
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
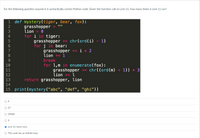
Transcribed Image Text:For the following question assume it is syntactically correct Python code. Given the function call on Line 15, how many times is Line 11 run?
1 def mystery(tiger, bear, fox):
grasshopper
lion = 0
for i in tiger:
grasshopper += chr(ord(i) - 1)
for j in bear:
grasshopper += i * 2
lion += 1
2
4
9.
break
10
for l,m in enumerate(fox):
grasshopper += chr((ord(m) + 1)) * 3
lion += l
11
12
13
return grasshopper, lion
14
15
print(mystery("abc", "def", "ghi"))
O 9
O 27
O 19683
3
Line 11 never runs.
O This code has an infinite loop.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In Phython Language: The DNA of a living organism consists of a string of 4 different bases represented with letters A, T, G, C. The DNA has a double helix structure which means these bases are paired in the string. An A base is always paired with a T base molecule and a C base is always paired with G molecule. Write a function matchingPair that accepts a single strand of the DNA structure as a string parameter and produces the pairing strand as a result and returns it. Strings can be considered as list of characters. Therefore the subscript notation that we use for lists is acceptable for strings as well. For example to reach to the 4th character of a string variable mystring, you may use the notation mystring[3]. Write another function search that accepts a long and a short DNA strand as parameters. The function should return the index positions of the occurrences of the short strand in the long strand as a list. Test your functions by accepting a long strand of DNA to find the…arrow_forwardPlease written by computer source solve the question in pythonarrow_forwardI do not know how to do this problem from my Computer Science ZyBooks Chapter 6 assignment. I have attatched an image of the problem, and I need to write the code in Python. I am not sure how to define the functions correctly or how to take a list as a parameter and return a boolean, so any help would be greatly appreciated! Thank you!arrow_forward
- Please can someone explain each line alongside each symbol of the expression Please please give a detailed explanation I will upvote it , explicitly pattern matchingarrow_forwardIn C++ Consider the following recursive function (Chapter 17, #9, modified) void recFun(int x) { if (x > 10) { recFun(x / 10); cout<< x % 10; } else cout<< x; } How can the code be modified so that the sum of all digits is printed?arrow_forwardMy question is for C programming. Write a complete program by using four helper functions The whole requested parts should be written in one single program. For all the functions, use the same prototype. Do not hard code any value, all the values must be given by the user in the whole code. The first function is getting a string and prints the given string, use the same given prototype: void myname ( char firstlastname[ ]); when you test the program, you will call the function in the main, the input will be your name ( you will prompt the user) and the functions prints it completely. The second function which you will add to the program will take 3 integer values and return the average all the 3 integer values, use the same prototype which is given here: double ave ( int num1, int num2, int num3); Call the function in the main, ask the user for 3 values. Test case for 3 given values by the user: 3 5 2 The third function will accept an array of numbers and prints it in the reverse…arrow_forward
- A recursive function in programming is a function that calls itself during its execution. The following two functions are examples of recursive functions: def function1(length): if length > 0: print(length) function1(length - 1) def function2(length): while length > 0: print(length) function2(length - 1) What can you say about the output of function1(3) and function2(3)? The two functions produce the same output 3 2 1. function1 produces the output: 3 2 1 and function2 runs infinitely. 3. function1 produces the output: 3 2 1 and function2 runs infinitely. 4. The two programs produce the same output: 1 2 3arrow_forwardObjective: Practice writing recursive functions in python3 Make the five recursive functions described below in python3 by using the starter code recursive_functions.py. For each function, figure out how to solve it conceptually : write down the base case (when recursion stops) and how each recursive function-call moves towards the base case. The functions should not print anything (except you may add temporary print statements to help debug them). You can test your program by using the provided program test_recursive_functions.py. Don't edit the test program. Put it into the same directory (folder) with your recursive_functions.py and run it. It will import your functions as a module, test your functions, and tell you when each function is returning correct results. 1. Factorial In math, if you have a number n, the factorial function (written n!) computes n x (n-1) x (n-2) x (n-3) x ... x 1. For example: 0! is defined to be 1 1! = 1 2! = 2 x 1=2 3! = 3 x 2 x 1=6 4! = 4 x 3…arrow_forward1. You are to create a well-formed Python recursive function (i.e, there must be a stopping/base case and the recursive case must present a smaller problem), along with a call to that function. 2. Trace your function and call. Remember that you must keep track of memory for each function call and provide output. How would I trace a function? and keep track of its memory for each function call?arrow_forward
- Write a recursive C function that returns the capital letters of a string str. The prototype of function must be: void F(char *str, *char cap); The capital letters of string must be saved in string cap.arrow_forwardA robot moves in a 2D lattice. The robot can only move north (N), south (S), east (E), and west (W) by a certain number of steps. Assume that the robot always starts at (0,0), and that the x axis is oriented east, while the y axis is oriented north. Write a Python function that, given a set of moves, calculates the final position of the robot. For example, if the set of moves provided as input is: N 2 E 4 S 1 W 3 then the final position of the robot is (1,1). The integer that follows a move is always positive. Follow this code skeleton: def robot_move (moves): X = 0 y = 0 # your code here return (x,y) The moves are provided as an array of tuples. The array can have any number of moves in any order. The example above is passed as input as follows: [('N',2), ('E',4), ('S',1), ('W',3)]arrow_forward-Python- Write a function get_letter_grade, such that when given * a lab grade score and * a list of the grade cutoffsreturns the letter grade of that score.Note: Your function automatically returns A for the values that are >= to the first cutoff-value in the list, then A- for the second cutoff-value, B+ for the third and so on. The function returns None for anything that's below the score for B-. You test that get_letter_grade(97, [93, 90, 87, 83, 80]) correctly returns an A, and get_letter_grade(93, [97, 90, 87, 83, 80]) returns A-. DO NOT hard-code the cutoffs, since they can change! You can copy/paste the following template: def get_letter_grade(score, cutoffs): if score ... : return 'A' ...: return 'A-' ...: return 'B+' ...: return 'B' ...: return 'B-'arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education