Calculated Heats of Reaction, AH=AHf(R')+ AHf(CH) – AHF(RCD, in kJ/mol: R=n-butyl R= sec-butyl R= tert-butyl R = crotyl Based on their Calculated Heats of Reaction, list these primary, secondary, tertiary, and allylic halides in order of increasing relative rates (slowest < fastest): Why is the allylic cation (crotyl) different in stability compared to a primary cation? (One word:)
Calculated Heats of Reaction, AH=AHf(R')+ AHf(CH) – AHF(RCD, in kJ/mol: R=n-butyl R= sec-butyl R= tert-butyl R = crotyl Based on their Calculated Heats of Reaction, list these primary, secondary, tertiary, and allylic halides in order of increasing relative rates (slowest < fastest): Why is the allylic cation (crotyl) different in stability compared to a primary cation? (One word:)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter5: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: Energy And Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 119SCQ: Sublimation of 1.0 g of dry ice. CO2(s), forms 0.36 L of CO2(g) (at 78 C and 1.01 105 Pa). The...
Related questions
Question
1
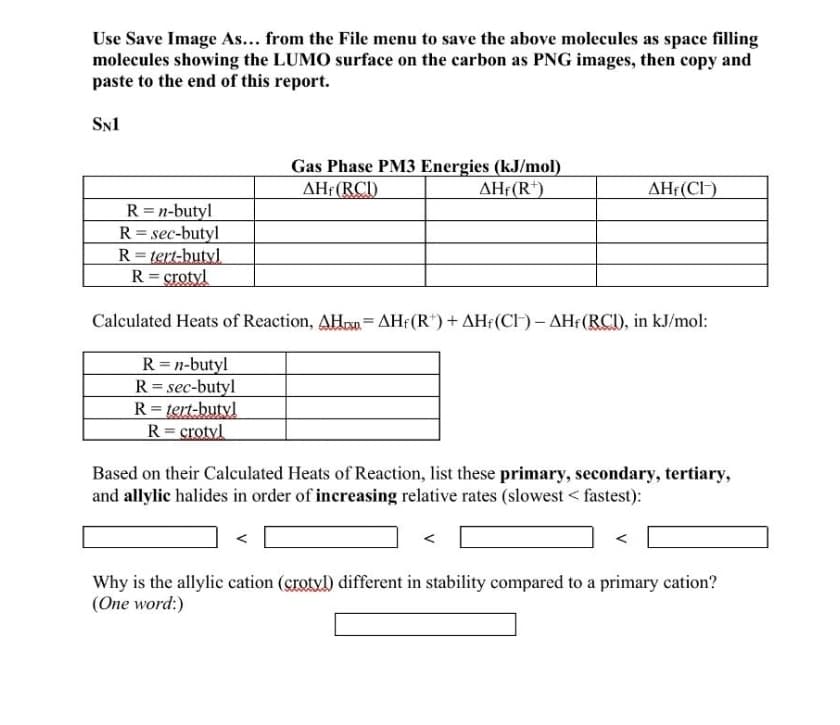
Transcribed Image Text:Use Save Image As... from the File menu to save the above molecules as space filling
molecules showing the LUMO surface on the carbon as PNG images, then copy and
paste to the end of this report.
SN1
Gas Phase PM3 Energies (kJ/mol)
AHf(RCI)
AHf(R*)
AHf(CIH)
R=n-butyl
R = sec-butyl
R= tert-butyl
R= crotyl
Calculated Heats of Reaction, AHon= AHf(R")+ AH¡(CH) - AHf(RCI), in kJ/mol:
%3D
R = n-butyl
R = sec-butyl
R= tert-butyl
R= crotyl
Based on their Calculated Heats of Reaction, list these primary, secondary, tertiary,
and allylic halides in order of increasing relative rates (slowest < fastest):
Why is the allylic cation (grotvl) different in stability compared to a primary cation?
(One word:)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning