Estimated Income Statements, using Absorption and Variable Costing Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results: Sales (40,000 x $90) $3,600,000 Manufacturing costs (40,000 units): Direct materials Direct labor Variable factory overhead Fixed factory overhead Fixed selling and administrative expenses Variable selling and administrative expenses The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 50,000 units instead of 40,000 units, thus creating an ending inventory of 10,000 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses. a. 1. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 40,000 and 50,000 units are manufactured in the absorption costing format. If an amount box does not require an entry leave it blank. Sales Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods manufactured Inventory, October 31 Total cost of goods sold Gross profit ✓ ✓ ✓ 1,440,000 480,000 240,000 120,000 75,000 200,000 Marshall Inc. Absorption Costing Income Statement For the Month Ending October 31 40,000 Units Manufactured $ ✓ 3,600,000 $ ✓ 2,280,000 2,280,000 $ ✓ 1,320,000 50,000 Units Manufactured $ ✓ 3,600,000 $ √ 2,820,000 564,000 $ ✓ 2,256,000 $ ✓ 1,344,000
Estimated Income Statements, using Absorption and Variable Costing Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results: Sales (40,000 x $90) $3,600,000 Manufacturing costs (40,000 units): Direct materials Direct labor Variable factory overhead Fixed factory overhead Fixed selling and administrative expenses Variable selling and administrative expenses The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 50,000 units instead of 40,000 units, thus creating an ending inventory of 10,000 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses. a. 1. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 40,000 and 50,000 units are manufactured in the absorption costing format. If an amount box does not require an entry leave it blank. Sales Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods manufactured Inventory, October 31 Total cost of goods sold Gross profit ✓ ✓ ✓ 1,440,000 480,000 240,000 120,000 75,000 200,000 Marshall Inc. Absorption Costing Income Statement For the Month Ending October 31 40,000 Units Manufactured $ ✓ 3,600,000 $ ✓ 2,280,000 2,280,000 $ ✓ 1,320,000 50,000 Units Manufactured $ ✓ 3,600,000 $ √ 2,820,000 564,000 $ ✓ 2,256,000 $ ✓ 1,344,000
Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Chapter7: Variable Costing For Management
analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8E: Estimated income statements, using absorption and variable costing Prior to the first month of...
Related questions
Question
100%
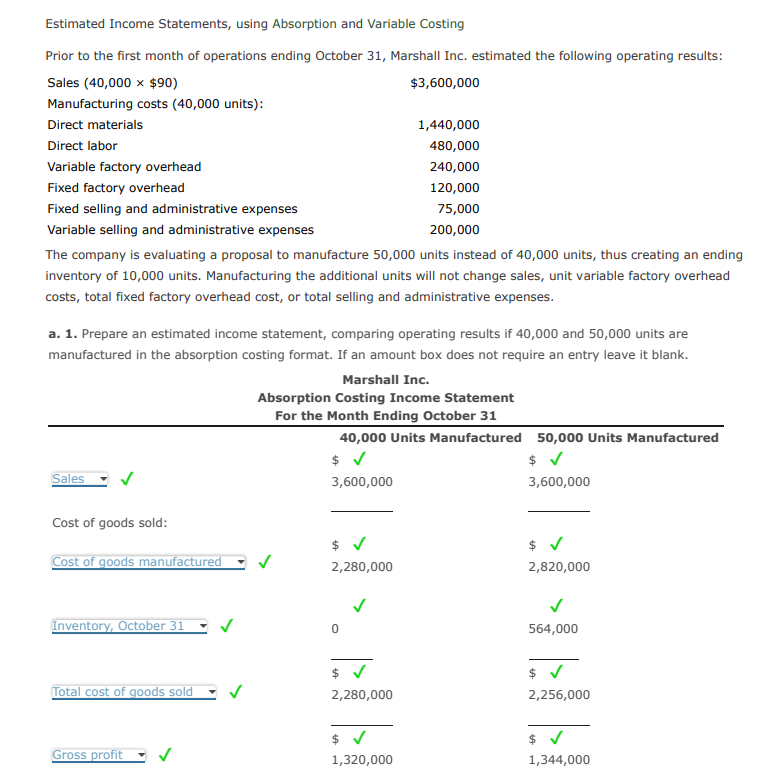
Transcribed Image Text:Estimated Income Statements, using Absorption and Variable Costing
Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results:
Sales (40,000 x $90)
$3,600,000
Manufacturing costs (40,000 units):
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable factory overhead
Fixed factory overhead
Fixed selling and administrative expenses
Variable selling and administrative expenses
The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 50,000 units instead of 40,000 units, thus creating an ending
inventory of 10,000 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead
costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses.
a. 1. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 40,000 and 50,000 units are
manufactured in the absorption costing format. If an amount box does not require an entry leave it blank.
Sales
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods manufactured
Inventory, October 31
Total cost of goods sold
Gross profit
✓
✓
✓
1,440,000
480,000
240,000
120,000
75,000
200,000
Marshall Inc.
Absorption Costing Income Statement
For the Month Ending October 31
40,000 Units Manufactured
$ ✓
3,600,000
$ ✓
2,280,000
2,280,000
$ ✓
1,320,000
50,000 Units Manufactured
$ ✓
3,600,000
$ √
2,820,000
564,000
$ ✓
2,256,000
$ ✓
1,344,000
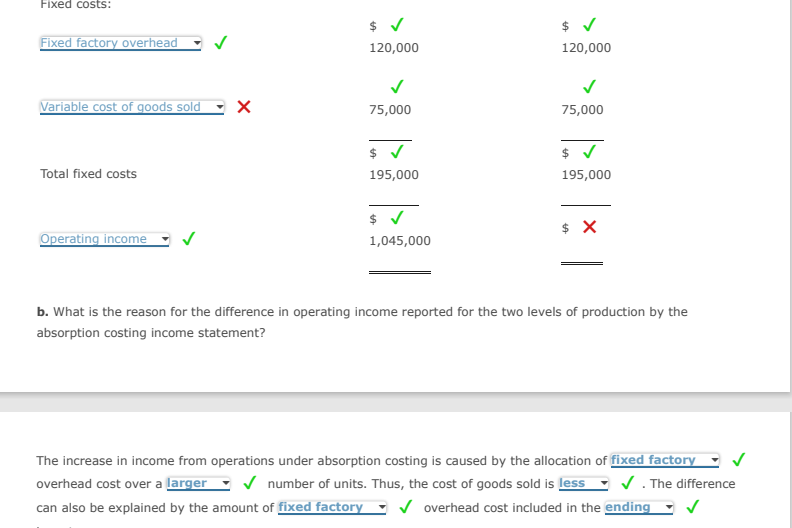
Transcribed Image Text:Fixed costs:
Fixed factory overhead
Variable cost of goods sold X
Total fixed costs
Operating income
$ ✓
120,000
75,000
$ ✓
195,000
$ ✓
1,045,000
$ ✓
120,000
75,000
$ ✓
195,000
$ X
b. What is the reason for the difference in operating income reported for the two levels of production by the
absorption costing income statement?
The increase in income from operations under absorption costing is caused by the allocation of fixed factory
overhead cost over a larger ✓ number of units. Thus, the cost of goods sold is less ✓. The difference
can also be explained by the amount of fixed factory ✓ overhead cost included in the ending ✓
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,