"he flow rate y (m/min) in a device used for air-quality measurement depends on the pressure drop x (in. of water) across the device's filter. Suppose that for x values between 5 and 20, the two variables are related ccording to the simple linear regression model with true regression line y = -0.14 + 0.095x. n USE SALT (a) What is the expected change in flow rate associated with a 1 in. Increase in pressure drop? (m/min) Explain. O we expect the change in flow rate (x) to be the y-intercept of the regression line. O we expect the change in flow rate (x) to be the slope of the regression line. O we expect the change in flow rate (y) to be the slope of the regression line. O we expect the change in flow rate (y) to be the y-Intercept of the regression llne. (b) What change in flow rate can be expected when pressure drop decreases by 5 in.? | (m³/min) (c) What is the expected flow rate for a pressure drop of 10 in.? A drop of 17 in.? | (m³/min) |(m³/min) 10 in. drop 17 in. drop (d) Suppose o - 0.025 and consider a pressure drop of 10 In. What is the probability that the observed value of flow rate will exceed 0.835? That observed flow rate will exceed 0.840? (Round your answers to four decimal places.) P(Y > 0.835) = P(Y > 0.840) (e) What is the probability that an observation on flow rate when pressure drop is 10 in. will exceed an observation on flow rate made when pressure drop is 11 in.? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
"he flow rate y (m/min) in a device used for air-quality measurement depends on the pressure drop x (in. of water) across the device's filter. Suppose that for x values between 5 and 20, the two variables are related ccording to the simple linear regression model with true regression line y = -0.14 + 0.095x. n USE SALT (a) What is the expected change in flow rate associated with a 1 in. Increase in pressure drop? (m/min) Explain. O we expect the change in flow rate (x) to be the y-intercept of the regression line. O we expect the change in flow rate (x) to be the slope of the regression line. O we expect the change in flow rate (y) to be the slope of the regression line. O we expect the change in flow rate (y) to be the y-Intercept of the regression llne. (b) What change in flow rate can be expected when pressure drop decreases by 5 in.? | (m³/min) (c) What is the expected flow rate for a pressure drop of 10 in.? A drop of 17 in.? | (m³/min) |(m³/min) 10 in. drop 17 in. drop (d) Suppose o - 0.025 and consider a pressure drop of 10 In. What is the probability that the observed value of flow rate will exceed 0.835? That observed flow rate will exceed 0.840? (Round your answers to four decimal places.) P(Y > 0.835) = P(Y > 0.840) (e) What is the probability that an observation on flow rate when pressure drop is 10 in. will exceed an observation on flow rate made when pressure drop is 11 in.? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter1: Equations And Graphs
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10T: Olympic Pole Vault The graph in Figure 7 indicates that in recent years the winning Olympic men’s...
Related questions
Question
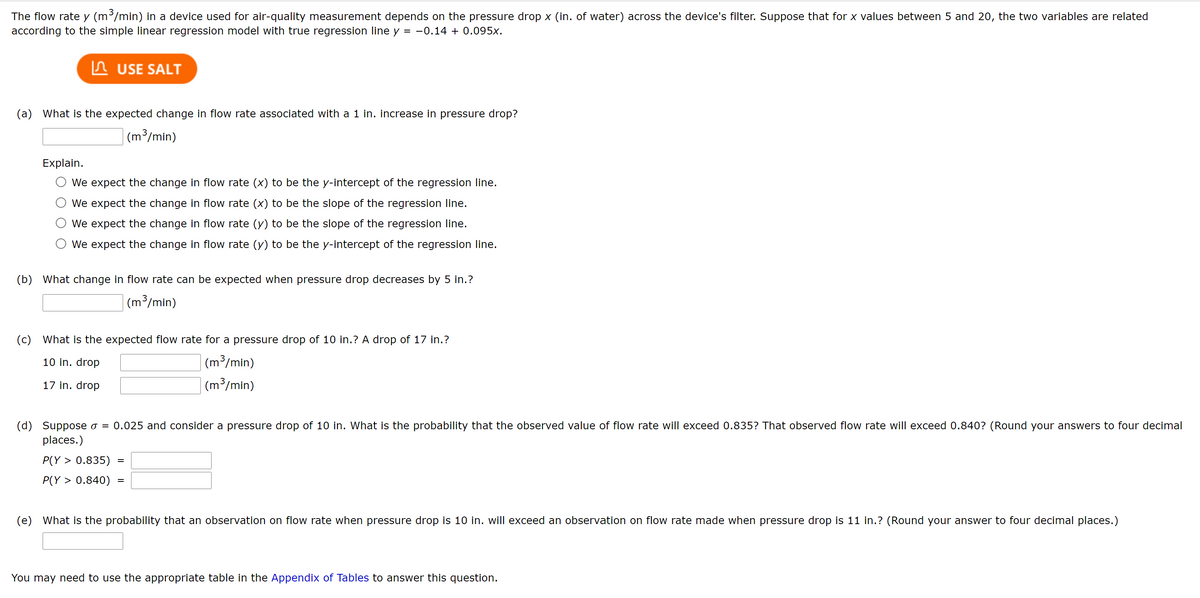
Transcribed Image Text:The flow rate y (m³/min) in a device used for air-quality measurement depends on the pressure drop x (in. of water) across the device's filter. Suppose that for x values between 5 and 20, the two variables are related
according to the simple linear regression model with true regression line y = -0.14 + 0.095x.
n USE SALT
(a) What is the expected change in flow rate associated with a 1 in. increase in pressure drop?
|(m³/min)
Explain.
We expect the change in flow rate (x) to be the y-intercept of the regression line.
We expect the change in flow rate (x) to be the slope of the regression line.
We expect the change in flow rate (y) to be the slope of the regression line.
We expect the change in flow rate (y) to be the y-intercept of the regression line.
(b) What change in flow rate can be expected when pressure drop decreases by 5 in.?
| (m³/min)
(c) What is the expected flow rate for a pressure drop of 10 in.? A drop of 17 in.?
10 in. drop
(m³/min)
17 in. drop
| (m3/min)
(d) Suppose o = 0.025 and consider a pressure drop of 10 in. What is the probability that the observed value of flow rate will exceed 0.835? That observed flow rate will exceed 0.840? (Round your answers to four decimal
places.)
P(Y > 0.835)
P(Y > 0.840)
(e) What is the probability that an observation on flow rate when pressure drop is 10 in. will exceed an observation on flow rate made when pressure drop is 11 in.? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
You may need to use the appropriate table in the Appendix of Tables to answer this question.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning