Chapter 4. Tyler is hoping to get a lot of custom cake and cookie orders in his new bakery for various parties and celebrations. He considers keeping a stock of celebratory helium balloons in his bakery so that he can sell them alongside the cakes and cookies to add more value for his customers. However, he knows that the demand for custom goods as well as the balloons is like to be probabilistic in nature instead of deterministic. He is trying to create a model of how many balloons to order to keep in stock to minimize the costs of inventory in his little bakery. He identifies the following characteristics and needs your help in filling out the table given below the information. • Ordering Cost is $22.00 per order Cost of balloons is $3.00 per balloon • The bakery uses the 15% annual holding cost rate for all inventory • The lead tỉme for a new order of helium balloons is 14 days. • Data from other bakeries indicate that the demand during the 14-day lead time follows a normal probability distribution with a weekly mean of 20 balloons and a standard deviation of 5 balloons per week. • The number of working days per year is 300 • Acceptable probability of a stock-out, for Tyler is 10% or 0.10. Average Inventory Level (Q'/2)+S balloons Optimal Inventory Policy Reorder Point r balloons Economic Order Quantity Q* balloons Annual Inventory Holding Cost H Number of Orders per Year (D/Q") dollars Annual Ordering Cost Cycle Time (Days) T days dollars Safety Stock S balloons Total Annual Cost TC dollars Maximum Inventory Level Q*+ S Expected Stockouts per Year SO balloons
Chapter 4. Tyler is hoping to get a lot of custom cake and cookie orders in his new bakery for various parties and celebrations. He considers keeping a stock of celebratory helium balloons in his bakery so that he can sell them alongside the cakes and cookies to add more value for his customers. However, he knows that the demand for custom goods as well as the balloons is like to be probabilistic in nature instead of deterministic. He is trying to create a model of how many balloons to order to keep in stock to minimize the costs of inventory in his little bakery. He identifies the following characteristics and needs your help in filling out the table given below the information. • Ordering Cost is $22.00 per order Cost of balloons is $3.00 per balloon • The bakery uses the 15% annual holding cost rate for all inventory • The lead tỉme for a new order of helium balloons is 14 days. • Data from other bakeries indicate that the demand during the 14-day lead time follows a normal probability distribution with a weekly mean of 20 balloons and a standard deviation of 5 balloons per week. • The number of working days per year is 300 • Acceptable probability of a stock-out, for Tyler is 10% or 0.10. Average Inventory Level (Q'/2)+S balloons Optimal Inventory Policy Reorder Point r balloons Economic Order Quantity Q* balloons Annual Inventory Holding Cost H Number of Orders per Year (D/Q") dollars Annual Ordering Cost Cycle Time (Days) T days dollars Safety Stock S balloons Total Annual Cost TC dollars Maximum Inventory Level Q*+ S Expected Stockouts per Year SO balloons
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter12: Queueing Models
Section12.5: Analytic Steady-state Queueing Models
Problem 30P
Related questions
Question
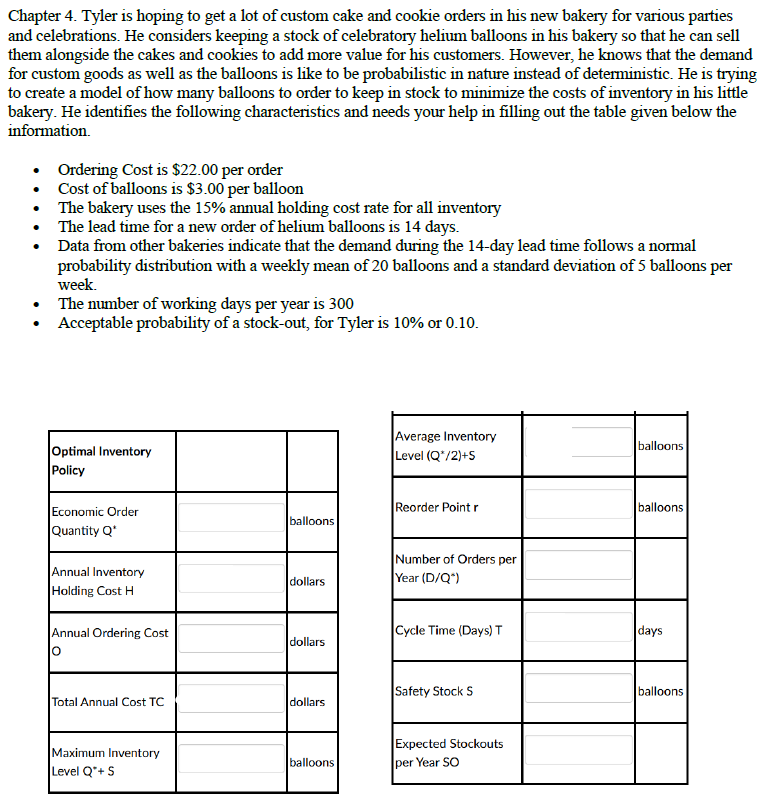
Transcribed Image Text:Chapter 4. Tyler is hoping to get a lot of custom cake and cookie orders in his new bakery for various parties
and celebrations. He considers keeping a stock of celebratory helium balloons in his bakery so that he can sell
them alongside the cakes and cookies to add more value for his customers. However, he knows that the demand
for custom goods as well as the balloons is like to be probabilistic in nature instead of deterministic. He is trying
to create a model of how many balloons to order to keep in stock to minimize the costs of inventory in his little
bakery. He identifies the following characteristics and needs your help in filling out the table given below the
information.
Ordering Cost is $22.00 per order
Cost of balloons is $3.00 per balloon
• The bakery uses the 15% annual holding cost rate for all inventory
The lead time for a new order of helium balloons is 14 days.
Data from other bakeries indicate that the demand during the 14-day lead time follows a normal
probability distribution with a weekly mean of 20 balloons and a standard deviation of 5 balloons per
week.
The number of working days per year is 300
Acceptable probability of a stock-out, for Tyler is 10% or 0.10.
Average Inventory
Level (Q*/2)+5
balloons
Optimal Inventory
Policy
Reorder Point r
balloons
Economic Order
Quantity Q*
balloons
Annual Inventory
Holding Cost H
Number of Orders per
Year (D/Q*)
dollars
Annual Ordering Cost
Cycle Time (Days) T
days
dollars
Safety Stock S
balloons
Total Annual Cost TC
dollars
Expected Stockouts
Maximum Inventory
Level Q*+ S
balloons
per Year SO

Transcribed Image Text:Chapter 5. (M/M/s/K Model). Leia is responsible for 8 computers in the IT offices in a small business called
DataWish. Each computer runs on an average for 3 weeks and requires an average of ½ or 0.5 weeks to get reset
by Leia before it can start up again. If we assign the Poisson distribution to the "arrival" of each computer for
service and an exponential distribution to the actual service provided, answer the following questions:
a. The arrival rate would bel
units per week and the service rate would be
units per week.
b. Calculate the following operating characteristics for the M/M/s/K system:
Utilization Factor (p)
Performance
Measures
c. If we assign a cost of waiting as $500 per week per
computer and $800 per week of hiring Leia, what is the
Total Time Cost per week cost of servicing the
machines?
PO (probability that
sytem is empty)
%
dollars
L (average units in
system)
units
d. If DataWish decides to hire another individual to
help Leia, what would the new Total Time Cost per
week be?
dollars.
Lq (average units
waiting in queue)
lunits
W (average time in the
weeks
system)
Wq (average time in
the queue)
weeks
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,