Calculate the equilibrium constant, K, at 25.0 °C for each of the reactions. Use the thermodynamic information provided in the table. The hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane. C,H, (g) + 2 H, (g) == C,H,(g) Compound AG; (kJ - mol"!) K = 42.39 CH,Cl(g) 48.50 -50.72 CH,(g) C,H,(g) C,H,(g) Cl,(8) H,(g) 209.2 -32.82 0.00 0.00 H,O(1) -237.13 HCI(g) -95.30 HNO, (aq) -111.25 NO(g) 86.55 51.31 NO,(g) Question Source: Atkins 7e - Chemical Principles | Publishe
Calculate the equilibrium constant, K, at 25.0 °C for each of the reactions. Use the thermodynamic information provided in the table. The hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane. C,H, (g) + 2 H, (g) == C,H,(g) Compound AG; (kJ - mol"!) K = 42.39 CH,Cl(g) 48.50 -50.72 CH,(g) C,H,(g) C,H,(g) Cl,(8) H,(g) 209.2 -32.82 0.00 0.00 H,O(1) -237.13 HCI(g) -95.30 HNO, (aq) -111.25 NO(g) 86.55 51.31 NO,(g) Question Source: Atkins 7e - Chemical Principles | Publishe
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter17: Chemcial Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17.107QE: Calculate the standard Gibbs free-energy change when SO3 forms from SO2 and O2 at 298 K. Why is...
Related questions
Question
it has part 1 & 2 pls answer this :(
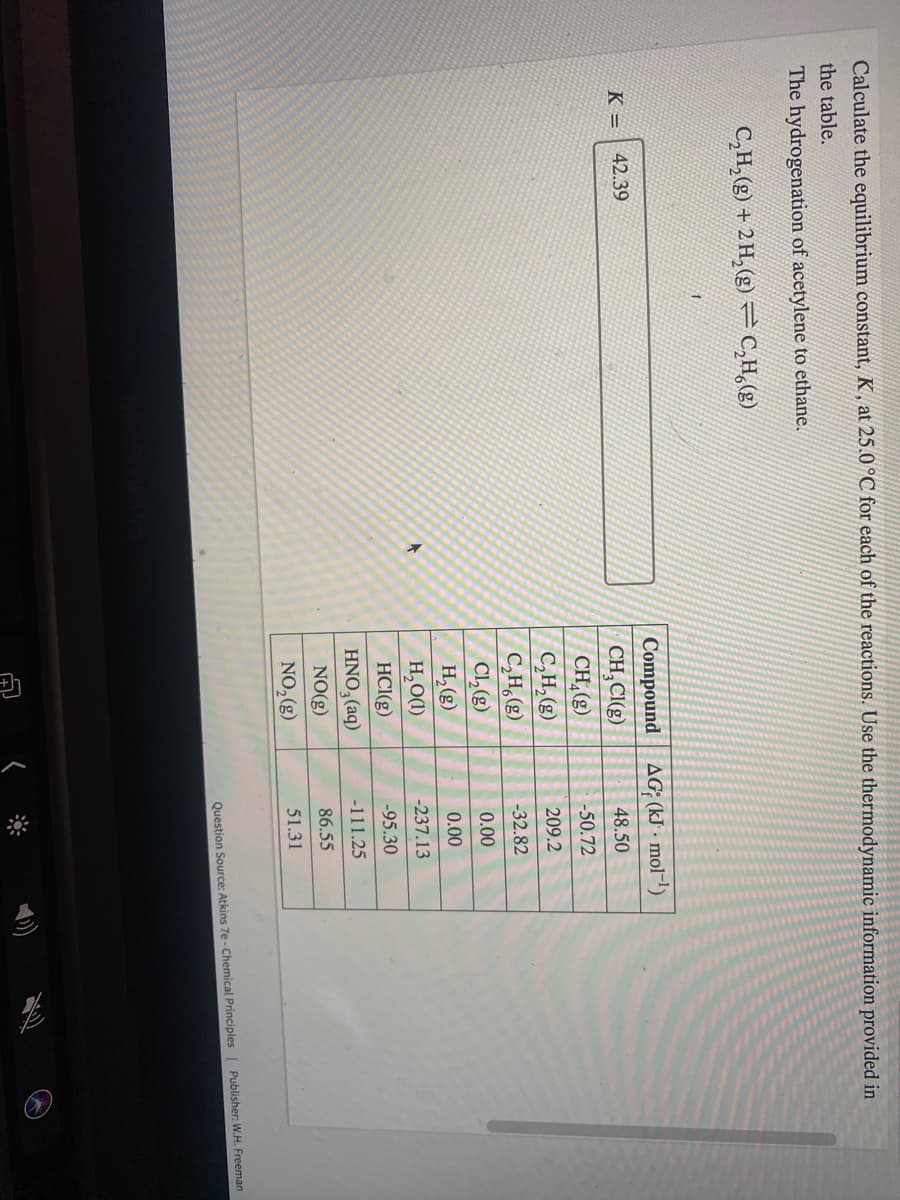
Transcribed Image Text:Calculate the equilibrium constant, K , at 25.0 °C for each of the reactions. Use the thermodynamic information provided in
the table.
The hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane.
C,H,(g) + 2 H, (g) = C,H,(g)
Compound AG; (kJ - mol-!)
K =
42.39
CH,CI(g)
48.50
CH,(g)
C,H,(g)
C,H,(2)
Cl,e)
H, (g)
-50.72
209.2
-32.82
0.00
0.00
H,O(1)
-237.13
HCI(g)
-95.30
HNO, (aq)
-111.25
NO(g)
86.55
NO,(g)
51.31
Question Source: Atkins 7e - Chemical Principles| Publisher: W.H. Freeman
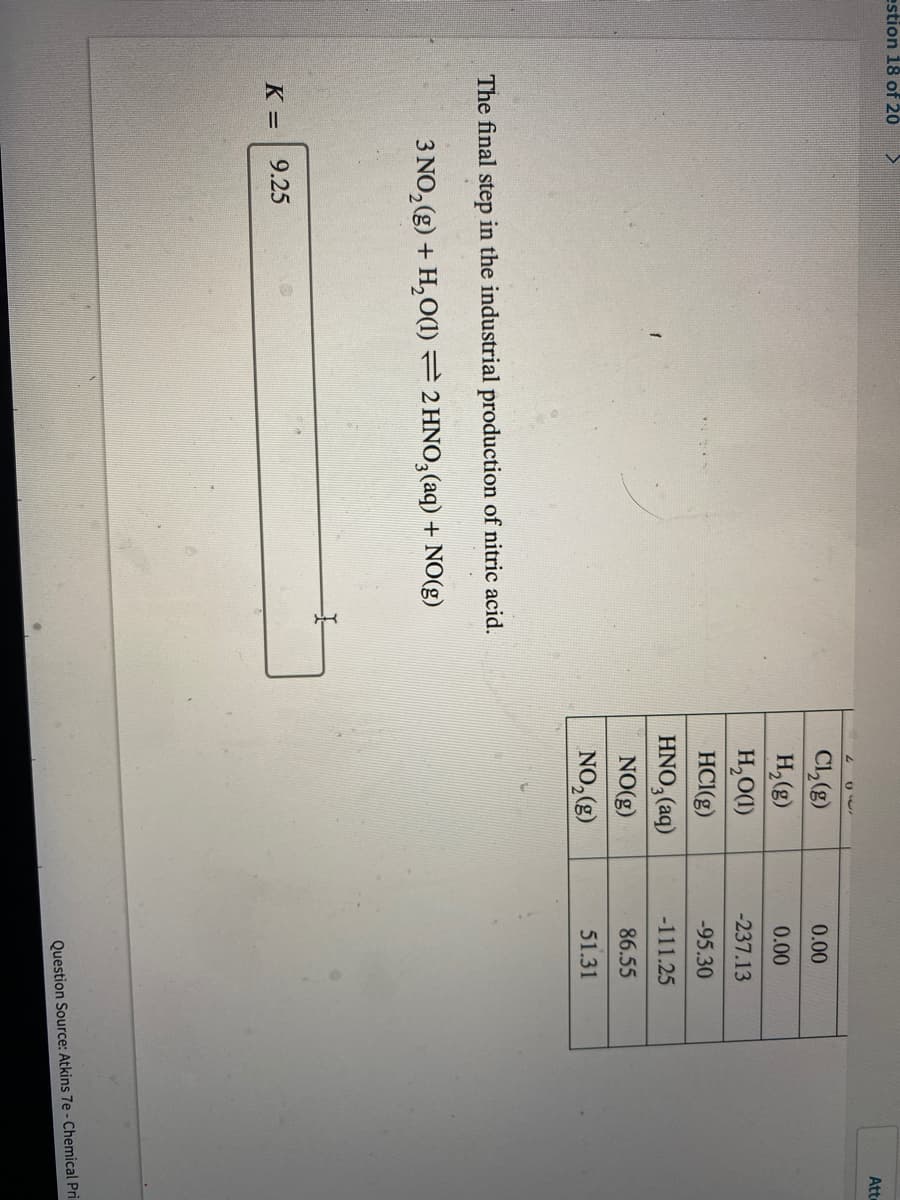
Transcribed Image Text:estion 18 of 20
Atte
7.
CL(g)
H,(g)
H,O(1)
0.00
0.00
-237.13
HCI(g)
-95.30
HNO, (aq)
-111.25
NO(g)
86.55
NO, (g)
51.31
The final step in the industrial production of nitric acid.
3 NO, (g) + H,O(1) = 2 HNO, (aq) + NO(g)
K =
9.25
Question Source: Atkins 7e - Chemical Pri
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning