Forty-minute workouts of one of the following activities three days a week will lead to a loss of weight. Suppose the following sample data show the number of calories burned during 40-minute workouts for three different activities. Swimming Tennis Cycling 413 410 385 380 485 255 425 455 295 400 420 397 422 525 273 Do these data indicate differences in the amount of calories burned for the three activities? Use a 0.05 level of significance. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O H: Mediang = Median, = Median. H: Median, Median, Mediane O Ho: All populations of calories burned are identical. H: Not all populations of calories burned are identical. O Hạ: Mediang - Median, - Mediane H: Mediang < Median, > Median. O H: Not all populations of calories burned are identical. H: All populations of calories burned are identical. O Hg: Median, + Median, + Mediane H: Mediang - Median, - Mediane Find the value of the test statistic. Find the p-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) D-value - What is your conclusion? O Reject Hg. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities. O Reject Hg. There is sufficient evidence to condlude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities. O Do not reject Hg. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities. O Do not reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities.
Forty-minute workouts of one of the following activities three days a week will lead to a loss of weight. Suppose the following sample data show the number of calories burned during 40-minute workouts for three different activities. Swimming Tennis Cycling 413 410 385 380 485 255 425 455 295 400 420 397 422 525 273 Do these data indicate differences in the amount of calories burned for the three activities? Use a 0.05 level of significance. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O H: Mediang = Median, = Median. H: Median, Median, Mediane O Ho: All populations of calories burned are identical. H: Not all populations of calories burned are identical. O Hạ: Mediang - Median, - Mediane H: Mediang < Median, > Median. O H: Not all populations of calories burned are identical. H: All populations of calories burned are identical. O Hg: Median, + Median, + Mediane H: Mediang - Median, - Mediane Find the value of the test statistic. Find the p-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) D-value - What is your conclusion? O Reject Hg. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities. O Reject Hg. There is sufficient evidence to condlude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities. O Do not reject Hg. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities. O Do not reject H. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter4: Equations Of Linear Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8SGR
Related questions
Question
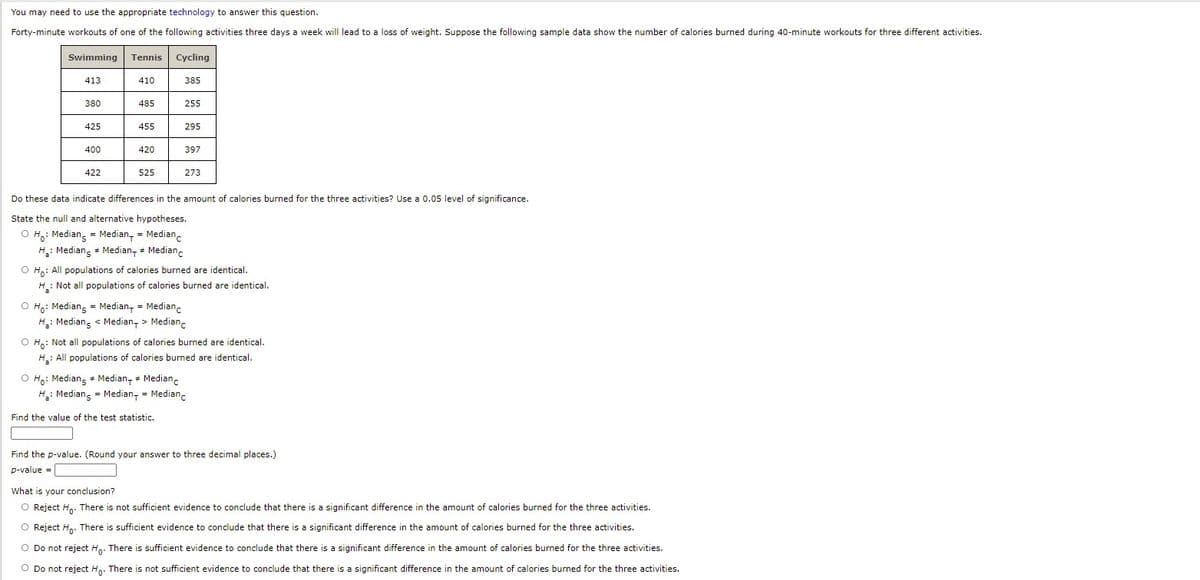
Transcribed Image Text:You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question.
Forty-minute workouts of one of the following activities three days a week will lead to a loss of weight. Suppose the following sample data show the number of calories burned during 40-minute workouts for three different activities.
Swimming
Tennis
Cycling
413
410
385
380
485
255
425
455
295
400
420
397
422
525
273
Do these data indicate differences in the amount of calories burned for the three activities? Use a 0.05 level of significance.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
O H,: Median, = Median, = Medianc
H: Mediang + Median, + Median.
O H.: All populations of calories burned are identical.
H: Not all populations of calories burned are identical.
O Ho: Mediang = Median, = Medianc
H: Mediang < Median, > Median.
O H,: Not all populations of calories burned are identical.
H: All populations of calories burned are identical.
O Ho: Mediang + Median, + Medianc
H: Mediang = Median, = Median.
Find the value of the test statistic.
Find the p-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
p-value =
What is your conclusion?
O Reject Ha. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities.
O Reject H.. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities.
O Do not reject H,. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities.
O Do not reject H,. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the amount of calories burned for the three activities.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning