
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Using Python to solve this problem. The output should be exactly the same as the picture.
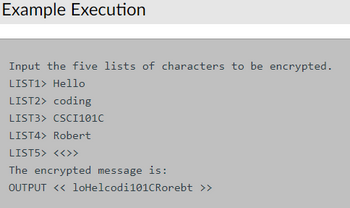
Transcribed Image Text:Example Execution
Input the five lists of characters to be encrypted.
LIST1> Hello
LIST2> coding
LIST3> CSCI101C
LIST4> Robert
LIST5> <<>>
The encrypted message is:
OUTPUT << 1oHelcodi101CRorebt >>
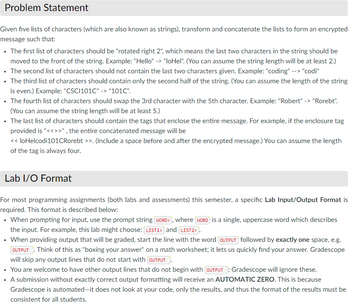
Transcribed Image Text:Problem Statement
Given five lists of characters (which are also known as strings), transform and concatenate the lists to form an encrypted
message such that:
• The first list of characters should be "rotated right 2", which means the last two characters in the string should be
moved to the front of the string. Example: "Hello" -> "loHel". (You can assume the string length will be at least 2.)
• The second list of characters should not contain the last two characters given. Example: "coding" --> "codi"
• The third list of characters should contain only the second half of the string. (You can assume the length of the string
is even.) Example: "CSC1101C" -> "101C".
• The fourth list of characters should swap the 3rd character with the 5th character. Example: "Robert" -> "Rorebt".
(You can assume the string length will be at least 5.)
• The last list of characters should contain the tags that enclose the entire message. For example, if the enclosure tag
provided is "<<>>", the entire concatenated message will be
<< loHelcodi101CRorebt >>. (Include a space before and after the encrypted message.) You can assume the length
of the tag is always four.
Lab I/O Format
For most programming assignments (both labs and assessments) this semester, a specific Lab Input/Output Format is
required. This format is described below:
• When prompting for input, use the prompt string WORD>, where WORD is a single, uppercase word which describes
the input. For example, this lab might choose: LIST1> and LIST2>.
• When providing output that will be graded, start the line with the word (OUTPUT followed by exactly one space, e.g.
OUTPUT. Think of this as "boxing your answer" on a math worksheet; it lets us quickly find your answer. Gradescope
will skip any output lines that do not start with OUTPUT
• You are welcome to have other output lines that do not begin with (OUTPUT); Gradescope will ignore these.
• A submission without exactly correct output formatting will receive an AUTOMATIC ZERO. This is because
Gradescope is automated-it does not look at your code, only the results, and thus the format of the results must be
consistent for all students.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- solve in python an give code. thankarrow_forwardPYTHON!!! For this question, we will use a simplified version of the Roman Numerals System to represent positive integers. The digits in this system are I, V, X, L, C, D and M. Each digit corresponds to a decimal value, as shown below: I = 1, V = 5, X = 10, L = 50, C = 100, D = 500, M = 1000 A number in the simplified Roman numerals system is a sequence of Roman digits, which follow these 2 rules: 1. The digits form a monotonically non-increasing sequence. That is the value of each digit is less than or equal to the value of the digit that came before it. For example, DLXXVI is a monotonically non-increasing sequence of Roman digits, but XIV is not. 2. There is no limit on the number of times that ‘M’ can appear in the number. ‘D’, ‘L’ and ‘V’ can each appear at most one time in the number. ‘C’, ‘X’ and ‘I’ can each appear at most four times in the number. For example: IIII, XVII, and MMMMMMDCCLXXXXVII are legal numbers in our simplified Roman numeral system, but IIIII, XIV, VVI and…arrow_forwardWrite a program in Python that will take any random integer as input and return the next odd number as output.arrow_forward
- Create a python program that will help user find a solution to any solvable Sudoku puzzle. You can simply start with writing text code which uses backtracking algorithm. What backtracking algorithm will do is that it will simply revert back to previous step if the solution found in current running step cannot solve the Sudoku.arrow_forwardwriting Python programs that use simple arithmeticexpressions. Follow below to write a simple Python program tosolve riddles like this one:Bush and Laura have 10 apples between them. Bush has 2 moreapples than Laura. How many apples does each have? Type the following in your editor window (the one labeled"Python Script"): input("How many apples are there in all?") We need to capture the value returned byinput() so that we can do something with it. We'll dothis by storing the result in a variable named "total_apples": total_apples = input("How many apples are there inall?") Translate this formula into Python. Start by assigning (total - 2)to a temporary variable. Divide the value of this variable by 2 andstore the result in a new variable for the first child. Add thedifference (2) to this value and store it in a new variable for thesecond child. We're almost done. Now that our calculations are finished, weshould print the results for the user. We can use theprint…arrow_forwardFind an example of a Python program on the Web that illustrates the program’s decisions using if and while statements. Provide a link for the source. What is happening in your programming example? Describe it in English as an algorithm. After the else statement executes, which program statement executes next in your example?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education