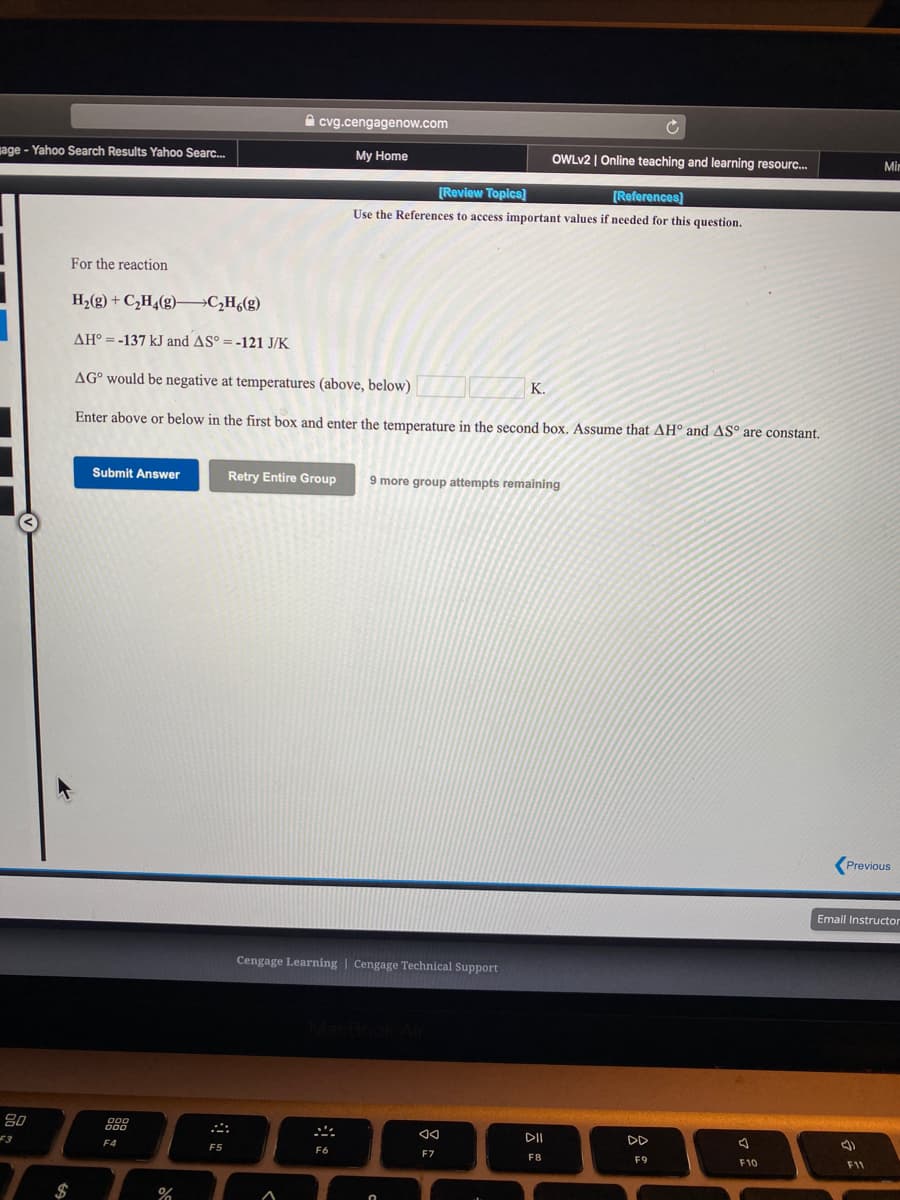
For the reaction H2(g) + C,H,(g)–C,H,(g) AH° =-137 kJ and AS° = -121 J/K AG° would be negative at temperatures (above, below) K. Enter above or below in the first box and enter the temperature in the second box. Assume that AH° and ASº are constant.
For the reaction H2(g) + C,H,(g)–C,H,(g) AH° =-137 kJ and AS° = -121 J/K AG° would be negative at temperatures (above, below) K. Enter above or below in the first box and enter the temperature in the second box. Assume that AH° and ASº are constant.
Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Chapter2: The First Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.32E: Many compressed gases come in large,heavy metal cylindersthat are so heavy that they need a special...
Related questions
Question
![A cvg.cengagenow.com
ge - Yahoo Search Results Yah00 Searc.
My Home
OWLV2 | Online teaching and learning resourc..
[Review Topics)
[References]
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
For the reaction
CACO3(s)CaO(s) + CO2(g)
AH° = 178 kJ and AS° = 161 J/K
AG° would be negative at temperatures (above, below)
K.
Enter above or below in the first box and enter the temperature in the second box. Assume that AH° and AS° are constant.
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
9 more group attempts remaining
<Prev
Email Inst.
Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support
80
888
DI
DD
F3
F4
F9
F5
F6
F7
F8
F10
F11
8.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F2b4165bd-b363-4d3f-855a-6d431dddeec9%2F75a3f8cf-3df9-4387-ba29-071b817d9756%2Fmkqmt3p_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:A cvg.cengagenow.com
ge - Yahoo Search Results Yah00 Searc.
My Home
OWLV2 | Online teaching and learning resourc..
[Review Topics)
[References]
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
For the reaction
CACO3(s)CaO(s) + CO2(g)
AH° = 178 kJ and AS° = 161 J/K
AG° would be negative at temperatures (above, below)
K.
Enter above or below in the first box and enter the temperature in the second box. Assume that AH° and AS° are constant.
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
9 more group attempts remaining
<Prev
Email Inst.
Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support
80
888
DI
DD
F3
F4
F9
F5
F6
F7
F8
F10
F11
8.
Transcribed Image Text:A cvg.cengagenow.com
jage - Yahoo Search Results Yahoo Searc.
My Home
OWLV2 | Online teaching and learning resourc.
Min
[Review Topics)
[References)
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
For the reaction
H2(g) + C,H4(g)–→C¸H6(g)
AH° = -137 kJ and AS° = -121 J/K
AG° would be negative at temperatures (above, below)
K.
Enter above or below in the first box and enter the temperature in the second box. Assume that AH° and AS° are constant.
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
9 more group attempts remaining
(Previous
Email Instructor
Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support
80
DII
DD
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
F10
F11
$
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,