At 1 atmosphere and room temperature (25°C), Supercritical faid 4. 729 atm would you expect solid carbon dioxide to melt to Liquid the liquid phase, or sublime to the gas phase? Solid S.1 atm 5. Some industrial processes require carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is stored on-site in large tanks Gas as liquid carbon dioxide. Assuming we lived at sea level (1 atm), how could carbon dioxide be liquefied? -785T -56.7 C Temperature (not to scale) 31 °C Generic Phase Diagram 6. Which section represents the solid phase? 7. What section represents the liquid phase? 1.0 8. What section represents the gas phase? A 9. What letter represents the triple point? 0.5 B 10. In your own words, what is the definition of a triple point? 11. What is this substance's normal melting point, at 1 45° 60° 100° 110° atmosphere of pressure? Temperature (°C) 12. What is this substance's normal boiling point, at 1 atmosphere of pressure? 13. Above what temperature is it impossible to liquefy this substance, no matter what the pressure? 14. At what temperature and pressure do all three phases coexist? 15. At a constant temperature, what would you do to cause this substance to change from the liquid phase to the solid phase? 16. What does sublimation mean? Pressure (Atmosphere) Pressure (not to scale)
At 1 atmosphere and room temperature (25°C), Supercritical faid 4. 729 atm would you expect solid carbon dioxide to melt to Liquid the liquid phase, or sublime to the gas phase? Solid S.1 atm 5. Some industrial processes require carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is stored on-site in large tanks Gas as liquid carbon dioxide. Assuming we lived at sea level (1 atm), how could carbon dioxide be liquefied? -785T -56.7 C Temperature (not to scale) 31 °C Generic Phase Diagram 6. Which section represents the solid phase? 7. What section represents the liquid phase? 1.0 8. What section represents the gas phase? A 9. What letter represents the triple point? 0.5 B 10. In your own words, what is the definition of a triple point? 11. What is this substance's normal melting point, at 1 45° 60° 100° 110° atmosphere of pressure? Temperature (°C) 12. What is this substance's normal boiling point, at 1 atmosphere of pressure? 13. Above what temperature is it impossible to liquefy this substance, no matter what the pressure? 14. At what temperature and pressure do all three phases coexist? 15. At a constant temperature, what would you do to cause this substance to change from the liquid phase to the solid phase? 16. What does sublimation mean? Pressure (Atmosphere) Pressure (not to scale)
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter8: Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 31Q
Related questions
Question
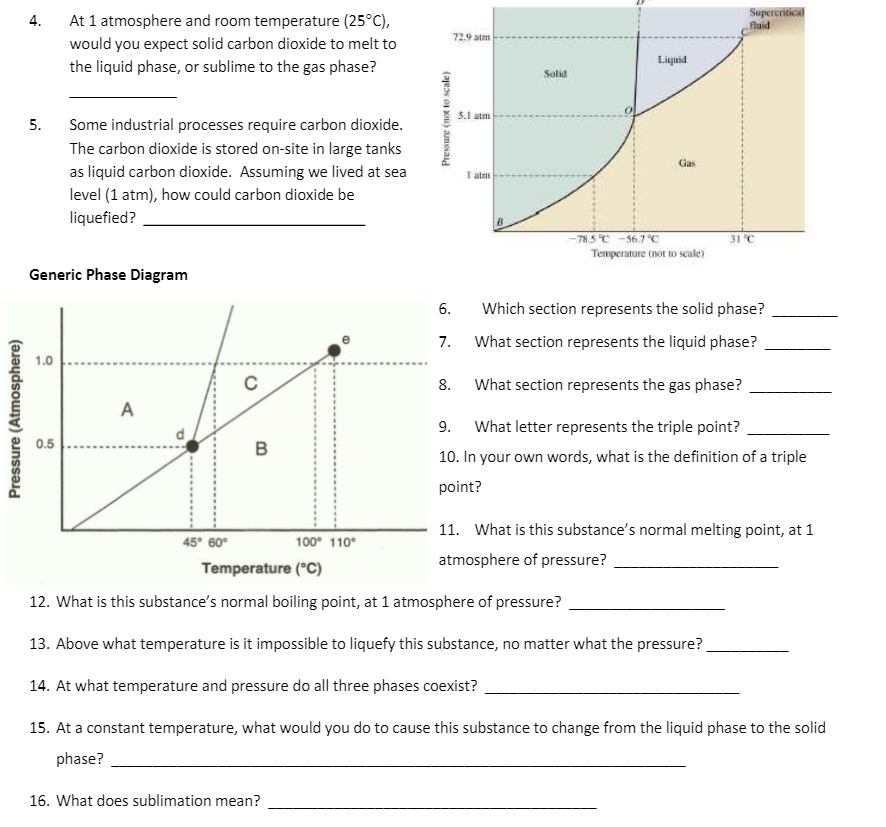
Transcribed Image Text:At 1 atmosphere and room temperature (25°C),
Supercritical
fuid
4.
72.9 atm
would you expect solid carbon dioxide to melt to
Liquid
the liquid phase, or sublime to the gas phase?
Solid
S.1 atm
5.
Some industrial processes require carbon dioxide.
The carbon dioxide is stored on-site in large tanks
Gas
as liquid carbon dioxide. Assuming we lived at sea
I alm
level (1 atm), how could carbon dioxide be
liquefied?
- 78.5 C -56.7°C
Temperature (not to scale)
31 °C
Generic Phase Diagram
6.
Which section represents the solid phase?
7.
What section represents the liquid phase?
1.0
8.
What section represents the gas phase?
A
9.
What letter represents the triple point?
0.5
B
10. In your own words, what is the definition of a triple
point?
11. What is this substance's normal melting point, at 1
45° 60°
100° 110°
atmosphere of pressure?
Temperature (°C)
12. What is this substance's normal boiling point, at 1 atmosphere of pressure?
13. Above what temperature is it impossible to liquefy this substance, no matter what the pressure?
14. At what temperature and pressure do all three phases coexist?
15. At a constant temperature, what would you do to cause this substance to change from the liquid phase to the solid
phase?
16. What does sublimation mean?
Pressure (Atmosphere)
Pressure (not to scale)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning