Consider the triangular panel made of two different isotropic materials as shown in Fig. 2. A constant temperature of T = 0°C is prescribed along edge 2–3. Edge 1–2 is fully insulated. A linearly-varying heat flux of q = 15x W m-1 is applied along edge 1-3. Heat sources can be ignored. The panel is approximated using two linear triangular elements as indicated in Fig. 2. 2 (1) (1) q = 0 T = 0°C 3 m N(1) N(2) k = 4W°C-1 |k = 8 W °C-1 (2) (3) (2) 3 -1 q = 15x W m' 2 m 2 m Figure 2: Bi-material triangular panel. (a) Compute the element conductance matrix Ke for element 1. (b) Compute the global flux vector f. (c) Compute the global conductance matrix after imposition of the essential bound- ary conditions.
Consider the triangular panel made of two different isotropic materials as shown in Fig. 2. A constant temperature of T = 0°C is prescribed along edge 2–3. Edge 1–2 is fully insulated. A linearly-varying heat flux of q = 15x W m-1 is applied along edge 1-3. Heat sources can be ignored. The panel is approximated using two linear triangular elements as indicated in Fig. 2. 2 (1) (1) q = 0 T = 0°C 3 m N(1) N(2) k = 4W°C-1 |k = 8 W °C-1 (2) (3) (2) 3 -1 q = 15x W m' 2 m 2 m Figure 2: Bi-material triangular panel. (a) Compute the element conductance matrix Ke for element 1. (b) Compute the global flux vector f. (c) Compute the global conductance matrix after imposition of the essential bound- ary conditions.
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter2: Steady Heat Conduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.15P: 2.15 Suppose that a pipe carrying a hot fluid with an external temperature of and outer radius is...
Related questions
Question
question A B and C
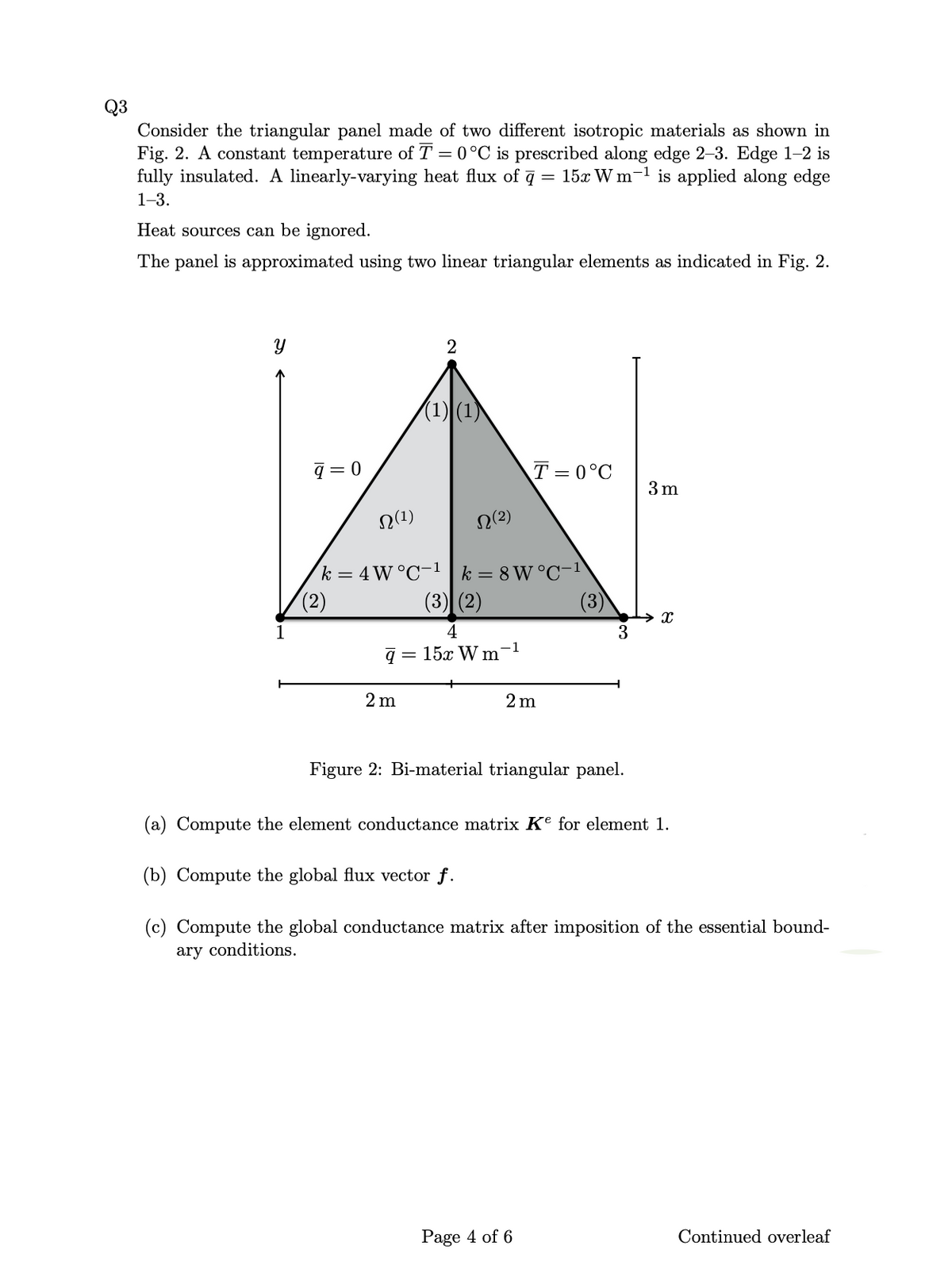
Transcribed Image Text:Q3
Consider the triangular panel made of two different isotropic materials as shown in
Fig. 2. A constant temperature of T = 0°C is prescribed along edge 2-3. Edge 1–2 is
fully insulated. A linearly-varying heat flux of ą
= 15x W m-1 is applied along edge
1-3.
Heat sources can be ignored.
The panel is approximated using two linear triangular elements as indicated in Fig. 2.
2
(1) (1)
q = 0
T = 0°C
3 m
N(1)
N(2)
k = 4W°C-1 |k = 8 W°C-1
(3) (2)
(2)
(3)
4
3
-1
q = 15x W m
2 m
2 m
Figure 2: Bi-material triangular panel.
(a) Compute the element conductance matrix Kº for element 1.
(b) Compute the global flux vector f.
(c) Compute the global conductance matrix after imposition of the essential bound-
ary conditions.
Page 4 of 6
Continued overleaf
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning