
Concept explainers
C
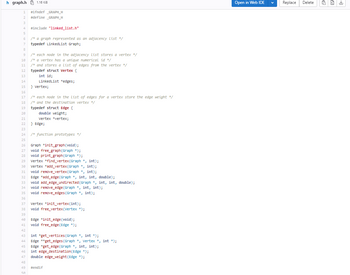
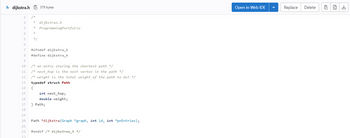
you are to write a TCP/IP server that can build up a graph of a network of
networks (using the supplied graph library and implementation of Dijkstra’s
query that graph to find out which link between two networks should be used as the next hop to
send a packet of data from one network to another within the network of networks (using the
supplied implementation of Dijkstra’s algorithm).
using the following program as a start point:
/*
* NetworkServer.c
* ProgrammingPortfolio Skeleton
*
*/
/* You will need to include these header files to be able to implement the TCP/IP functions */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
/* You will also need to add #include for your graph library header files */
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
int serverSocket = -1;
printf("Programming Portfolio 2022 Implementation\n");
printf("=========================================\n\n");
/* Insert your code here to create, and the TCP/IP socket for the Network Server
*
* Then once a connection has been accepted implement protocol described in the coursework description.
*/
return 0;
}
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- An example would help me understand distance vectors, link state vectors, and route vector routing.arrow_forwardDistance vector routing is used. Router L receives distance vectors from routers I, H, and K as shown below.(image) The distance from L to I is 30, from L to H is 10, and from L to K is 9. Show L’s updated routing table based on the vectors.arrow_forwardunique please Your task for this assignment is to identify a spanning tree in one connected undirected weighted graph using C++. Implement a spanning tree algorithm using C++. A spanning tree is a subset of the edges of a connected undirected weighted graph that connects all the vertices together, without any cycles. The program is interactive. Graph edges with respective weights (i.e., v1 v2 w) are entered at the command line and results are displayed on the console. Each input transaction represents an undirected edge of a connected weighted graph. The edge consists of two unequal non-negative integers in the range 0 to 9 representing graph vertices that the edge connects. Each edge has an assigned weight. The edge weight is a positive integer in the range 1 to 99. The three integers on each input transaction are separated by space. An input transaction containing the string “end-of-file” signals the end of the graph edge input. After the edge information is read, the process…arrow_forward
- How precisely does the routing work? Could you provide any clarification on the distance vector routing?arrow_forward3. Consider the M/M/1 queue discussed in class. Assume that packets arrive to a queue with average arrival rate A [pkts/s]. The average service rate of the queue is denoted by u [pkts/s]. (a) Write expressions for: (i) the mean time between packet arrivals to the queue, i.e., the average inter-arrival time; and (ii) the mean service time, i.e., the average time needed to transmit a packet onto the outgoing link. (b) Let N denote the number of packets in the system in steady-state. Suppose A = 850 and u 1000. Find the smallest value of B such that P(N > B) < e = 10¬4. Hint: Use MATLAB or some other computational tool (you could even use an Excel spreadsheet) to test different values of B. 4. Consider the M/M/1 queue from Problem 3. (a) Find an expression for E[N], i.e., the average number of packets in the system in steady- state. For the values of A and µ specified in Problem 4(b), compute the value of E[N]. What happens when A→ µ? (b) Find an expression for Var[N], i.e., the variance…arrow_forwardIs it possible to implement other network topologies, and if so, which of them do you like the most?arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





