
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
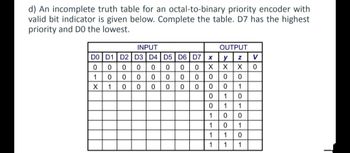
Transcribed Image Text:d) An incomplete truth table for an octal-to-binary priority encoder with
valid bit indicator is given below. Complete the table. D7 has the highest
priority and DO the lowest.
DO
0
1
X
INPUT
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 x y
0
0
0
1
olo
OOO
0
COO
200
800
0
0 0 0
boo
0
XXO
0
1-000
OUTPUT
Z
X 0
اداد
0
0
1
0
1
1
0 0
1 0 1
OXK
1
1 1
1
ox
ol
0
1
V
lo
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following runtime stack: BEFORE 00001000 00000006 ESP 00000FFC 00000FF 8 00000FF 4 00000FF0 What would be the value of ESP after pushing the 32-bit value shown below onto the stack? 000000A5 O 00001020 O 00000FF8 O 00000FFC O 000000A5arrow_forwardDesign a sequence detector that detects the pattern “1101” in a sequence of binary input x. The output z goes to ‘1’ when the last ‘1’ in the pattern is input. z is '0' otherwise. The last '1' in a pattern can be considered as the first '1' in the next pattern.arrow_forwardComplete the Hamming code below for the given 4-bit hex values. Insert the ODD parity bits into positions 1, 2, and 4. For this problem, P means POSITION, not parity. The parity bit in P1 checks bits P1, P3, P5, and P7. The parity bit in P2 checks bits P2, P3, P6, and P7. The parity bit in P4 checks bits P4, P5, P6, and P7. Hex 0: 7: A: P1 P2 P3 0 P4 P5 0 1 ? P6 0 1 ? P7 0 1 ?arrow_forward
- HELP WITH THISSarrow_forward2. Perform subtraction on the following unsigned binary number using 2's- complement of the subtrahend. a) 11011 - 11001 b) 11010 - 10101 c) 1011 - 11000 d) 101010 - 11011arrow_forwardWhat parity bit, P, should be added to the following data if the parity is EVEN? If the parity is ODD? a. 1111100 b. 1010110 c. 0001101arrow_forward
- Utilizing Hamming Code check bits, Identify where the error is in the following stored 8-bit data word (with required parity bits). Assume even parity! b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8 b9 b10 b11 b12 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 Identify the position of the bit error with the four check bits C8 C4 C2 C0 identified in the order shown left to right.arrow_forwardGrey converters are often used in industrial circuits where the normal sequence of binary numbers may produce ambiguity during transition. This is elliminated with the Grey code, as only one bit changes, during a normal transition of sequential numbers. Show the logic required to convert a 10-bit binary number to Gray code and use that logic to convert the following to Gray code: a) 1010101010 b) 1111100000 c) 0000001110 d) 1111111111arrow_forwardPlease, the number is should be 4 number in the result number not 5 numberarrow_forward
- Plz solve within 40min I vill give definitely upvote and vill give positive feedback thank you sirarrow_forwardEach of the eight full-adders in an 8-bit parallel ripple carry adder exhibits the following propagationdelay:A to © and Cout: 20 nsB to © and Cout: 20 nsCin to ©: 30 nsCin to Cout: 25 nsDetermine the maximum total time for the addition of two 8-bit numbers.arrow_forwardQ3) The value of the DS register is 3032H. And the BX register contains a 16 bit value which is equal to 3032H. 0008H is added to BX. ADD BX, 0008H The register AX contains some value which needs to be stored at a location as follows: MOV [BX], AX Calculate the address at which the value of the AX will be stored.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,