|cans and charge s ], so the daily total industry profit in the beer market is 5 When they act as a profit-maximizing cartel, each company will produce |per can. Given this information, each firm earns a daily profit of S Oligopolists often behave noncooperatively and act in their own self-interest even though this decreases total profit in the market. Again, assume the two companies form a cartel and decide to work together. Both firms initially agree to produce half the quantity that maximizes total industry profit. Now, suppose that Mays decides to break the collusion and increase its output by 50%, while McCovey continues to produce the amount set under the collusive agreement.
|cans and charge s ], so the daily total industry profit in the beer market is 5 When they act as a profit-maximizing cartel, each company will produce |per can. Given this information, each firm earns a daily profit of S Oligopolists often behave noncooperatively and act in their own self-interest even though this decreases total profit in the market. Again, assume the two companies form a cartel and decide to work together. Both firms initially agree to produce half the quantity that maximizes total industry profit. Now, suppose that Mays decides to break the collusion and increase its output by 50%, while McCovey continues to produce the amount set under the collusive agreement.
Chapter28: Antitrust And Regulation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3E
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:When they act as a profit-maximizing cartel, each company will produce
cans and charge s
per can. Given this
information, each firm earns a daily profit of$
so the daily total industry profit in the beer market is s
Oligopolists often behave noncooperatively and act in their own self-interest even though this decreases total profit in the market. Again, assume the
two companies form a cartel and decide to work together. Both firms initially agree to produce half the quantity that maximizes total industry profit.
Now, suppose that Mays decides to break the collusion and increase its output by 50%, while McCovey continues to produce the amount set under the
collusive agreement.
Mays's deviation from the collusive agreement causes the price of a can of beer to
to
per can. Mays's profit is now
while McCovey's profit is nowS
Therefore, you can conclude that total industry profit
when
Mays increases its output beyond the collusive quantity.
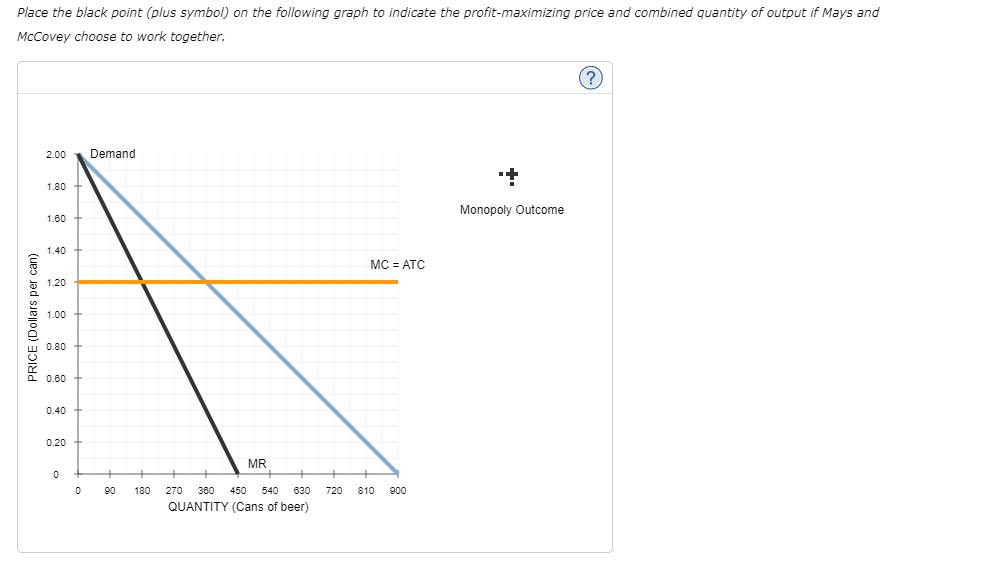
Transcribed Image Text:Place the black point (plus symbol) on the following graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and combined quantity of output if Mays and
McCovey choose to work together.
2.00
Demand
1.80
Monopoly Outcome
1.60
1.40
MC = ATC
1.20
1.00
0.80
0.60
0.40
0.20
MR
90
180
270 360 450 540 630
720 810 900
QUANTITY (Cans of beer)
PRICE (Dollars per can)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
