Consider the following reaction where K. = 0.159 at 723 K. N½(g) + 3Hz(g)=2NH3(g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 4.18×10² moles of Na(g), 3.79×102 moles of Hz(2) and 5.18×104 moles of NH3(g), in a 1.00 liter container. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what direction must it run in order to reach equilibrium? The reaction quotient, Qe equals | The reaction A. must run in the forward direction to reach equilibrium. B. must run in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium. C. is at equilibrium.
Consider the following reaction where K. = 0.159 at 723 K. N½(g) + 3Hz(g)=2NH3(g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 4.18×10² moles of Na(g), 3.79×102 moles of Hz(2) and 5.18×104 moles of NH3(g), in a 1.00 liter container. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what direction must it run in order to reach equilibrium? The reaction quotient, Qe equals | The reaction A. must run in the forward direction to reach equilibrium. B. must run in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium. C. is at equilibrium.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter13: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3ALQ: For the reactionH2(g)+I2(g)2HI(g), consider two possibilities: (a) you mix 0.5 mole of each...
Related questions
Question
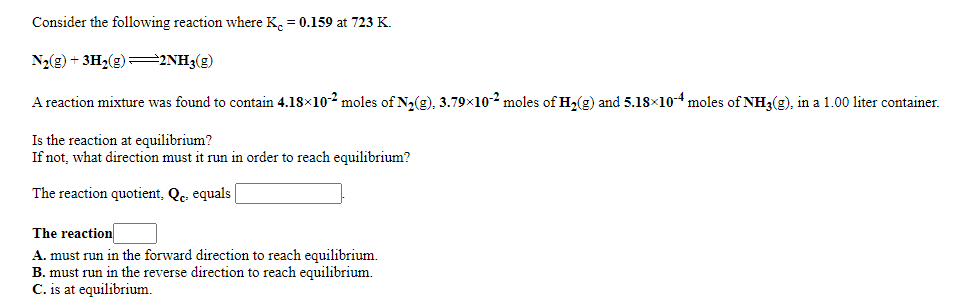
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following reaction where K. = 0.159 at 723 K.
N2(g) + 3H2(g)=2NH3(g)
A reaction mixture was found to contain 4.18×102 moles of N2(g), 3.79x102 moles of H2(g) and 5.18×10-4 moles of NH3(g), in a 1.00 liter container.
Is the reaction at equilibrium?
If not, what direction must it run in order to reach equilibrium?
The reaction quotient, Qc. equals|
The reaction
A. must run in the forward direction to reach equilibrium.
B. must run in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium.
C. is at equilibrium.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas to form ammonia:
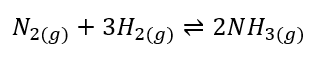
At the given state the concentration of different species is as follows:
N2 = 4.18x10-2 M
H2 = 3.79x10-2 M
NH3 = 5.18x10-4 M
Note the volume of the solution is one liter, hence the concentration of all reactants and products is equal to the moles of these species.
Step 2
The value of the reaction quotient is given by:
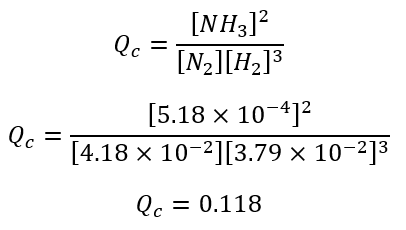
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning