b. a) Instead, suppose that the firm holds monopsony power in the market for labor and faces the labor supply curve below. Continue to assume that the firm is perfectly competitive in the market for their output where the equilibrium price is $10 and that their production function is as defined above. Determine the profit maximizing quantity and wage for their labor. (Hint: to calculate the marginal cost of labor, first calculate total cost at each level of employment (workers wage), then calculate marginal cost per usual i.e. for each additional worker how do costs change?) .
b. a) Instead, suppose that the firm holds monopsony power in the market for labor and faces the labor supply curve below. Continue to assume that the firm is perfectly competitive in the market for their output where the equilibrium price is $10 and that their production function is as defined above. Determine the profit maximizing quantity and wage for their labor. (Hint: to calculate the marginal cost of labor, first calculate total cost at each level of employment (workers wage), then calculate marginal cost per usual i.e. for each additional worker how do costs change?) .
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter14: Labor Markets And Income
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8SCQ: Table 14.13 shows information from the supply curve for labor for a monopsonist, that is, the wage...
Related questions
Question
Can someone please help me answer part b please? Refer to the table in the second attached image to help solve the problem. Thank you!

Transcribed Image Text:b.
a) Instead, suppose that the firm holds monopsony power in the market for labor
and faces the labor supply curve below. Continue to assume that the firm is perfectly
competitive in the market for their output where the equilibrium price is $10 and that their
production function is as defined above. Determine the profit maximizing quantity and wage
for their labor. (Hint: to calculate the marginal cost of labor, first calculate total cost at each
level of employment (workers wage), then calculate marginal cost per usual i.e. for each
additional worker how do costs change?)
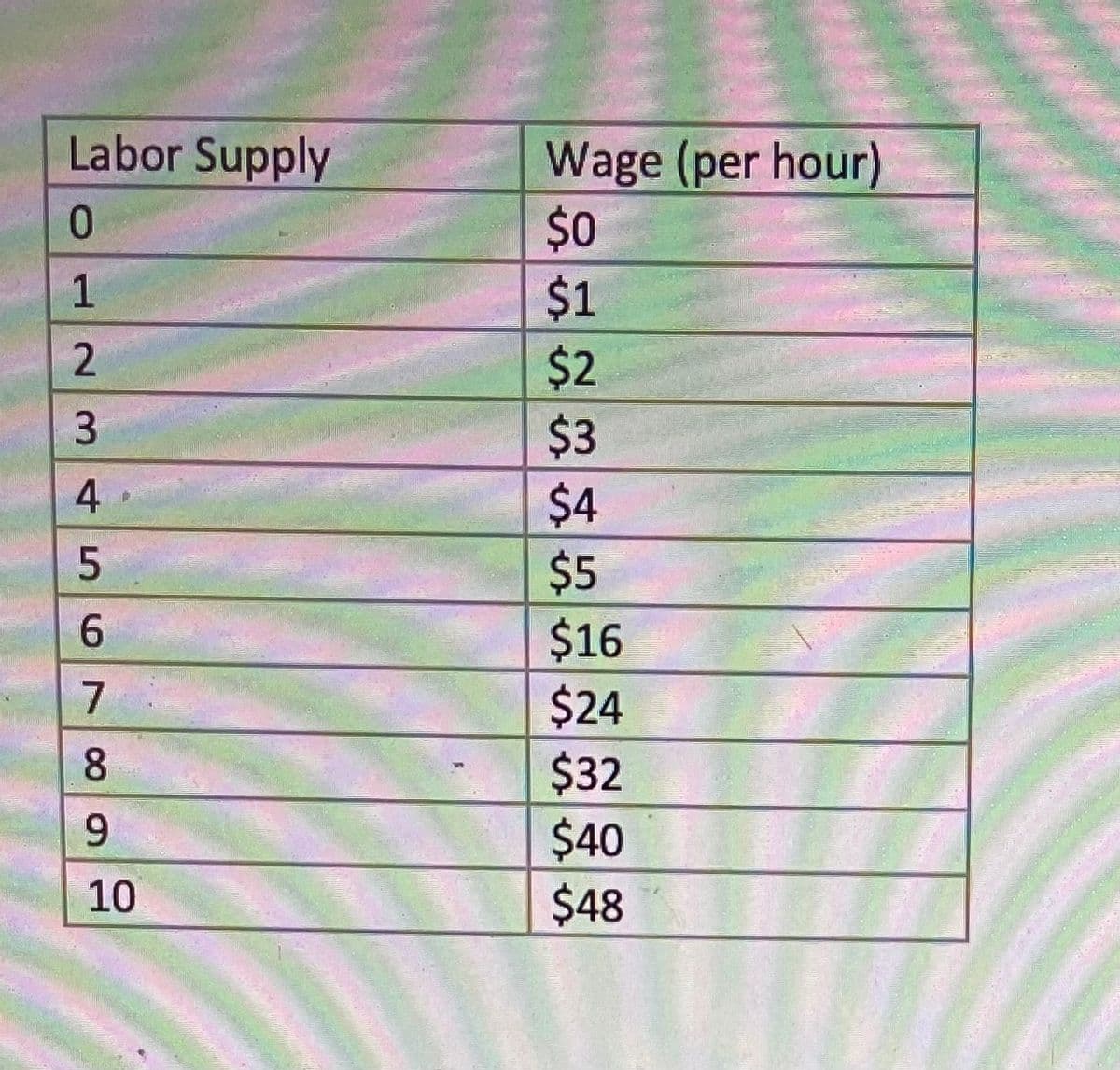
Transcribed Image Text:Labor Supply
0
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
9
10
Wage (per hour)
$0
$1
$2
$3
$4
$5
$16
$24
$32
$40
$48
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning