Carefully study the following table: Radius Ratio Predicted Limiting Values Coordination Number Geometry Examples Tetrahedral ZnS 0.414 Square planar None 6. Octahedral NaCl, TiO, (rutile) 0.732 8 Cubic CSCI, CaF, (fluorite) 1.00 No ionic examples, but many metals are 12-coordinate. 12 Cubooctahedron Calcium fluoride has fluoride ions in a simple cubic arrangement and calcium ions in alternate body centre positions such that the radius ratio (r. / r.) is 0.97. (Note: r. = radius of the cation and r- = radius of the anion) a) Determine the predicted coordination number of the two ions using the radius ratio rule and the table above. b) Predict the coordination numbers (CN) of Ca²* in CaCl2 and CaBr2 using the table data and given the following information: lonic radius of Ca?* = 114 pm in CN = 6; and 126 pm in CN = 8 lonic radius of Cl¯ = 167 pm in CN = 6 lonic radius of Br¯ = 182 pm in CN = 6 %3D
Carefully study the following table: Radius Ratio Predicted Limiting Values Coordination Number Geometry Examples Tetrahedral ZnS 0.414 Square planar None 6. Octahedral NaCl, TiO, (rutile) 0.732 8 Cubic CSCI, CaF, (fluorite) 1.00 No ionic examples, but many metals are 12-coordinate. 12 Cubooctahedron Calcium fluoride has fluoride ions in a simple cubic arrangement and calcium ions in alternate body centre positions such that the radius ratio (r. / r.) is 0.97. (Note: r. = radius of the cation and r- = radius of the anion) a) Determine the predicted coordination number of the two ions using the radius ratio rule and the table above. b) Predict the coordination numbers (CN) of Ca²* in CaCl2 and CaBr2 using the table data and given the following information: lonic radius of Ca?* = 114 pm in CN = 6; and 126 pm in CN = 8 lonic radius of Cl¯ = 167 pm in CN = 6 lonic radius of Br¯ = 182 pm in CN = 6 %3D
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter3: Atomic Shells And Classical Models Of Chemical Bonding
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2P
Related questions
Question
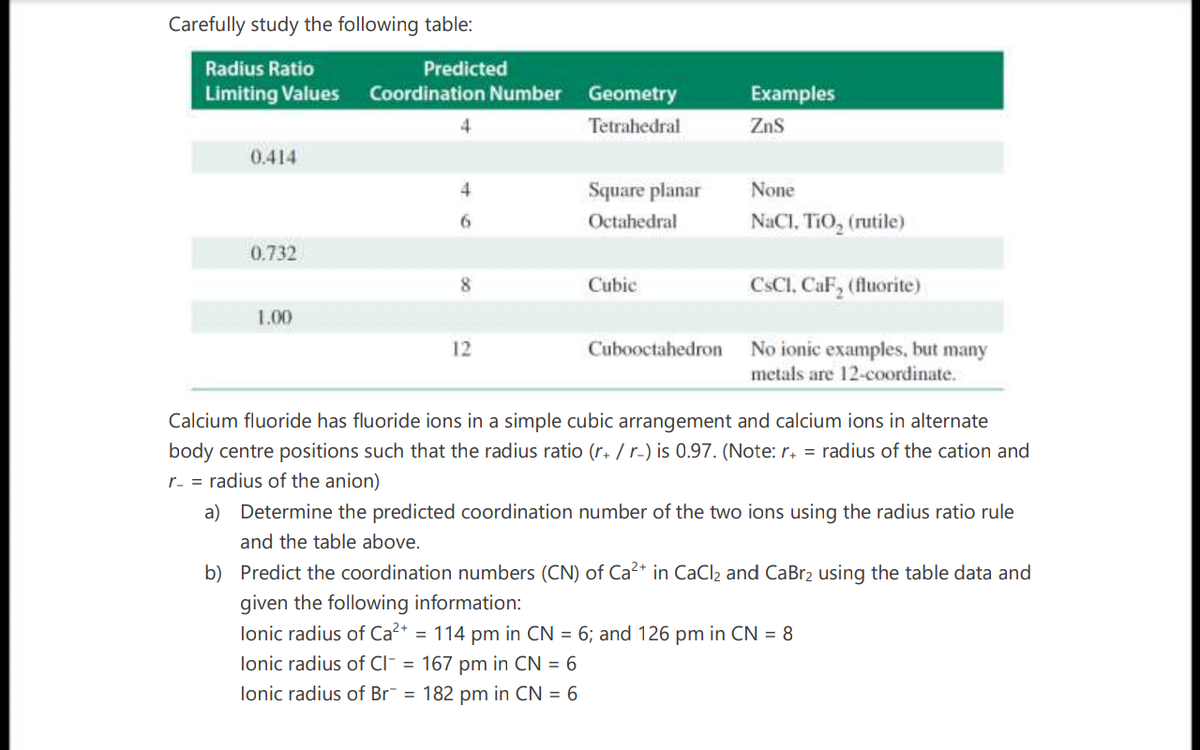
Transcribed Image Text:Carefully study the following table:
Radius Ratio
Predicted
Limiting Values
Coordination Number
Geometry
Examples
4
Tetrahedral
Zns
0.414
4
Square planar
None
6.
Octahedral
NaCl, TiO, (rutile)
0.732
8
Cubic
CSCI, CaF, (fluorite)
1.00
No ionic examples, but many
metals are 12-coordinate.
12
Cubooctahedron
Calcium fluoride has fluoride ions in a simple cubic arrangement and calcium ions in alternate
body centre positions such that the radius ratio (r+ / r-) is 0.97. (Note: r. = radius of the cation and
r- = radius of the anion)
a) Determine the predicted coordination number of the two ions using the radius ratio rule
and the table above.
b) Predict the coordination numbers (CN) of Ca2+ in CaCl2 and CaBr2 using the table data and
given the following information:
lonic radius of Ca²* = 114 pm in CN = 6; and 126 pm in CN = 8
lonic radius of CI¯ = 167 pm in CN = 6
lonic radius of Br¯ = 182 pm in CN = 6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning