Explain the code (Do not use flowchart). See attached photo for the problem. It doesn't have to be long as long as you explain the important parts of the code int removeHead() { if(!isEmpty()) { return remove_between(head->next); } return 0; } int removeTail() { if(!isEmpty()) { return remove_between(tail->prev); } return 0; } int add(int num) { addTail(num); return index; } int remove(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int pos = 0; while(currnode != tail) { pos++; if(currnode->element == num) { remove_between(currnode); return pos; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } return 0; } bool addAt(int num, int pos) { node* currnode; int count; bool start_from_head = true; if (pos > index/2) { start_from_head = false; } if (start_from_head) { // START FROM HEAD currnode = head->next; count = 0; while (currnode != NULL) { count++; if (count == pos) { add_between(num, currnode->prev, currnode); return true; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } } else { // START FROM TAIL currnode = tail->prev; count = index + 1; while (currnode != NULL) { count--; if (count == pos - 1) { add_between(num, currnode, currnode->next); return true; } else { currnode = currnode->prev; } } } return false; } int removeAt(int pos) { node* currnode; int count; bool start_from_head = true; if (pos > index/2) { start_from_head = false; } if (start_from_head) { // START FROM HEAD currnode = head->next; count = 0; while (currnode != NULL) { count++; if (count == pos) { int elem = currnode->element; remove_between(currnode); return elem; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } } else { // START FROM TAIL currnode = tail->prev; count = index + 1; while (currnode != NULL) { count--; if (count == pos) { int elem = currnode->element; remove_between(currnode); return elem; } else { currnode = currnode->prev; } } } return -1; } int removeAll(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int count = 0; while(currnode != tail) { if(currnode->element == num) { count++; node* newcurrnode = currnode->next; remove_between(currnode); currnode = newcurrnode; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } return count; } int contains(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int pos = 0; while(currnode != NULL) { pos++; if(currnode->element == num) { return pos; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } return 0; } int count(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int ctr = 0; while(currnode != NULL) { if(currnode->element == num) { ctr++; } currnode = currnode->next; } return ctr; } bool move(int pos1, int pos2) { int elem = removeAt(pos1); if(elem == -1) { return false; } bool success = addAt(elem, pos2); if(!success) { addAt(elem, pos1); } return success; } bool isEmpty() { return index == 0; } void clear() { while(!isEmpty()){ removeHead(); } }
Explain the code (Do not use flowchart). See attached photo for the problem. It doesn't have to be long as long as you explain the important parts of the code int removeHead() { if(!isEmpty()) { return remove_between(head->next); } return 0; } int removeTail() { if(!isEmpty()) { return remove_between(tail->prev); } return 0; } int add(int num) { addTail(num); return index; } int remove(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int pos = 0; while(currnode != tail) { pos++; if(currnode->element == num) { remove_between(currnode); return pos; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } return 0; } bool addAt(int num, int pos) { node* currnode; int count; bool start_from_head = true; if (pos > index/2) { start_from_head = false; } if (start_from_head) { // START FROM HEAD currnode = head->next; count = 0; while (currnode != NULL) { count++; if (count == pos) { add_between(num, currnode->prev, currnode); return true; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } } else { // START FROM TAIL currnode = tail->prev; count = index + 1; while (currnode != NULL) { count--; if (count == pos - 1) { add_between(num, currnode, currnode->next); return true; } else { currnode = currnode->prev; } } } return false; } int removeAt(int pos) { node* currnode; int count; bool start_from_head = true; if (pos > index/2) { start_from_head = false; } if (start_from_head) { // START FROM HEAD currnode = head->next; count = 0; while (currnode != NULL) { count++; if (count == pos) { int elem = currnode->element; remove_between(currnode); return elem; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } } else { // START FROM TAIL currnode = tail->prev; count = index + 1; while (currnode != NULL) { count--; if (count == pos) { int elem = currnode->element; remove_between(currnode); return elem; } else { currnode = currnode->prev; } } } return -1; } int removeAll(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int count = 0; while(currnode != tail) { if(currnode->element == num) { count++; node* newcurrnode = currnode->next; remove_between(currnode); currnode = newcurrnode; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } return count; } int contains(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int pos = 0; while(currnode != NULL) { pos++; if(currnode->element == num) { return pos; } else { currnode = currnode->next; } } return 0; } int count(int num) { node* currnode = head->next; int ctr = 0; while(currnode != NULL) { if(currnode->element == num) { ctr++; } currnode = currnode->next; } return ctr; } bool move(int pos1, int pos2) { int elem = removeAt(pos1); if(elem == -1) { return false; } bool success = addAt(elem, pos2); if(!success) { addAt(elem, pos1); } return success; } bool isEmpty() { return index == 0; } void clear() { while(!isEmpty()){ removeHead(); } }
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PE
Related questions
Question
100%
Explain the code (Do not use flowchart). See attached photo for the problem. It doesn't have to be long as long as you explain the important parts of the code
int removeHead() {
if(!isEmpty()) {
return remove_between(head->next);
}
return 0;
}
int removeTail() {
if(!isEmpty()) {
return remove_between(tail->prev);
}
return 0;
}
int add(int num) {
addTail(num);
return index;
}
int remove(int num) {
node* currnode = head->next;
int pos = 0;
while(currnode != tail) {
pos++;
if(currnode->element == num) {
remove_between(currnode);
return pos;
} else {
currnode = currnode->next;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool addAt(int num, int pos) {
node* currnode;
int count;
bool start_from_head = true;
if (pos > index/2) {
start_from_head = false;
}
if (start_from_head) {
// START FROM HEAD
currnode = head->next;
count = 0;
while (currnode != NULL) {
count++;
if (count == pos) {
add_between(num, currnode->prev, currnode);
return true;
} else {
currnode = currnode->next;
}
}
} else {
// START FROM TAIL
currnode = tail->prev;
count = index + 1;
while (currnode != NULL) {
count--;
if (count == pos - 1) {
add_between(num, currnode, currnode->next);
return true;
} else {
currnode = currnode->prev;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int removeAt(int pos) {
node* currnode;
int count;
bool start_from_head = true;
if (pos > index/2) {
start_from_head = false;
}
if (start_from_head) {
// START FROM HEAD
currnode = head->next;
count = 0;
while (currnode != NULL) {
count++;
if (count == pos) {
int elem = currnode->element;
remove_between(currnode);
return elem;
} else {
currnode = currnode->next;
}
}
} else {
// START FROM TAIL
currnode = tail->prev;
count = index + 1;
while (currnode != NULL) {
count--;
if (count == pos) {
int elem = currnode->element;
remove_between(currnode);
return elem;
} else {
currnode = currnode->prev;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int removeAll(int num) {
node* currnode = head->next;
int count = 0;
while(currnode != tail) {
if(currnode->element == num) {
count++;
node* newcurrnode = currnode->next;
remove_between(currnode);
currnode = newcurrnode;
} else {
currnode = currnode->next;
}
}
return count;
}
int contains(int num) {
node* currnode = head->next;
int pos = 0;
while(currnode != NULL) {
pos++;
if(currnode->element == num) {
return pos;
} else {
currnode = currnode->next;
}
}
return 0;
}
int count(int num) {
node* currnode = head->next;
int ctr = 0;
while(currnode != NULL) {
if(currnode->element == num) {
ctr++;
}
currnode = currnode->next;
}
return ctr;
}
bool move(int pos1, int pos2) {
int elem = removeAt(pos1);
if(elem == -1) {
return false;
}
bool success = addAt(elem, pos2);
if(!success) {
addAt(elem, pos1);
}
return success;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return index == 0;
}
void clear() {
while(!isEmpty()){
removeHead();
}
}
![bool addAt(int num, int pos) [remember the note)
This method will add the integer num to the posth position of
the list and returns true if the value of pos is valid.
Performing addAt(20, 2) in the example list will add 20 at the
2nd position and the linked list will now look like this: h + 1o
+ 20 + 30 + 40 + 50 + t.
When the value of pos is invalid i.e. greater than the size + 1 or
less than one, return false.
int removeAt(int pos) [remember the note]
Removes the number in the posth position of the list and
returns the element removed.
Performing removeAt(3) in the example list will remove the 3rd
element of the linked list and the updated list will be: h + 1O
+ 30 + 50 +t
When the value of pos is greater than the size or less than one,
return -1.
int removeAll(int num)
Removes all instances of num in the linked list and returns the
number of instances removed.
In this list h + 10 10 20 + 30 + 10 +t, performing
removeAll(10) will remove all three 10's and the list will look
like this: 20 → 30. Then, it will return the number of instances
removed, in this case, 3.
int contains(int num)
This will return the position of the first instance of the element
num in the list. If num is not found, return 0. In the example,
having the method contains(30) will return 2 as it is located in
the second position.
int count (int num)
This will return the count of the instances of the element num
in the list. In the linked list in removeAll method, having the
method count(10) will return 3 as there are three 10's in the
linked list.
• bool move(int pos1, int pos2) [remember the note)
This method will move the element at position post to the
position specified as pos2 and will return true if the move is
successful. This will return false if either the specified
positions is invalid. In the example stated, operating the
method move(1, 3) will move the 1st element and shall now
become the 3rd element. The linked list shall now look like: h +
> 30 + 40 + 10 + 50 +t](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F2cb11186-80ff-4474-bc75-6eff69002743%2Fdb7bda19-e5bd-42ff-ae3a-d129d13ac856%2Fm6clfbl_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:bool addAt(int num, int pos) [remember the note)
This method will add the integer num to the posth position of
the list and returns true if the value of pos is valid.
Performing addAt(20, 2) in the example list will add 20 at the
2nd position and the linked list will now look like this: h + 1o
+ 20 + 30 + 40 + 50 + t.
When the value of pos is invalid i.e. greater than the size + 1 or
less than one, return false.
int removeAt(int pos) [remember the note]
Removes the number in the posth position of the list and
returns the element removed.
Performing removeAt(3) in the example list will remove the 3rd
element of the linked list and the updated list will be: h + 1O
+ 30 + 50 +t
When the value of pos is greater than the size or less than one,
return -1.
int removeAll(int num)
Removes all instances of num in the linked list and returns the
number of instances removed.
In this list h + 10 10 20 + 30 + 10 +t, performing
removeAll(10) will remove all three 10's and the list will look
like this: 20 → 30. Then, it will return the number of instances
removed, in this case, 3.
int contains(int num)
This will return the position of the first instance of the element
num in the list. If num is not found, return 0. In the example,
having the method contains(30) will return 2 as it is located in
the second position.
int count (int num)
This will return the count of the instances of the element num
in the list. In the linked list in removeAll method, having the
method count(10) will return 3 as there are three 10's in the
linked list.
• bool move(int pos1, int pos2) [remember the note)
This method will move the element at position post to the
position specified as pos2 and will return true if the move is
successful. This will return false if either the specified
positions is invalid. In the example stated, operating the
method move(1, 3) will move the 1st element and shall now
become the 3rd element. The linked list shall now look like: h +
> 30 + 40 + 10 + 50 +t
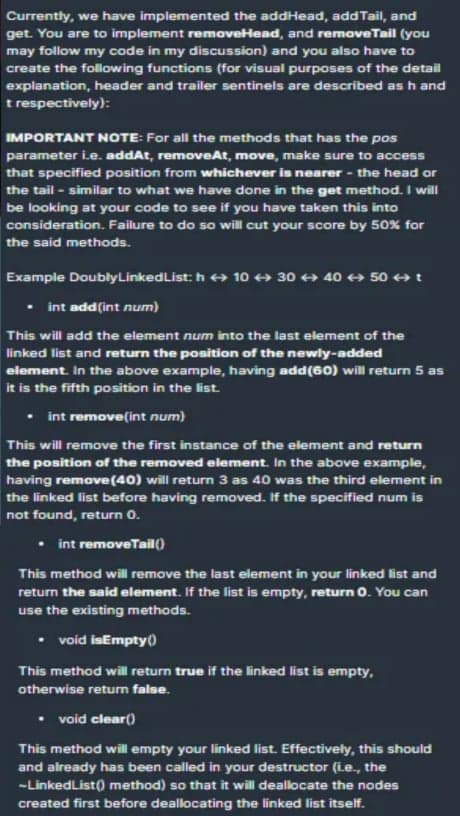
Transcribed Image Text:Currently, we have implemented the addHead, add Tail, and
get. You are to implement removeHead, and removeTail (you
may follow my code in my discussion) and you also have to
create the following functions (for visual purposes of the detail
explanation, header and trailer sentinels are described as h and
t respectively):
IMPORTANT NOTE: For all the methods that has the pos
parameter ie. addAt, removeAt, move, make sure to access
that specified position from whichever is nearer - the head or
the tail - similar to what we have done in the get method. I will
be looking at your code to see if you have taken this into
consideration. Failure to do so will cut your score by 50% for
the said methods.
Example DoublyLinkedList: h + 10 + 30 + 40 + 50 + t
int add(int num)
This will add the element num into the last element of the
linked list and return the position of the newly-added
element. In the above example, having add(60) will return 5 as
it is the fifth position in the list.
int remove(int num)
This will remove the first instance of the element and return
the position of the removed element. In the above example,
having remove(40) will return 3 as 40 was the third element in
the linked list before having removed. If the specified num is
not found, return 0.
int removeTail()
This method will remove the last element in your linked list and
return the said element. If the list is empty, return 0. You can
use the existing methods.
void isEmpty)
This method will return true if the linked list is empty,
otherwise return false.
• void clear(0
This method will empty your linked list. Effectively, this should
and already has been called in your destructor (Le., the
-LinkedList0 method) so that it will deallocate the nodes
created first before deallocating the linked list itself.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780133976892
Author:
Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337627900
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education