
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
You must not use any of the following:
- dictionaries or dictionary methods
- try-except
- break and continue statements
- recursion
- map / filter
- any type of sorting function for second_largest
![def second_largest(lst: List[int]) -> int:
II II II
Given a list <lst> of integers, return the second largest item in the list
without modifying <lst>. You cannot use any of python's builtin sorting
functions. Do not attempt to sort the list yourself either.
As a sanity check, you can ensure that your function returns what
"return sorted (lst)[-2]" would. (DO NOT COPY THIS)
For example, an input [1, 2, 3] should return an output of 2, since 2 is
the second largest integer in the list.
Note that when we say second largest, we do not mean second largest
distinct element. That means that [1, 2, 4, 4] should return 4, not 2.
Precondition: the input list has at least 2 elements.
Something extra to think about (not graded): is it possible to write this
function with an extra argument <n> and return the nth largest number in
the list? Can you do this without sorting the list?
pass](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/2e9e339e-2841-4d7f-bb32-e8e5b2ddcf58/26aa5cd3-1917-4d38-bd4b-19b426671a27/rydghb8_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:def second_largest(lst: List[int]) -> int:
II II II
Given a list <lst> of integers, return the second largest item in the list
without modifying <lst>. You cannot use any of python's builtin sorting
functions. Do not attempt to sort the list yourself either.
As a sanity check, you can ensure that your function returns what
"return sorted (lst)[-2]" would. (DO NOT COPY THIS)
For example, an input [1, 2, 3] should return an output of 2, since 2 is
the second largest integer in the list.
Note that when we say second largest, we do not mean second largest
distinct element. That means that [1, 2, 4, 4] should return 4, not 2.
Precondition: the input list has at least 2 elements.
Something extra to think about (not graded): is it possible to write this
function with an extra argument <n> and return the nth largest number in
the list? Can you do this without sorting the list?
pass
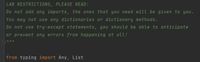
Transcribed Image Text:LAB RESTRICTIONS, PLEASE READ:
Do not add any imports, the ones that you need will be given to you.
You may not use any dictionaries or dictionary methods.
Do not use try-except statements, you should be able to anticipate
or prevent any errors from happening at all!
from typing import Any, List
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Lab Goal : This lab was designed to teach you more about recursion. Lab Description : luckyThrees will return a count of the 3s in the number unless the 3 is at the start. A 3 at the start of the number does not count. /* luckyThrees will return the count of 3s in the number* unless the 3 is at the front and then it does not count* 3 would return 0* 31332 would return 2* 134523 would return 2* 3113 would return 1* 13331 would return 3* 777337777 would return 2* the solution to this problem must use recursion*/public static int luckyThrees( long number ){} Sample Data : 331332134523311313331777337777 Sample Output : 022132arrow_forwardc++ language using addition, not get_sum function with this pseudocode: Function Main Declare Integer Array ages [ ] Declare integer total assign numbers = [ ] assign total = sum(ages) output "Sum: " & total end fucntion sum(Integer Array array) declare integer total declare integer index assign total = 0 for index = 0 to size(array) -1 assign total = total + array[ ] end return integer totalarrow_forwarddef is_balanced(root): return __is_balanced_recursive(root) def __is_balanced_recursive(root): """ O(N) solution """ return -1 != __get_depth(root) def __get_depth(root): """ return 0 if unbalanced else depth + 1 """ if root is None: return 0 left = __get_depth(root.left) right = __get_depth(root.right) if abs(left-right) > 1 or -1 in [left, right]: return -1 return 1 + max(left, right) # def is_balanced(root):# """# O(N^2) solution# """# left = max_height(root.left)# right = max_height(root.right)# return abs(left-right) <= 1 and is_balanced(root.left) and# is_balanced(root.right) # def max_height(root):# if root is None:.arrow_forward
- In C#, how would you compile a program that declares a 5 element double array that uses a loop to read values for each element from the user. The program should then use an additional loop to compute and output the sum of the elements in the array.arrow_forwarddata structure (java)arrow_forwardpython def factorial(n):pass # replace this line with your lines of recursive codedef sum_recursively(n):pass # replace this line with your lines of recursive codedef sumlist_recursively(l):pass # replace this line with your lines of recursive codedef reverse_recursively(l):pass # replace this line with your lines of recursive code#EXTRA CREDITdef multiply_recursively(n, m):pass # replace this line with your lines of recursive codearrow_forward
- Memory Management Programming Assignment Please if this can be coded in Java or C++ i would appreciate implement and test the GET-MEMORY algorithm This algorithm uses the Next-Fit(First-Fit-With-A-Roving-Pointer) technique. implement and test the FREE-MOMORY algorithm Implement the “GET_MEMORY” and “FREE_MEMORY” algorithms. Comprehensive testing must be done for each algorithm. Following are sample run results for each: GET_MEMORY IS RUNNING……… Initial FSB list FSB# Location Size 1 7 4 2 14 10 3 30 20 . . . . . . Rover is 14 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Allocation request for 5 words Allocation was successful Allocation was in location 14 FSB# Location Size 1 7 4 2 19 5 3 30 20 . . . . . . Rover is 30 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Allocation request for 150 words Allocation was not successful . . . __________________________________________________________ FREE_MEMORY…arrow_forwardSubmerging is the phenomenon wherein the pointer vanishes when you move it too quickly.arrow_forwardJava - When using an array to do a binary search, what additional requirement is placed on the array?arrow_forward
- Data structures remove_char(str_list:list, char:str) -> list This function will be given a list of strings and a character. You must remove all occurrences of the character from each string in the list. The function should return the list of strings with the character removed. Example: str_list = ['adndj', 'adjdlaa', 'aa', 'djoe'] char: a output = ['dndj', 'djdl', '', 'djoe']arrow_forward1) Code that takes number of rows and columns from the user using the concept of multidimensional arrays using java. 2) Ask the user for the elements to be stored 3) Print the elements by row 4) Print the sum of the elements by row Enter number of rows: 3 Enter number of columns : 3 Enter contents of the table: a[0][0]: 1 a[0][1]: 2 a[0][2]: 3 a[1][0]: 4 a [1][1]: 10 a[1] [2]: 20 a[2][0]: 30 a[2][1]: 70 a[2][2]: 5 The contents of the table are: Row 0 ==Y [ 1 2 3 Row 1 ==V Row 2 ==> [4 10 20 [ 30 70 5 ]Sum of Row 0 is = 6 ] Sum of Row 1 is = 34 ]Sum of Row 2 is = 105arrow_forwardPointers can be compared using the == operator. A) True B) Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education