Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Question
You and your team attempt to isolate the gene coding for the defective enzyme. The gene sequence is shown in the table below; the number at the end of the row is the numerical position of the last base in that row, so the 60th position has a “G”.
You compare the sequence of the gene from your patient with three other patients you have had with the same symptoms; the mutations for each patient in the table below. What is the amino acid change in the enzyme from your patient (you’ll need to refer to the genetic code)? What amino acid changes are associated with the enzymes from the other three patients? Explain how each of these amino acid changes would lead to non-functional enzymes.
| Patient | Base pair location | Mutation |
| Justin | 319 | C ---> A |
| Patient A | 374 | G ---> A |
| Patient B | 1004 | G ---> C |
| Patient C | 1144 | C ---> T |
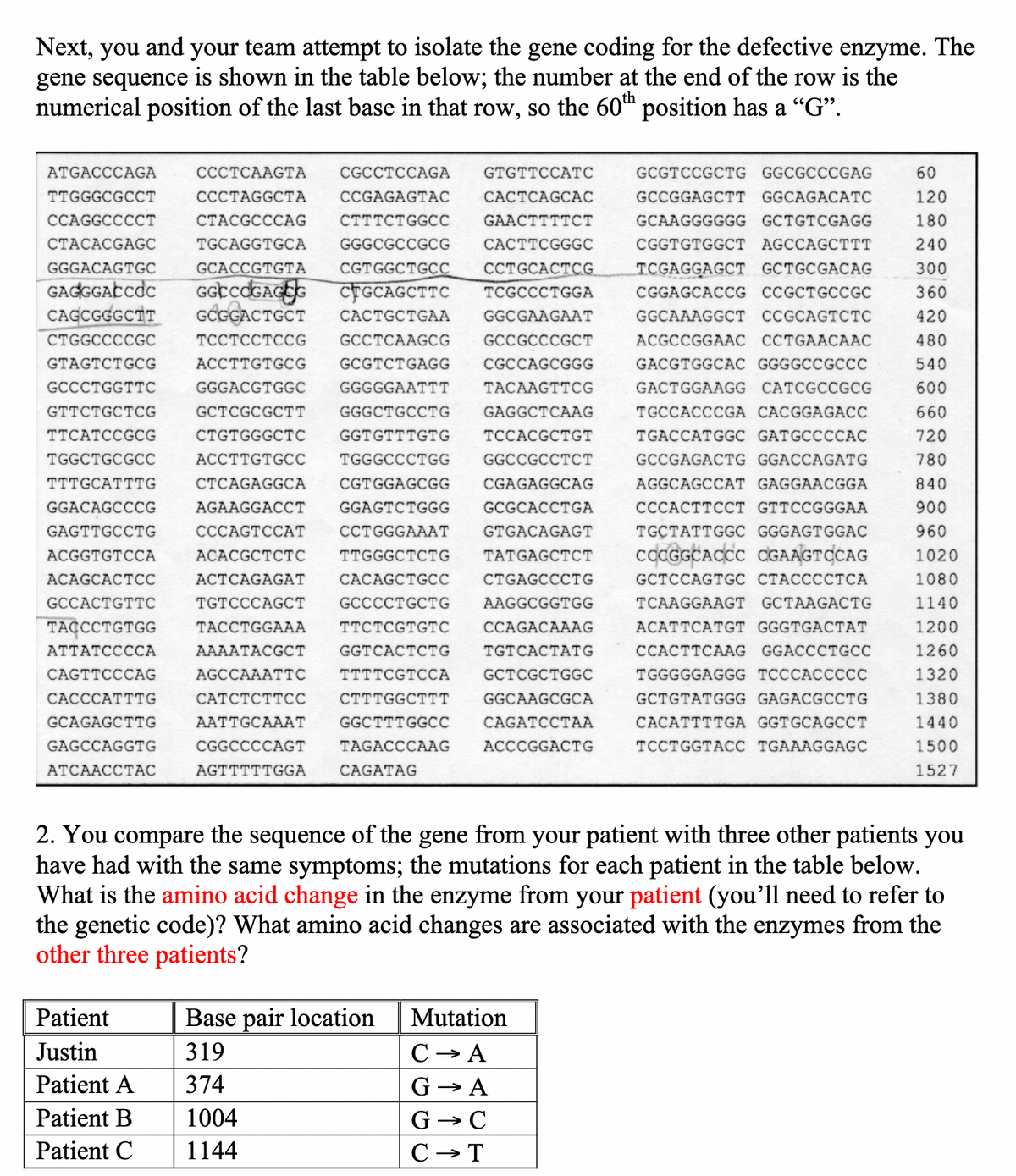
Transcribed Image Text:Next, you and your team attempt to isolate the gene coding for the defective enzyme. The
gene sequence is shown in the table below; the number at the end of the row is the
numerical position of the last base in that row, so the 60th position has a "G”.
ATGACCCAGA
TTGGGCGCCT
CCAGGCCCCT
CCCTCAAGTA CGCCTCCAGA GTGTTCCATC
CCCTAGGCTA CCGAGAGTAC CACTCAGCAC
CTACGCCCAG CTTTCTGGCC GAACTTTTCT
TGCAGGTGCA GGGCGCCGCG CACTTCGGGC
CGTGGCTGCC CCTGCACTCG
CTACACGAGC
GGGACAGTGC
GCACCGTGTA
GAGGGACCOC GGCCOGAGEG CTGCAGCTTC TCGCCCTGGA
TGGCTGCGCC
TTTGCATTTG
GGACAGCCCG
GAGTTGCCTG
CAGCGGGCTT GCGGACTGCT CACTGCTGAA GGCGAAGAAT
CTGGCCCCGC TCCTCCTCCG GCCTCAAGCG GCCGCCCGCT
GTAGTCTGCG ACCTTGTGCG GCGTCTGAGG CGCCAGCGGG
GCCCTGGTTC GGGACGTGGC GGGGGAATTT TACAAGTTCG
GTTCTGCTCG GCTCGCGCTT GGGCTGCCTG GAGGCTCAAG
TTCATCCGCG CTGTGGGCTC GGTGTTTGTG TCCACGCTGT
ACCTTGTGCC TGGGCCCTGG GGCCGCCTCT
CTCAGAGGCA CGTGGAGCGG CGAGAGGCAG
AGAAGGACCT GGAGTCTGGG GCGCACCTGA
CCCAGTCCAT CCTGGGAAAT GTGACAGAGT
ACACGCTCTC TTGGGCTCTG TATGAGCTCT
ACTCAGAGAT CACAGCTGCC CTGAGCCCTG
TGTCCCAGCT GCCCCTGCTG AAGGCGGTGG
TACCTGGAAA TTCTCGTGTC CCAGACAAAG
AAAATACGCT GGTCACTCTG TGTCACTATG
AGCCAAATTC TTTTCGTCCA GCTCGCTGGC
CATCTCTTCC CTTTGGCTTT GGCAAGCGCA
AATTGCAAAT GGCTTTGGCC CAGATCCTAA
CGGCCCCAGT TAGACCCAAG ACCCGGACTG
AGTTTTTGGA CAGATAG
ACGGTGTCCA
ACAGCACTCC
GCCACTGTTC
TACCCTGTGG
ATTATCCCCA
CAGTTCCCAG
CACCCATTTG
GCAGAGCTTG
GAGCCAGGTG
ATCAACCTAC
Patient
Justin
Patient A
Patient B
Patient C
Base pair location
319
374
1004
1144
GCGTCCGCTG GGCGCCCGAG
GCCGGAGCTT GGCAGACATC
GCAAGGGGGG GCTGTCGAGG
CGGTGTGGCT AGCCAGCTTT
TCGAGGAGCT GCTGCGACAG
CGGAGCACCG CCGCTGCCGC
GGCAAAGGCT CCGCAGTCTC
ACGCCGGAAC CCTGAACAAC
GACGTGGCAC GGGGCC GCCC
GACTGGAAGG CATCGCCGCG
TGCCACCCGA CACGGAGACC
TGACCATGGC GATGCCCCAC
GCCGAGACTG GGACCAGATG
AGGCAGCCAT GAGGAACGGA
CCCACTTCCT GTTCCGGGAA
TGCTATTGGC GGGAGTGGAC
COCGGCACCC CGAAGTCCAG
GCTCCAGTGC CTACCCCTCA
TCAAGGAAGT GCTAAGACTG
ACATTCATGT GGGTGACTAT
CCACTTCAAG GGACCCTGCC
TGGGGGAGGG TCCCACCCCC
GCTGTATGGG GAGACGCCTG
CACATTTTGA GGTGCAGCCT
TCCTGGTACC TGAAAGGAGC
2. You compare the sequence of the gene from your patient with three other patients you
have had with the same symptoms; the mutations for each patient in the table below.
What is the amino acid change in the enzyme from your patient (you'll need to refer to
the genetic code)? What amino acid changes are associated with the enzymes from the
other three patients?
Mutation
C → A
G→ A
G → C
C → T
60
120
180
240
300
360
420
480
540
600
660
720
780
840
900
960
1020
1080
1140
1200
1260
1320
1380
1440
1500
1527
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education