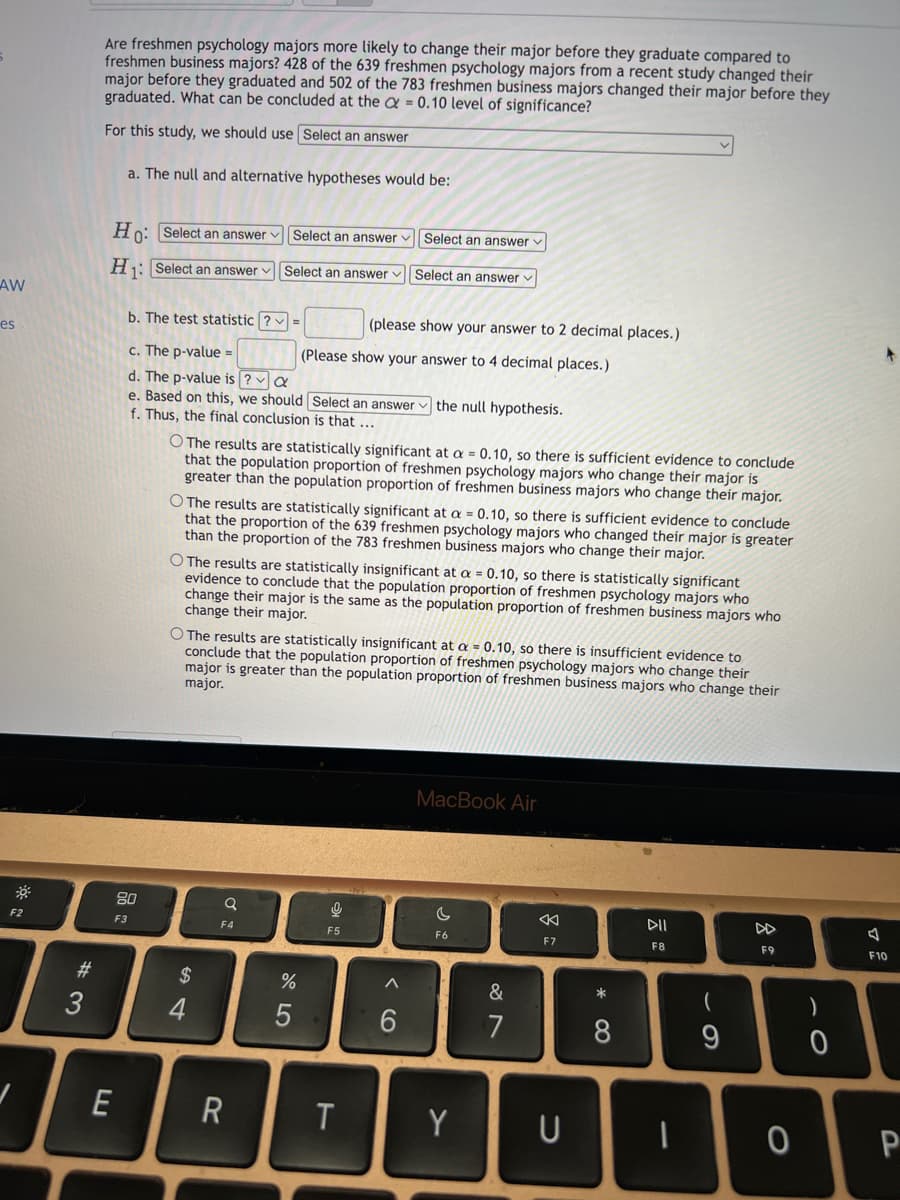
Transcribed Image Text:Are freshmen psychology majors more likely to change their major before they graduate compared to
freshmen business majors? 428 of the 639 freshmen psychology majors from a recent study changed their
major before they graduated and 502 of the 783 freshmen business majors changed their major before they
graduated. What can be concluded at the a = 0.10 level of significance?
For this study, we should use Select an answer
a. The null and alternative hypotheses would be:
Ho: Select an answer v Select an answer v| Select an answer v
H: Select an answer v Select an answer v| Select an answer v
AW
b. The test statistic ? v =
(please show your answer to 2 decimal places.)
es
c. The p-value =
(Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)
d. The p-value is ? a
e. Based on this, we should Select an answer
f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ...
the null hypothesis.
O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.10, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is
greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major.
O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.10, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the proportion of the 639 freshmen psychology majors who changed their major is greater
than the proportion of the 783 freshmen business majors who change their major.
O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.10, so there is statistically significant
evidence to conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who
change their major is the same as the population proportion of freshmen business majors who
change their major.
O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.10, so there is insufficient evidence to
conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their
major is greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their
major.
MacBook Air
80
DD
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
F10
#
$
&
3
7
8
9
E
Y
P
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning