Esterase hydrolyzes ester bonds. For simplicity, only the amino acids whose side-chains interact with the substrate are shown. Each circled interaction is important for the binding of the substrate to the enzyme.
Esterase hydrolyzes ester bonds. For simplicity, only the amino acids whose side-chains interact with the substrate are shown. Each circled interaction is important for the binding of the substrate to the enzyme.
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter27: Metabolic Integration And Organ Specialization
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Figure 27.3 illustrates the response of R (ATP-regenerating) and U (ATP-utilizing) enzymes to energy...
Related questions
Question
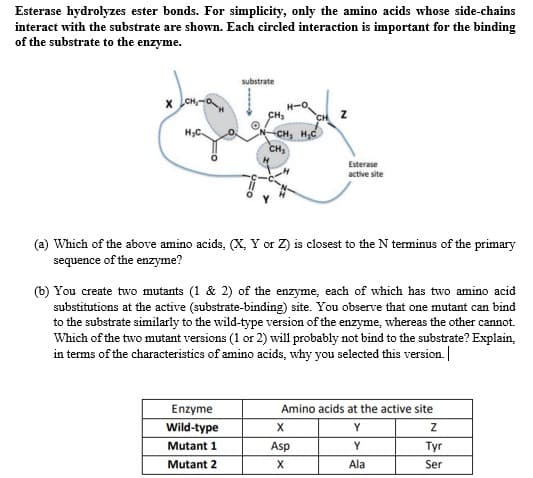
Transcribed Image Text:Esterase hydrolyzes ester bonds. For simplicity, only the amino acids whose side-chains
interact with the substrate are shown. Each circled interaction is important for the binding
of the substrate to the enzyme.
substrate
x CH
H-O
CH3
CH Z
CH, H,C
CH,
Esterase
active site
(a) Which of the above amino acids, (X, Y or Z) is closest to the N terminus of the primary
sequence of the enzyme?
(b) You create two mutants (1 & 2) of the enzyme, each of which has two amino acid
substitutions at the active (substrate-binding) site. You observe that one mutant can bind
to the substrate similarly to the wild-type version of the enzyme, whereas the other cannot.
Which of the two mutant versions (1 or 2) will probably not bind to the substrate? Explain,
in terms of the characteristics of amino acids, why you selected this version.
Enzyme
Wild-type
Amino acids at the active site
X
Y
Mutant 1
Asp
Y
Tyr
Mutant 2
X
Ala
Ser
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning