CH3 H3C. CH3 Br HBr CH2 CH3 H3C H3C ČH3 Electrophilic addition of HBr to alkenes yields a bromoalkane. The reaction begins with an attack on the hydrogen of the electrophilic HBr by the a electrons of the double bond to give a carbocation. This step follows Markovnikov's rule with the electrophilic H atom adding to the sp2 carbon containing the most hydrogens, leading to the formation of the most stable carbocation (1°<2°<3°). If possible, a 1,2-shift of either a neighboring hydride or methyl group can occur prior to the last step in order to form a more stable carbocation. In the final step of the reaction, nucleophilic bromide adds to the carbocation to give the neutral product. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 CH3 H3C. CH3 CH3 H3C H3C ČH3 Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining
CH3 H3C. CH3 Br HBr CH2 CH3 H3C H3C ČH3 Electrophilic addition of HBr to alkenes yields a bromoalkane. The reaction begins with an attack on the hydrogen of the electrophilic HBr by the a electrons of the double bond to give a carbocation. This step follows Markovnikov's rule with the electrophilic H atom adding to the sp2 carbon containing the most hydrogens, leading to the formation of the most stable carbocation (1°<2°<3°). If possible, a 1,2-shift of either a neighboring hydride or methyl group can occur prior to the last step in order to form a more stable carbocation. In the final step of the reaction, nucleophilic bromide adds to the carbocation to give the neutral product. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 CH3 H3C. CH3 CH3 H3C H3C ČH3 Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter19: Enolate Anions And Enamines
Section19.9: Crossed Enolate Reactions Using Lda
Problem JQ
Related questions
Question
this is the last part to the previous question.
thanks
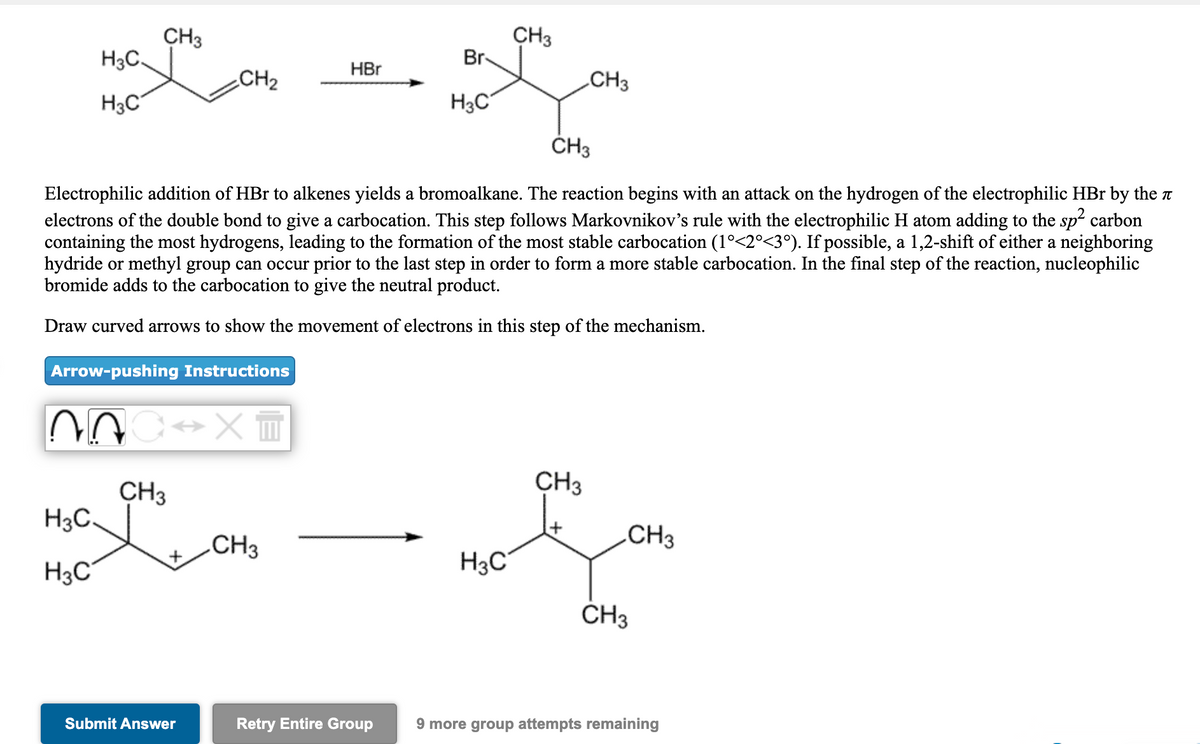
Transcribed Image Text:CH3
H3C.
CH3
Br
HBr
CH2
CH3
H3C
H3C
ČH3
Electrophilic addition of HBr to alkenes yields a bromoalkane. The reaction begins with an attack on the hydrogen of the electrophilic HBr by the T
electrons of the double bond to give a carbocation. This step follows Markovnikov's rule with the electrophilic H atom adding to the sp carbon
containing the most hydrogens, leading to the formation of the most stable carbocation (1°<2°<3°). If possible, a 1,2-shift of either a neighboring
hydride or methyl group can occur prior to the last step in order to form a more stable carbocation. In the final step of the reaction, nucleophilic
bromide adds to the carbocation to give the neutral product.
Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
Arrow-pushing Instructions
CH3
CH3
H3C.
CH3
.CH3
H3C°
H3C°
ČH3
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
9 more group attempts remaining
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning