It became clear to the owners of RBC that the initial financial model was not adequate for answering these types of questions. After further research, RBC created another financial model that provided the following information for the first year of operations. Sales Beer sales (44% of total sales) Food sales (46% of total sales) Other sales (10% of total sales) Total sales Variable Costs $910,800 952, 200 207,000 $2,070,000 Beer (14% of beer sales) Food (34% of food sales) Other (31% of other sales) Wages of employees (20% of sales) Supplies (2% of sales) Utilities (4% of sales) Other: credit card, misc. (3% of sales) Total variable costs Contribution margin Fixed Costs $127,512 323,748 64,170 414,000 41,400 82,800 62,100 $1,115,730 $ 954, 270 Salaries: manager, chef, brewer Maintenance Advertising Other: cleaning, menus, misc Insurance and accounting Property taxes Depreciation Debt service (interest on debt) Total fixed costs $137,000 29,000 19,000 33,000 36,000 23,000 91,000 129,000 $ 497,000 $ 457,270 Operating profit Required: Perform a sensitivity analysis by answering the following questions: a. What is the break-even point in sales dollars for RBC? b. What is the margin of safety for RBC? c. What sales dollars would be required to achieve an operating profit of $110,000? $490,000?
It became clear to the owners of RBC that the initial financial model was not adequate for answering these types of questions. After further research, RBC created another financial model that provided the following information for the first year of operations. Sales Beer sales (44% of total sales) Food sales (46% of total sales) Other sales (10% of total sales) Total sales Variable Costs $910,800 952, 200 207,000 $2,070,000 Beer (14% of beer sales) Food (34% of food sales) Other (31% of other sales) Wages of employees (20% of sales) Supplies (2% of sales) Utilities (4% of sales) Other: credit card, misc. (3% of sales) Total variable costs Contribution margin Fixed Costs $127,512 323,748 64,170 414,000 41,400 82,800 62,100 $1,115,730 $ 954, 270 Salaries: manager, chef, brewer Maintenance Advertising Other: cleaning, menus, misc Insurance and accounting Property taxes Depreciation Debt service (interest on debt) Total fixed costs $137,000 29,000 19,000 33,000 36,000 23,000 91,000 129,000 $ 497,000 $ 457,270 Operating profit Required: Perform a sensitivity analysis by answering the following questions: a. What is the break-even point in sales dollars for RBC? b. What is the margin of safety for RBC? c. What sales dollars would be required to achieve an operating profit of $110,000? $490,000?
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course List)
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305627734
Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Chapter8: Time Series Analysis And_forecasting
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1C: The Vintage Restaurant, on Captiva Island near Fort Myers, Florida, is owned and operated by Karen...
Related questions
Question
Three entrepreneurs were looking to start a new brewpub near Sacramento, California, called Rosevill Brewing Company (RBC)
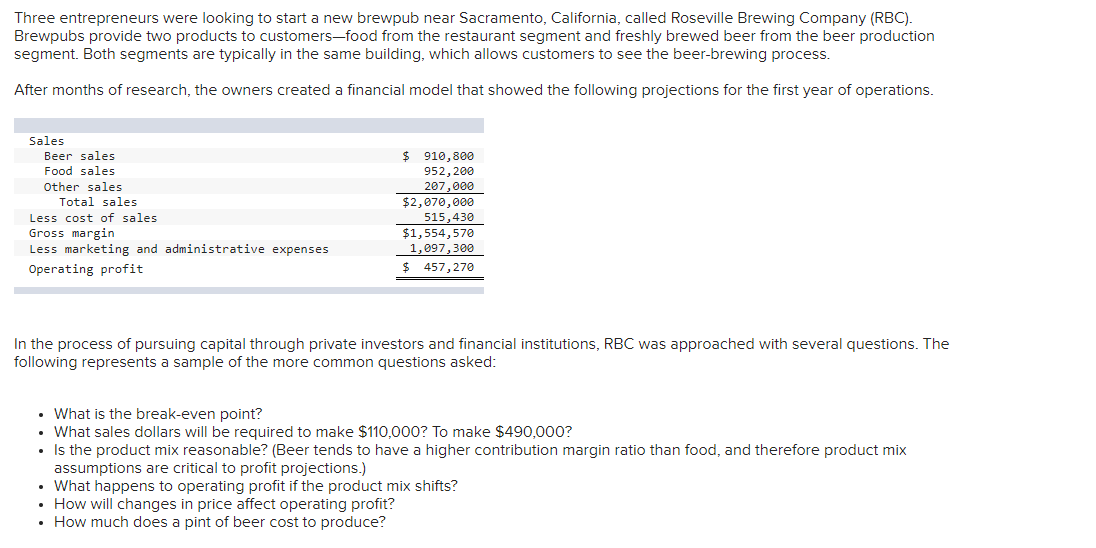
Transcribed Image Text:Three entrepreneurs were looking to start a new brewpub near Sacramento, California, called Roseville Brewing Company (RBC).
Brewpubs provide two products to customers-food from the restaurant segment and freshly brewed beer from the beer production
segment. Both segments are typically in the same building, which allows customers to see the beer-brewing process.
After months of research, the owners created a financial model that showed the following projections for the first year of operations.
Sales
Beer sales
Food sales
$ 910,800
Other sales
Total sales
952, 200
207,000
$2,070,000
Less cost of sales
Gross margin
Less marketing and administrative expenses
515,430
$1,554,570
1,097,300
$ 457,270
Operating profit
In the process of pursuing capital through private investors and financial institutions, RBC was approached with several questions. The
following represents a sample of the more common questions asked:
What is the break-even point?
What sales dollars will be required to make $110,000? To make $490,000?
• Is the product mix reasonable? (Beer tends to have a higher contribution margin ratio than food, and therefore product mix
assumptions are critical to profit projections.)
• What happens to operating profit if the product mix shifts?
How will changes in price affect operating profit?
• How much does a pint of beer cost to produce?
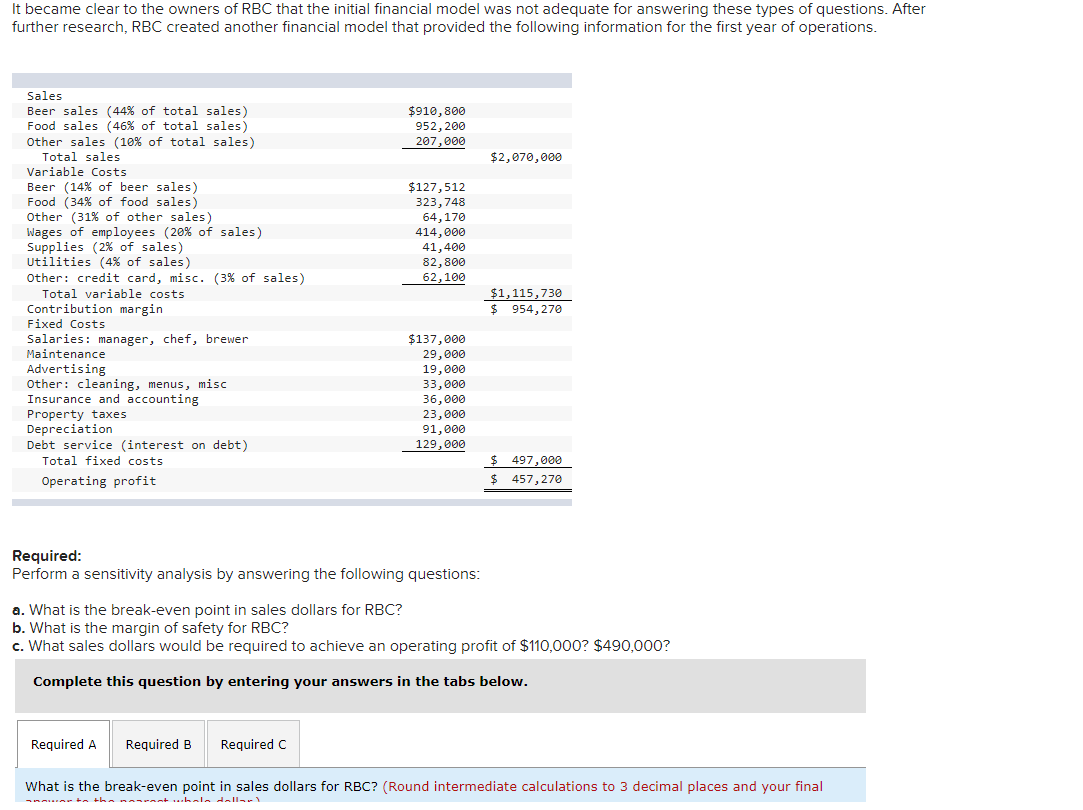
Transcribed Image Text:It became clear to the owners of RBC that the initial financial model was not adequate for answering these types of questions. After
further research, RBC created another financial model that provided the following information for the first year of operations.
Sales
Beer sales (44% of total sales)
Food sales (46% of total sales)
Other sales (10% of total sales)
$910,800
952, 200
207,000
Total sales
$2,070,000
Variable Costs
Beer (14% of beer sales)
$127,512
Food (34% of food sales)
Other (31% of other sales)
Wages of employees (20% of sales)
Supplies (2% of sales)
Utilities (4% of sales)
323,748
64,170
414, 000
41,400
82,800
Other: credit card, misc. (3% of sales)
Total variable costs
Contribution margin
Fixed Costs
Salaries: manager, chef, brewer
62,100
$1,115,730
$ 954,270
$137,000
Maintenance
29,000
Advertising
Other: cleaning, menus, misc
Insurance and accounting
19,000
33,000
36,000
23,000
91,000
129,000
Property taxes
Depreciation
Debt service (interest on debt)
Total fixed costs
$ 497,000
$ 457,270
Operating profit
Required:
Perform a sensitivity analysis by answering the following questions:
a. What is the break-even point in sales dollars for RBC?
b. What is the margin of safety for RBC?
c. What sales dollars would be required to achieve an operating profit of $110,000? $490,000?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required A
Required B
Required C
What is the break-even point in sales dollars for RBC? (Round intermediate calculations to 3 decimal places and your final
...hale dallar'
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305080577
Author:
Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub