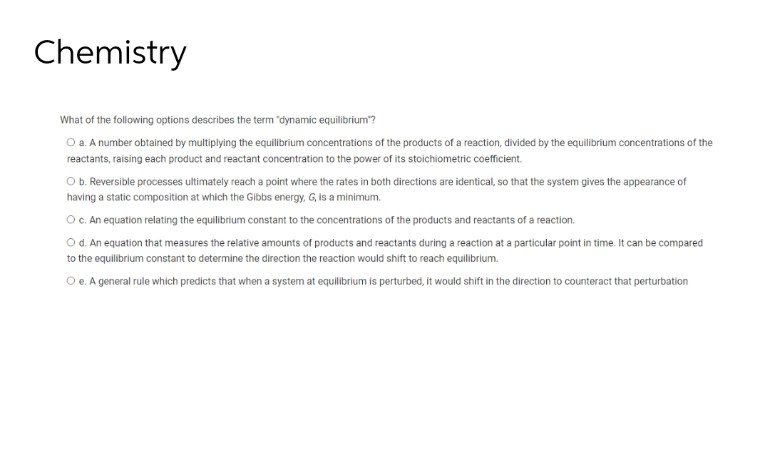
Chemistry What of the following options describes the term "dynamic equilibrium"? O a. A number obtained by multiplying the equilibrium concentrations of the products of a reaction, divided by the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants, raising each product and reactant concentration to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient. O b. Reversible processes ultimately reach a point where the rates in both directions are identical, so that the system gives the appearance of having a static composition at which the Gibbs energy, G, is a minimum. O c. An equation relating the equilibrium constant to the concentrations of the products and reactants of a reaction. O d. An equation that measures the relative amounts of products and reactants during a reaction at a particular point in time. It can be compared to the equilibrium constant to determine the direction the reaction would shift to reach equilibrium. O e. A general rule which predicts that when a system at equilibrium is perturbed, it would shift in the direction to counteract that perturbation
Chemistry What of the following options describes the term "dynamic equilibrium"? O a. A number obtained by multiplying the equilibrium concentrations of the products of a reaction, divided by the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants, raising each product and reactant concentration to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient. O b. Reversible processes ultimately reach a point where the rates in both directions are identical, so that the system gives the appearance of having a static composition at which the Gibbs energy, G, is a minimum. O c. An equation relating the equilibrium constant to the concentrations of the products and reactants of a reaction. O d. An equation that measures the relative amounts of products and reactants during a reaction at a particular point in time. It can be compared to the equilibrium constant to determine the direction the reaction would shift to reach equilibrium. O e. A general rule which predicts that when a system at equilibrium is perturbed, it would shift in the direction to counteract that perturbation
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.40PAE: Because carbonic acid undergoes a second ionization, the student in Exercise 12.39 is concerned that...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Chemistry
What of the following options describes the term "dynamic equilibrium"?
O a. A number obtained by multiplying the equilibrium concentrations of the products of a reaction, divided by the equilibrium concentrations of the
reactants, raising each product and reactant concentration to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient.
O b. Reversible processes ultimately reach a point where the rates in both directions are identical, so that the system gives the appearance of
having a static composition at which the Gibbs energy, G, is a minimum.
O c. An equation relating the equilibrium constant to the concentrations of the products and reactants of a reaction.
O d. An equation that measures the relative amounts of products and reactants during a reaction at a particular point in time. It can be compared
to the equilibrium constant to determine the direction the reaction would shift to reach equilibrium.
O e. A general rule which predicts that when a system at equilibrium is perturbed, it would shift in the direction to counteract that perturbation
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning