C1 (a). A lubricating oil having the dynamic viscosity of 0.056 poise and specific gravity of 1.17. Calculate (i) the density of oil in kg/m3, (ii) the weight density of oil in N/m3, (iii) the kinematic viscosity in stokes, and (iv) the specific volume in m2/kg. C1 (b). The capillary effect in a glass tube of 2.8 mm diameter, when immersed in (1) water and (2) mercury are 7.7 mm and -3.5 mm respectively. Calculate the value of surface tension in contact with air for water and mercury in N/m. Take, the contact angle for water =0° and mercury =130°.
C1 (a). A lubricating oil having the dynamic viscosity of 0.056 poise and specific gravity of 1.17. Calculate (i) the density of oil in kg/m3, (ii) the weight density of oil in N/m3, (iii) the kinematic viscosity in stokes, and (iv) the specific volume in m2/kg. C1 (b). The capillary effect in a glass tube of 2.8 mm diameter, when immersed in (1) water and (2) mercury are 7.7 mm and -3.5 mm respectively. Calculate the value of surface tension in contact with air for water and mercury in N/m. Take, the contact angle for water =0° and mercury =130°.
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter5: Analysis Of Convection Heat Transfer
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.5P: Evaluate the dimensionless groups hcD/k,UD/, and cp/k for water, n-butyl alcohol, mercury, hydrogen,...
Related questions
Question
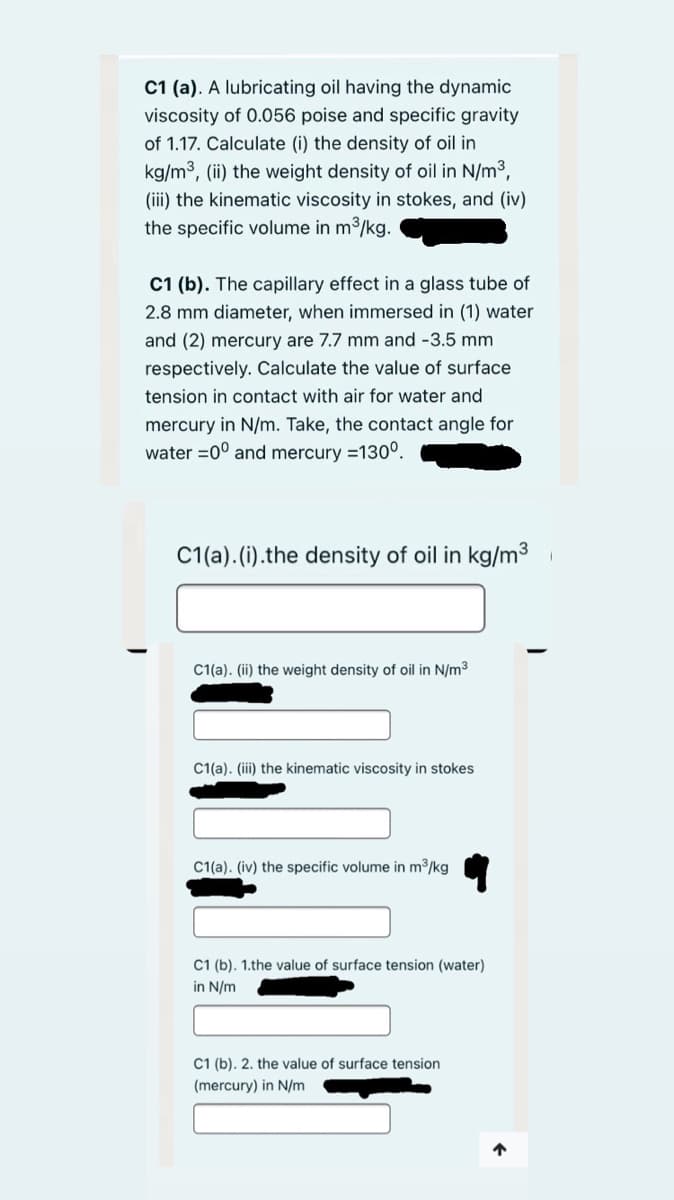
Transcribed Image Text:C1 (a). A lubricating oil having the dynamic
viscosity of 0.056 poise and specific gravity
of 1.17. Calculate (i) the density of oil in
kg/m3, (ii) the weight density of oil in N/m3,
(iii) the kinematic viscosity in stokes, and (iv)
the specific volume in m3/kg.
C1 (b). The capillary effect in a glass tube of
2.8 mm diameter, when immersed in (1) water
and (2) mercury are 7.7 mm and -3.5 mm
respectively. Calculate the value of surface
tension in contact with air for water and
mercury in N/m. Take, the contact angle for
water =0° and mercury =130°.
C1(a). (i).the density of oil in kg/m3
C1(a). (ii) the weight density of oil in N/m3
C1(a). (iii) the kinematic viscosity in stokes
C1(a). (iv) the specific volume in m3/kg
C1 (b). 1.the value of surface tension (water)
in N/m
C1 (b). 2. the value of surface tension
(mercury) in N/m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning