
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
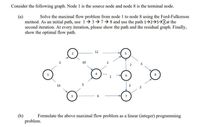
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following graph. Node I is the source node and node 8 is the terminal node.
(a)
Solve the maximal flow problem from node 1 to node 8 using the Ford-Fulkerson
method. As an initial path, use 1 3→7 8 and use the path 12→5→8at the
second iteration. At every iteration, please show the path and the residual graph. Finally,
show the optimal flow path.
12
10
1
13
5
3
(b)
Formulate the above maximal flow problem as a linear (integer) programming
problem.
2.
3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 7. We have computed the shortest path between all the nodes in a weighted graph. Then all the edges increase their costs by adding the same value c > 0. Will the shortest paths change? If your answer is NO, prove so, if the answer is YES, give an example of a graph where at least one shortest path changes.arrow_forwardFind the cost of a shortest path between a and d in the given weighted graph.arrow_forwardCompute the maximum flow in the following flow network using Ford-Fulkerson's algorithm. 12 8 14 15 11 2 5 1 3 d 7 f 6 What is the maximum flow value? A minimum cut has exactly which vertices on one side? 4.arrow_forward
- A weighted graph is given below. Compute the following metrics for this graph. You can use a calculator if necessary. 1) Eccentricity for each vertex; 2) Average length of the shortest paths from each vertex; 3) Count of triangles of each vertex; 4) Count of triples of each vertex; 5) Radius of the graph; 6) Diameter of the graph; 7) Average path length of the graph; 8) Characteristic path length of the graph; 9) Network transitivity of the graph; 10) Network density of the graph.arrow_forward4. Graph Theory and Approximation Algorithms- (a) Find the maximum flow possible from vertex s to vertex t in the given graph. Show all your steps Given an example to show why reverse flow edges should be included to get the optimal flow 12 vi V4 20 16 8 4 9. 14 V3 v2 15 (b) Given below are the distances between A, B, C, D, E, F. You have to start from A, visit all the vertices and return back to the A. Find the optimal path using the approximation algorithm discussed in class. Show all your steps. () | A BC D E F A0 4 4 3 5 5 в| 4 0 2 4 C 4 2 D 3 4 E 5 3 6 F 5 3 4 3 3 6. 4 5 4 5 4 5 5 0 inarrow_forwardProblem 3. Let G = (V, E) be a bipartite graph with verter partition V = LUR, and let G' be its corresponding flow network. Give a good upper bound on the length of any augmenting path found in G' during the execution of algorithm. FORD-FULKERSONarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education